- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Chickenpox is an infectious disease of a viral nature. The causative agent of pathology is Varicella zoster. The microorganism is one of the representatives of the herpesvirus family. If a person has had a disease at least once, his body has a specific immunity to the pathogen. For a long time it was believed that neither adults nor children develop chickenpox again. However, there are also contradictory cases in medical practice.
Can a child get chickenpox again
Some parents are convinced that their child, having had smallpox once, will never be infected again. This is an erroneous conclusion. In children, chickenpox is repeated. Moreover, medicine knows cases of infection for the third time.
In this situation, the main task of parents is to find a competent specialist. This is due to the fact that chickenpox in children recurs somewhat differently than in the firstonce. The doctor in this case is obliged to qualitatively conduct a differential diagnosis and prescribe the most effective treatment regimen.
Main reasons for reinfection:
- Contact with sick children. The clinical manifestations of chickenpox occur due to the fact that the body produces an insufficient amount of antibodies that can cope with the pathogen.
- Transition of Varicella zoster from dormant to active phase. In this case, the disease proceeds in the form of herpes zoster. After the primary infection, it is customary to talk about the acquisition of "non-sterile" immunity. In other words, the pathogen related to herpes viruses remains in the body in a dormant state. Under the influence of favorable factors, his vital activity is activated.
When chickenpox recurs, the child is contagious. In this regard, it is necessary to exclude his contact with other children.
Chance of re-infection
This situation is not common. According to statistics, chickenpox in children develops again in 3% of cases. In addition, the activation of the active life of the pathogen occurs only under the influence of certain provoking factors.
Regarding whether it is possible to get chickenpox again to an infant. These kids are just at risk. This is due to the fact that their immune system is not fully matured. As a result, the body produces an insufficient amount of antibodies, the task of which is todestruction of the pathogen.
Repeated chickenpox in children can also develop if they have already suffered a pathology ever, but the disease proceeded in a very mild form. For example, their body temperature rose slightly or a small amount of rashes appeared on the skin.
It is important to understand that the probability of re-infection with chickenpox depends only on external factors and individual characteristics of the organism. In children, the immune system is getting weaker every year. That is why cases of re-infection are being detected more and more often.
Provoking factors
The disease is transmitted by airborne droplets. The infection process itself occurs at the moment when the carrier's saliva enters the mucous membranes or skin of a he althy child.
Most parents believe that they only get sick once. Few people are interested in whether a child can have chickenpox again. However, after contact with an infected person, the risk of developing pathology a second time remains.
Doctors identify a number of provoking factors that contribute to secondary infection:
- Vaccination for immunosuppressed people.
- Regular contact with a large number of children.
- Immunodeficiency.
- Period after chemotherapy.
- Long-term treatment with drugs belonging to the group of glucocorticosteroids.
- Infant age.
- The period after the transplantation of any donorbody.
- Presence of malignant neoplasms.
In some cases, after the primary infection, for some reason, stable immunity is not formed. In these situations, chickenpox always develops in children again.
It is important to know that in the presence of at least one of the listed provoking factors, the process of transition of the pathogen from a dormant form to an active one can start.
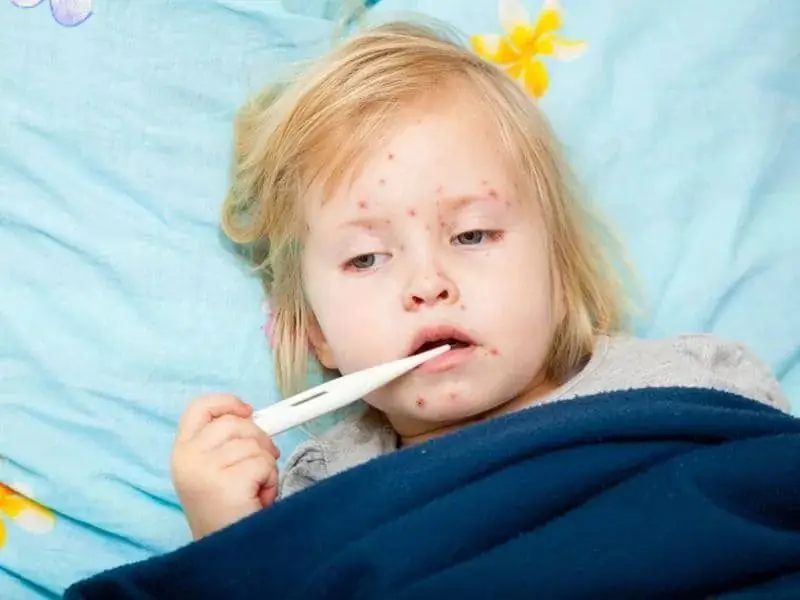
Clinical manifestations
With repeated chickenpox in children, the symptoms are much more pronounced. In most cases, the disease is so severe that even death is possible.
