- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
The human body is a separate state, where every organ, every tissue and even cells have their own functions and responsibilities. Nature made sure that they were performed as best as possible. Red bone marrow is one of the most important and responsible organs of the human body. It ensures the formation of blood.

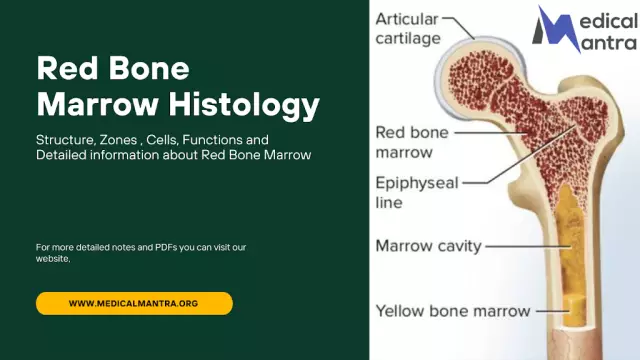
It should first be said what the human bone marrow is in general. This is one of the main components of the human body, carrying out hematopoiesis. It includes two main components - red bone marrow and yellow, the latter for the most part consists of adipose tissue. The yellow type of bone marrow replaces the second with age, thereby slowing down the formation of blood cells, as well as reducing the level of the body's natural defenses.
Red bone marrow looks like a dark brown viscous substance. It is located inside human bones (in different bones, depending on the age of the person) and plays a crucial role in the formation of newblood cells, and is also responsible for the strength of human immunity.
In adults, red bone marrow is located in the bones of a flat type, as well as in each of the vertebrae. It begins to form during the intrauterine development of the child.

When the fetus is a little more than one and a half months old, red bone marrow begins to form in the collarbones. At the sixth month of a child's development in the womb, this organ already fully performs all its functions, accounting for just over one and a half percent of the child's body weight. In an adult body, this ratio increases and amounts to six percent of the weight.
There are a large number of related medical disciplines that study red bone marrow - histology (the science of the structure of body tissues), cytology (the science that studies cells), anatomy, biology and many others. All these sciences draw attention to the uniqueness of this body: it consists of young or "underformed" cells that are responsible for the creation of the three main types of human blood cells (which are leukocytes, platelets and erythrocytes). In an adult developed organism, red bone marrow is mainly concentrated in the bones of the pelvis.

Since hematopoietic cells have the appearance and properties of "unfinished" cells, they are very similar in properties to malignant tumor (cancerous) cells. That is why, in the case of treatment of malignant neoplasms with chemotherapy drugs, significant damage is also done to the bone marrow.cells. The thing is that chemical radiation, in comparison with ordinary cells of the body, is more susceptible to forming elements, which are both "enemy" particles of tumors and "friendly" hematopoietic "hard workers". This similarity is the reason for the need for bone marrow transplantation in patients with cancer and leukemia. However, cancers are still killed somewhat faster with chemotherapy, so with such treatment, patients always have hope for recovery.