- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-06-01 06:18.
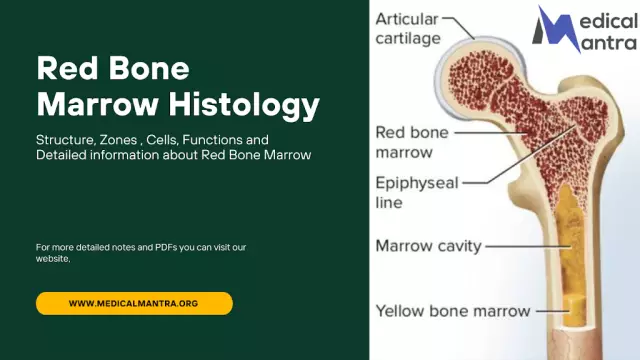
Bone marrow examination is the most informative method for diagnosing diseases associated with its defeat. This substance is found in the tubular and flat bones of the body. It is in it that the formation of stem cells occurs, which are capable of further differentiation into mature blood cells. Most often, a bone marrow test is performed to confirm or refute the diagnosis of blood cancer.
Indications for the procedure
Why do a bone marrow test? Only with the help of this method it is possible to diagnose blood diseases already in the early stages. Therefore, doctors refer a patient for examination if the patient has the following conditions:
- decrease in the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin (anemia);
- an increase in the number of white blood cells (leukocytosis);
- an increase in the number of platelets (thrombocytosis);
- decreased platelet count (thrombocytopenia);
- suspicion of malignantblood diseases: blood cancer (leukemia), myelodysplastic syndrome, paraproteinemia;
- Suspicion of bone marrow metastases in oncology of other organs.
Bone marrow examination is an invasive procedure associated with damage to the skin and requires a highly qualified specialist. Therefore, this method is used only when strictly necessary. Only in the case when other diagnostic methods turned out to be uninformative, or the patient is most likely to have blood cancer, the doctor sends the patient to take a bone marrow test.
Also, this method is done to control the therapy of the disease. Then the analysis is carried out before and after the course of therapy.
Puncture is done to find out if bone marrow tissue is suitable for transplantation.

Procedure technique: first stage
The essence of the method is to puncture the bone with the taking of the material and its subsequent examination with a microscope. That is, a puncture and analysis of the bone marrow is performed.
The puncture is made with a special hollow needle in the middle of the sternum at the level of the attachment of the third rib. This is where the bone is most malleable.
The needle must be dry and sterile. All clothing above the waist is removed from the patient. After the puncture site is treated with an antiseptic solution. Men shave their chest hair.
To prevent the needle from penetrating too deep, put on a fuse on it. The depth of its fixation is selected individually depending on the thickness of the subcutaneous tissue.the patient's fat, his age.
The needle is inserted simultaneously, perpendicular to the patient's torso. With the right technique, there should be a feeling of failure. In order to be able to take the bone marrow for examination, the needle must be attached absolutely motionless. With cancer metastases to the bone, inflammation of the bone tissue (osteomyelitis), this is difficult to achieve. Then the fuse must be moved higher, and the needle should be advanced a little deeper.
Next, a syringe clings to the needle and the bone marrow is sucked out in a minimum volume (1 ml).
This is the first stage of the bone marrow analysis is almost over. The doctor had only to remove the needle and seal the puncture site with a band-aid.
Procedure technique: second stage
The next step is the actual examination of the bone marrow. Cells are carefully examined under a microscope. To do this, the material is placed on a glass slide. Since the bone marrow tends to fold quickly, the surface of the glass is wiped with sodium citrate.

This analysis allows not only to diagnose bone marrow cancer, but also to determine its type. The tactics of further treatment and the prognosis for recovery will depend on the results obtained.
Features of trepanobiopsy
The disadvantage of bone marrow puncture is that the material is taken from its liquid part. Therefore, the likelihood of mixing with blood increases. This may skew the final results.
Trepanobiopsy is a method of analyzing the solid part of the bone marrow. For herimplementation, a trocar is used. This instrument is similar to a sternal puncture needle, but larger.
In this case, the puncture is not made in the sternum, but in the upper iliac spine. The patient lies on his side or on his stomach. The doctor sets the needle perpendicularly and sharply inserts it into the bone with rotational movements. Local anesthesia is preliminarily performed.
After taking the material, one part of it is placed on a glass slide, the other is placed in a vial with formalin.
The disadvantage of the procedure is its length. It takes about 20 minutes, during which time the patient must lie absolutely still.
Some time after the procedure, pain in the puncture area is possible. However, they are well removed by anti-inflammatory drugs ("Nimesulide", "Paracetamol").

Puncture of other bones
Blood cancer is one of the most common oncological diseases in children. How is a puncture and bone marrow analysis done for children?
Because the sternum is softer and more pliable in children than in adults, it is more likely to develop a complication in the form of a puncture through it. Therefore, other bones are selected for small patients to take bone marrow. Most often - femoral.
The puncture is made in the area of the bone, which is located closer to the pelvis. The patient lies on the opposite side. The doctor punctures not perpendicularly, but at an angle of 60 ° to the femur.
You can also make a puncture above the knee. In this case, the patient also lies on his side, andput a roller under the knee. The needle is inserted to a depth of 2 cm after preliminary anesthesia.