Characteristic clinical manifestations for secondary infection:
- Increase in body temperature to critical levels.
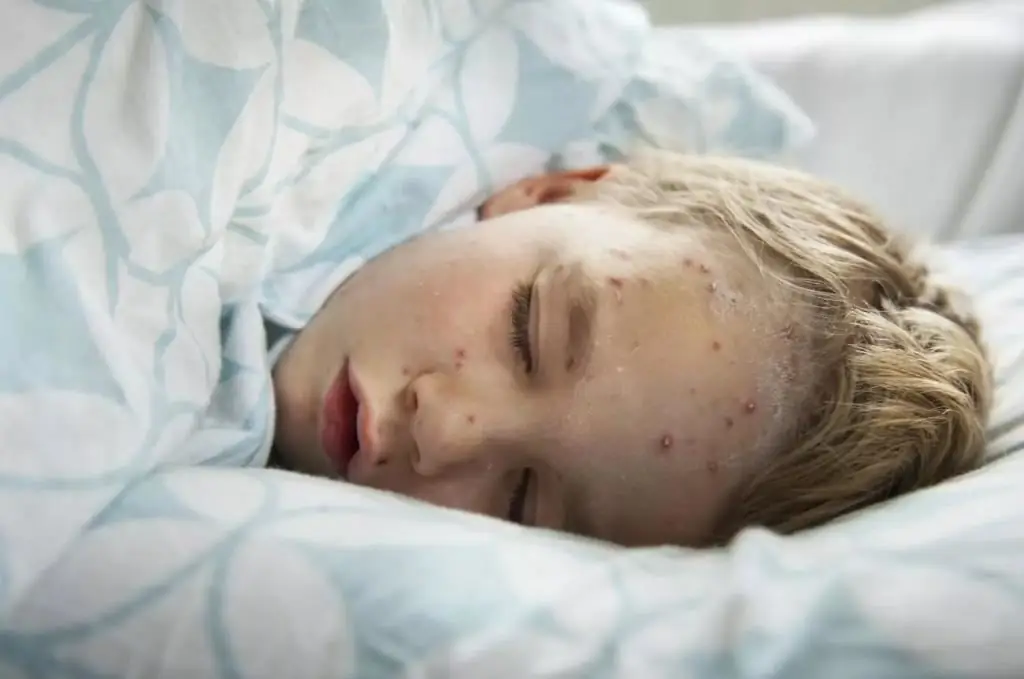
- Presence of profuse rashes. Most of them are on the palms and soles of the feet. The rash can even appear in the mouth, on the ears, scalp and conjunctiva of the eyes.
- The rash is more prominent.
- Itching. This symptom is so pronounced that the unpleasant sensation is unbearable.
- Frequent episodes of migraine and dizziness.
- Signs of the strongest intoxication process.
- Disturbance of appetite up to its complete loss.
The duration of the course of the disease is an average of 3 weeks.
Shingles as a manifestation of secondary infection
As mentioned above, the pathogen does not leave the human bodyafter treatment for chickenpox. The pathogen is localized in the nerve roots and is in a dormant state. In rare cases, under the influence of any provoking factor, the pathogen enters the active phase, while chickenpox manifests itself in the form of shingles.
The development of the disease begins with the appearance of severe itching, pain and burning in the area in which rashes will soon appear. A specific sign of shingles is the defeat of only a certain part of the body. For example, the rash appears only on the right or left side of the trunk.
