- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
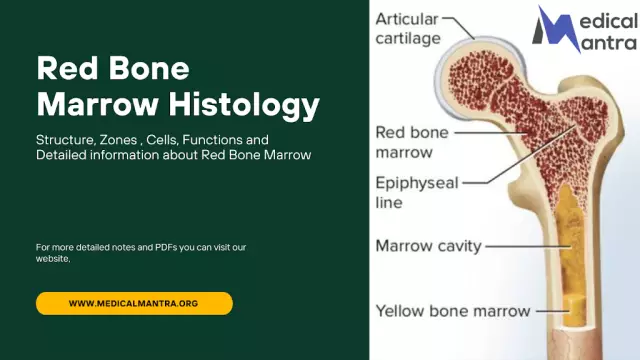
Inside the bone is the marrow. When it becomes inflamed, osteomyelitis begins to develop. The disease spreads to the spongy and compact substance, and then gradually to the periosteum. Inflammation of the bone marrow is a dangerous and complex disease that is difficult to detect in the initial stages, which is why various complications often develop. Such a condition is life-threatening and necessarily requires urgent care and long-term treatment.
Features of the disease
Inflammation of the bone marrow is an infectious disease that is difficult to treat and can cause many unpleasant consequences. Pathogenic microorganisms penetrate into bone tissue through the bloodstream or from nearby organs. The infection may initially develop in the bone when it is damaged due to a fracture or a gunshot wound.
In pediatric patientsthe disease affects mainly the long bones of the limbs. In an adult, the incidence of the pathological process increases significantly. If a person suffers from diabetes, then the disease can affect the bones of the foot.

In the case when pathogens are weakened and immunity is high, bone marrow inflammation can become chronic without suppuration and changes in bone structure. With the course of osteomyelitis, dead tissue is formed, which is rejected after a while. Vessel thrombosis gradually forms around it, the process of blood circulation and bone nutrition is disturbed.
In addition, cells of the immune system gradually accumulate, creating a kind of granulation shaft. It manifests itself in the form of a thickening of the periosteum and is called periostitis. Such a shaft clearly distinguishes between dead tissue and he althy parts. Periostitis refers to one of the specific signs of osteomyelitis.
Main classification
Depending on the cause of inflammation of the bone marrow, several forms of the course of the disease are distinguished, differing in the nature of the course, as well as the method of diagnosis and treatment. Among the main types of damage, it is necessary to highlight:
- tuberculous;
- actinomycotic;
- brucellosis;
- gonorrheal;
- syphilitic.
Tuberculosis type of the course of the disease is often found in children, adolescents.
Actinomycotic type of pathology is accompanied by significant damage to the periosteum with subsequent formationfistulas and separation of purulent contents.
Brucellosis is caused by a lesion of the spine in the lumbar region and affects nearby organs and nerve endings.
The syphilitic type of the disease occurs in the tertiary form and is localized in the cervical region. It has a chronic course and is accompanied by the formation of abscesses.

The gonorrheal type of the disease occurs against the background of an existing sexual infection, is localized in the lumbar region and, in its signs, resembles the course of sciatica. In addition, doctors distinguish nonspecific inflammation of the bone marrow of the spine, namely:
- psoriatic;
- ankylosing;
- aseptic;
- reactive;
- hematogenous.
Ankylosing type of pathology belongs to the group of rheumatic diseases, often occurs against the background of rheumatoid arthritis, leads to impaired motor activity and gradually progresses.
Reactive is formed during various failures of the immune system after infection with an intestinal or sexual infection. This affects the lumbar spine.
Psoriatic type of the disease occurs against the background of severe psoriasis.
Hematogenous osteomyelitis is formed when a staphylococcal infection enters the body.
Aseptic inflammation of the bone marrow is not associated with the course of the infectious process, but develops with back injuries, which provokes necrosis.
Given the existing symptoms,allocate such forms of osteomyelitis as:
- spicy;
- primary chronic;
- chronic;
- atypical.
Basically, the pathology begins quite acutely and, with its most unfavorable course, passes into a chronic form. The acute period lasts several days. Chronic damage can last for several years.
Causes of occurrence
Inflammation of the bone marrow of the spine and joints is provoked by various infectious processes. Pathogenic microorganisms can penetrate through the vessels. This is a hematogenous route of transmission and often occurs in children and adolescents.
Contact type is formed in case of infection of the bone with inflammation of the soft tissues. Aseptic course of the disease is observed during operations and closed fractures. Basically, the pathology is provoked by Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa or E. coli, and sometimes streptococcus.
Among the causes of osteomyelitis should be highlighted:
- fractures, ulcers, wounds;
- presence of foci of infection;
- decreased immunity;
- prone to allergies;
- physical exhaustion;
- uncontrolled use of psychotropic drugs and steroids;
- diabetes;
- heart and kidney failure.
There are also many other reasons, such as the use of untreated injection needles, medical catheters.
What could be the signs
Among the main symptoms of inflammation of the bone marrow of the spine, it is necessary to highlight suchlike:
- bone pain;
- chills and fever;
- swelling of the affected area;
- impaired functioning of the affected limb;
- fistula formation;
- not feeling well.
In some cases, the disease is almost asymptomatic. Seek medical attention if you have bone pain and fever. The chronic form of osteomyelitis always occurs after an acute process. A pathological cavity is formed in the bones. It contains particles of dead tissue and liquid purulent contents, which are periodically released through fistulas on the surface of the skin.
The course of the disease is undulating, gradually closing the fistulas is replaced by a new period of exacerbation and pus release. When the acute stage subsides, a person's well-being quickly improves. The temperature drops and the pain gradually subsides. At the same time, blood counts are approaching normal. During this period, new sequesters begin to gradually accumulate in the bone substance, which eventually begin to be rejected and provoke an exacerbation. The duration of remission can be up to several years.