Types of bone marrow examinations
As already mentioned above, after taking the material from the bone, it is sent to the laboratory for further research. There are two ways to analyze under a microscope: cytological and histological.
The results of the cytological analysis are ready the very next day. From them, the doctor learns about the type of cells that the patient has in the bone marrow, their number, shape and structure features.
Histological analysis takes longer (up to 10 days), but is more informative. With its help, you can not only learn about the structure of cells, but also about their environment (collagen fibers, blood vessels, interstitial fluid).
After the puncture, the doctor will know the following indicators of bone marrow analysis:
- features of the structure of hematopoietic tissue cells;
- number of these cells their percentage;
- presence or absence of pathology;
- the number of blast cells, that is, those that should further turn into mature blood cells.
The last indicator is especially important in the diagnosis of acute leukemia. With this pathology, a sharp increase in their number is characteristic.
Actions after the procedure
Bone marrow analysis is a serious procedure. At least an hour after it, the doctor carefully monitors the patient. It checks the level of blood pressure, pulse, measures the temperature and monitors the general condition.
The patient canreturn home on the day of the procedure. But he must exclude heavy physical labor, not drive, as this will lead to a deterioration in general well-being.
To prevent deterioration after the puncture, the patient must adhere to a number of rules:
- avoid alcohol and smoking for a few days after the procedure;
- cancel swimming for three days;
- taking any medications must be agreed with the doctor;
- treatment with traditional methods should also be agreed.
The hole after the puncture should not be treated with alcohol, brilliant green or any other antiseptics.
Possible Complications
Difficulties in analysis are extremely rare if they are performed by a qualified specialist. Much depends on how the bone marrow is taken for analysis, whether sterility is adhered to, whether the technique is correct.
If aseptic conditions are violated, infection may enter the patient's body.
Too sensitive patients may pass out. In the worst case, a sharp drop in blood pressure with the development of shock is possible.
If the doctor violates the technique of the procedure, this leads to a fracture of the sternum or its through puncture.
In general, this is a really safe and harmless procedure. It is widely mastered by most doctors. Therefore, proper preparation of the patient in most cases allows you to get rid of unwanted phenomena.

Bone marrow cancer: blood test
What other methodsdiagnostics, except for puncture and trepanobiopsy, are used to make a diagnosis?
First of all, the doctor must conduct a thorough conversation with the patient. Only after a detailed analysis of complaints, anamnesis of the disease, heredity, additional examination methods are prescribed.
First, a complete blood count is done. It allows you to see the number of blood cells (leukocytes, platelets and erythrocytes), the percentage of different forms of leukocytes, or the leukocyte formula.
Next, a biochemical blood test is performed to determine the presence of tumor markers in it.
Other diagnostic methods
In addition to diagnosing bone marrow cancer with blood tests, the following examinations are used:
- general urinalysis - to determine the he alth of the kidneys;
- X-ray of the chest organs - to search for metastases or, conversely, the localization of the primary tumor;
- computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging - a more informative method for finding metastases;
- scintigraphy, the essence of which is the accumulation of a radioactive drug in tumor cells.
But only a bone marrow test can make a final diagnosis, as well as clarify the type of cancer.

Changes in the blood in acute leukemia
Acute leukemia is a form of bone marrow cancer. In this disease, blast cells in the bone marrow are completely unable to transform into mature blood cells. Therefore, there is an excessive number of blasts and a reduced levelblood cells.
Indicators of a blood test for bone marrow cancer by type of acute leukemia are characterized by the following features:
- Progressive decrease in the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin. Erythrocytes decrease to 1 × 1012/L at a rate of 5-5.5 × 1012/L. The hemoglobin level drops to 30-50 g/l, while the norm is 140-150 g/l.
- Platelets decrease to 20 × 109/L, normally they should be 200-400 × 109/L.
- The level of leukocytes can be different depending on the form of leukemia. Leukopenic forms are more common, with them the leukocytes decrease to 0.1-0.3 × 109/l (the norm is 4-9 × 109 /l).
- Up to 99% of blast cells are observed at a rate of 1-5%.
There are forms of acute leukemia in which blasts are not detected in the blood. Then they talk about the aleukemic form of the disease. In such cases, the diagnosis is difficult. Only a bone marrow test will help distinguish leukemia from aplastic anemia.
Changes in the blood in chronic leukemia
The results of a blood test for chronic leukemia depend on the type of disease. Myeloid leukemia and lymphocytic leukemia are distinguished.
The indicators of the blood test, as well as the symptoms, in bone marrow cancer of the type of chronic myelogenous leukemia depend on the stage of the disease. At the initial stage, when the patient is practically not bothered by anything, a slight increase in the level of leukocytes is detected in the blood (20.0-30.0 × 109/l). But at this stage, the diagnosis is rarely made, since the patient simply does not have a reason to see a doctor.
Most often, help is needed already in more advanced stages, with the addition of an intoxication syndrome. Then the level of leukocytes reaches 200.0-300.0 × 109/l. A large number of young forms of white blood cells (promyelocytes, myelocytes) appear.
In the terminal stages, when the patient's condition worsens, a blood test shows a decrease in the level of platelets (10-20 × 109/l).
In chronic lymphocytic leukemia, the number of lymphocytes increases. This is one of the forms of leukocytes. The level of the latter also rises slightly. If timely therapy is not carried out, leukocytosis increases and reaches the same numbers as with meloleukemia.

Results
Complete blood count is an informative method for diagnosing bone marrow cancer or leukemia. But only a cytological and histological examination of the bone marrow allows you to establish an accurate diagnosis. This is an affordable and highly informative method.
Despite the frightening technique at first glance, this technique is absolutely painless and practically harmless. Only in extraordinary cases can complications develop.
Therefore, every patient to whom a doctor has ordered a bone marrow test must undergo this examination. After all, the benefits of it many times exceed the possible harm.