With shingles, the child is also contagious. If he passes the virus on to another baby who has not had smallpox, the latter will develop the classic symptoms of chickenpox. In all cases, treatment involves symptomatic therapy. The duration of the pathology is no more than three weeks.
Who to contact
When the first warning signs appear, it is recommended to make an appointment with an infectious disease specialist. The doctor will take an anamnesis, conduct an examination and, based on the results of the primary diagnosis, issue directions for laboratory tests.
At present, tests are prescribed in almost all cases. This is due to the need for an accurate diagnosis. It is possible that the primary infection with another disease with similar clinical manifestations was mistaken for symptoms of chickenpox.
Diagnosis
To confirm or exclude the presence of pathology, the infectious disease specialist prescribes a general and biochemical blood test. In addition, it is shownone of the following studies:
- REEF. This method refers to express methods. The essence of the immunofluorescence reaction is to detect antibodies and antigens. Based on the results of the study, the doctor will be able to provide parents with information about whether the child may have had chickenpox again or whether the diagnosis of the initial smallpox infection was still erroneous.
- ELISA. In the process of carrying out enzyme immunoassay, antibodies of classes G or M to the pathogen are detected. In addition, the doctor gets the opportunity to find out the stage of development of the pathological process and find out if the child had chickenpox in the past.
- PCR. The study allows you to identify the pathogen at any stage of the development of the disease. The advantage of the method is that the biological material can be blood, saliva, and even sputum.
If the pathology proceeds with complications, a virological study is prescribed. Its essence is to analyze the fluid taken from the bubbles on the child's body.

Features of treatment
Currently, there is no drug capable of destroying the virus. In this regard, the treatment of pathology, both in primary and in re-infection, is exclusively symptomatic.
The purpose of therapeutic measures is to normalize body temperature and relieve itching, burning and pain. The child must be isolated for the period of treatment.
The classic treatment regimen is shown in the table below.
| Treatment stage | Transcript |
| Food | Readjusting your diet is a must. The menu should include vegetables, fruits and dairy products. The consistency of the dishes should be liquid or puree. The ideal option is one in which the child is fed soups and decoctions. Babies under 12 months are recommended to offer pureed cottage cheese and semi-liquid cereals |
| Drinking | It should be abundant. It is recommended to give preference to clean water without gas. In addition, the child can be offered decoctions based on herbs and unsweetened compotes |
| Hygiene | Contrary to popular belief, bathing children with chickenpox is necessary. Water procedures contribute to a faster recovery. During bathing, it is forbidden to use aggressive detergents and washcloths. It is unacceptable to dry the child with a rough towel |
| Medicines |
As a rule, the following remedies are prescribed:
|
Rashes must be lubricated with brilliant green. Alternatively, you can use more expensive drugs, such as "Tsindol" or "Calamine".

Possible Complications
In some cases there are negative consequences. As a rule, their development is associated with the untimely appeal to an infectious disease specialist.
Possiblecomplications:
- Accession of a secondary infection, usually of a bacterial nature.
- Encephalitis.
- Meningitis.
- Destruction of nerve fibers in certain areas, which can lead to hearing or vision impairment.
If there is at least a minimal risk of complications, the child is indicated for emergency hospitalization.
Prevention
If a he althy baby has come into contact with a sick baby, the following measures should be taken:
- Regularly ventilate the room where the child lives.
- How often to wet clean.
- Offer the child an antiviral agent, such as Acyclovir. The drug will not save you from the disease, but against the background of taking it, the pathology will proceed in a milder form.
In addition, smallpox vaccine is now being administered as needed.
In conclusion
Chickenpox is a pathology of an infectious nature, the causative agent of which is a microorganism belonging to the herpesvirus family. Contrary to popular belief, a disease can occur more than once throughout life. At the same time, parents are extremely rarely interested in whether children get chickenpox again. Meanwhile, every year cases of secondary infection are diagnosed more and more often. A feature of the pathology is that it proceeds more severely. In addition, with re-infection, the risk of developing dangerous complications is much higher.