Signs of relapse in many ways resemble the course of acute osteomyelitis. In this case, acute pain and inflammation occur, phlegmon develops.
When the bone marrow of the femur becomes inflamed, a single round-shaped cavity forms in the bone substance. The abscess contains pus. The disease is sluggish, and there are no special signs of the inflammatory process. With an exacerbationthere is severe pain in the leg, especially at night. In this case, fistulas are not formed.
Sclerosing osteomyelitis is accompanied by an increase in bone density, as well as layering of the periosteum. The bone thickens and becomes like a spindle. This form of pathology is rather difficult to treat.
In acute inflammation of the bone marrow, the symptoms are quite pronounced. A similar disorder is mainly observed in boys. In this case, phlegmonous inflammation is formed.
The toxic form of the disease proceeds almost immediately and can lead to the death of the patient. The disease begins suddenly. In this case, there is a feeling of strong bursting and a sharp pain in the limbs, often near the shoulder, knee or elbow joint. Pain and discomfort are greatly aggravated by movement. The temperature rises slightly.
Paleness of the skin, lethargy, rapid breathing and pulse, drowsiness are noted. Over the inflamed area there is swelling and redness of the skin. X-ray changes are observed only 2 weeks after the onset of the disease.
Diagnostics
If there are signs of inflammation of the bone marrow of the joint or spine, you should consult a doctor who will conduct a comprehensive examination and prescribe therapy. Initially, the doctor examines the area located near the injured bone to determine the presence of swelling, soreness, and redness of the tissues. A blunt probe is used to examine fistulas.
Detect signs of leakageinflammation is possible during laboratory tests, the results of which will show an increase in ESR and the number of leukocytes. Blood and discharge from fistulas are subjected to a thorough microbiological examination to determine the type of pathogens and the choice of antibacterial agents.

X-rays are used to identify necrotic areas of bone. Fistulography implies the introduction of a special substance into the fistulous passages, and then a study of the internal structure of the fistula is carried out. It should be noted that at the initial stages of the course of the disease, X-ray examination is not informative enough.
Tomography involves performing a series of x-rays from different positions. When conducting their analysis, a three-dimensional image of the affected bone is formed. This is a safe research method that allows you to recreate the image of the surrounding soft tissues as much as possible.
A bone biopsy is ordered to confirm the diagnosis. It is performed during the operation under general anesthesia. In this case, the surgeon carefully dissects the tissue and takes a piece of the test material. This allows you to determine the type of pathogens. In some cases, a biopsy is performed with a thin, long needle under local anesthesia. The whole process is controlled by radiography.
Features of treatment
In case of acute inflammation of the bone marrow of the femur or spine, hospitalization is required. Treatmentperformed with the help of surgery and the use of medications. The operation involves making a hole in the bone, cleansing and subsequent drainage of the resulting cavity. With a particularly complex course of the pathology, the existing purulent areas in the muscles are opened, and bone trepanation is performed.
After the cavity is completely cleansed of pus, antimicrobial agents are introduced into it through catheters. Treatment for inflammation of the bone marrow of the spine includes:
- high dose antibacterials;
- detoxification;
- stimulating tissue repair;
- immunity boosters and vitamins.
If the disease was provoked by staphylococcus, then specific immunotherapy techniques can be used. A prerequisite is the immobilization of the limb with a splint. After the acute inflammation subsides, physiotherapy is prescribed, in particular, such as a magnetic field, UHF and many others.
In the course of the chronic form of the disease, the treatment of inflammation of the bone marrow implies an operation. At the same time, fistulas are excised and the bone cavity is cleaned.
Drug therapy
Since inflammation of the bone marrow of the knee joint and spine is provoked by pathogens, antibiotic therapy is recommended. However, it is worth remembering that not all types of infection are amenable to this type of treatment. The drug is selected on the basis of a laboratory study. In this case, it is necessary to determine the effect of which particular antibioticpathogens are the most susceptible. The drug is injected directly into the bone cavities.

In case of severe intoxication of the body, the use of droppers with saline is indicated. This allows you to remove accumulated toxic substances from the body. This procedure is especially important if sepsis is formed. In addition, saline helps the body cope with antibiotics.
In addition, immunostimulants and probiotics are prescribed, since with prolonged use of antibacterial agents, the intestinal microflora is destroyed, which leads to a decrease in the body's defenses. Considering that during the course of such a pathology, soft tissues are also affected, local drugs are prescribed to a person, in particular gels and ointments. Treatment of the affected skin is carried out daily.
Operating
In case of inflammation of the red bone marrow, an operation is indicated, since such a condition can be very dangerous. In addition, there are other indications for intervention, namely:
- purulent inflammatory processes;
- fistula;
- chronic disease.

Surgical intervention involves opening the periosteum, as this will allow you to get to the source of purulent inflammation. Initially, the affected area is treated with an antiseptic, a soft tissue incision is made. Part of the periosteum is removed, the opened internal canal is cleaned withantibacterial agents.
Possible Complications
It is very important to know the dangers of inflammation of the bone marrow and exactly how to prevent complications. Consequences can be local and general. Local complications should include such as:
- phlegmon and abscess;
- spontaneous fractures;
- purulent arthritis;
- loss of joint mobility.
General complications include secondary anemia, sepsis and autoimmune diseases.
Carrying out preventive measures
Osteomyelitis prevention is very important, which means:
- good sleep and rest;
- he althy lifestyle;
- no stress;
- balanced nutrition;
- strengthening immunity;
- timely treatment of infections.

If you feel the slightest deterioration, it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor, as this will prevent the occurrence of inflammation and complications of this pathology.