- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Each bacteriophage can only infect certain types of bacteria. That is why bacteriophages have a strictly specific effect that does not affect the natural microflora in the body.

The action of bacteriophages
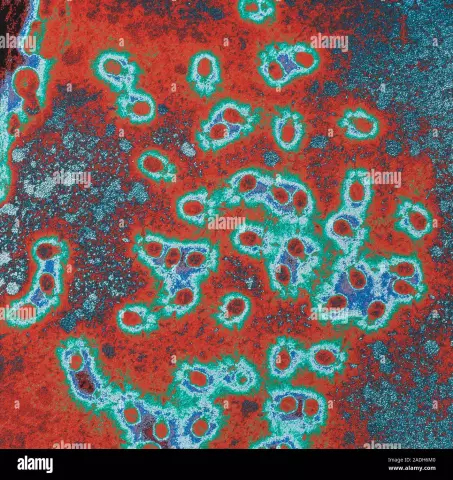
When a virus enters a cell of a pathogenic bacterium, it is introduced into its genome, and its reproduction begins. When a certain amount of new viral particles accumulate inside a bacterial cell, it is destroyed, and the viruses go outside and begin to infect new bacterial cells
There are two types of bacteriophages:
1. Temperate bacteriophages
These are phages that can slowly multiply inside infected bacterial cells. They can be transmitted among a bacterial colony from one generation to another, destroying microbial cells from time to time. This effect is called lysogenic.

2. Virulent bacteriophages
These are phages that, when a microbe enters a cell, begin to multiply rapidly and thereby lead to the rapid destruction of the affected cell. This effect is called lytic.
Use
Today, Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteriophage is used to treat infections caused by Proteus, Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, Pseudomonas, Escherichia, Klebsiella. Before the advent of antibiotics, bacteriophages were the only tool used to treat infectious diseases. But when antibiotics appeared, the situation changed dramatically, as simple and effective drugs appeared that did not require such detailed selection as for bacteriophages.
Where apply
The point is that bacteriophages are resistant. Bacteria can become desensitized to the effects of antibiotics. Therefore, the pharmaceutical industry has to relentlessly synthesize others. But, as is known, the potentials for the synthesis of antibiotics are limited. Also, antibiotics are very difficult to adapt to the action of bacteriophages, and according to experts, microbes are completely incapable of developing resistance to a complex of several phages. In addition, bacteriophages are drugs that have practically no side effects, they rarely cause allergies, they can be combined with any drugs. Currently, bacteriophages have proven themselves in the treatment of purulent processes in surgery, urological diseases, intestinal infections in newborns.

Negative impact
Bacteriophages are strictly specific drugs, so it is quite difficult to select them. If the body does not have the desired bacterium, and the bacteria that caused the disease are somewhat different, thenthe duration of the virus in the body is no more than 2-6 days, after which it is destroyed.
Treatment with bacteriophages
The use of bacteriophages for the purpose of treatment requires quite a long time. Antibiotic treatment usually takes 5-7 days, and phages are prescribed in three courses of 7-20 days at intervals. It is believed that bacteriophages have the ability to transfer from one bacterium to another part of its genome - this means that resistance to antibiotics, pathogenicity is transferred.