- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Food infections and poisoning cause human ailments. With a large accumulation of pathogens, the body is damaged in a large number of individuals. Understanding the problems of infection, you need to take into account all the risks and prevent diseases.
Contagion problem
Food infections differ from poisoning in that microorganisms are easily transmitted to others if sanitary and hygienic standards are not observed. When the infection becomes widespread, the sick should be de alt with by specialists. Prevention should be carried out, especially if ailments occurred in preschool and school institutions.

Dangerous are the states when there is a decline in the body's strength. Human immunity allows other pathogenic microorganisms to pass through, favorable conditions are created for the acquisition of chronic diseases. Some infections can stay inside for life. Practical events made it possible to create incidence statistics, according to which the main causes of infection were identified.
Basic definitions
Pathogenicmicroorganisms cause foodborne infections depending on the species:
- Dangerous bacteria for animals - zoonoses.
- Causing ailments only in humans - anthroponoses.
- Mixed types of microorganisms - zooanthroponoses, they infect a person from livestock.
Food infections are different, depending on the pathogens that caused them:
- zooanthroponoses provoke brucellosis, plague, anthrax;
- anthroponoses cause dysentery, cholera, typhoid fever.
Both animals and humans may not have symptoms of illness, but at the same time be carriers of the infection. Often, infection occurs through untested milk or meat.

Isolating ailments:
- of bacterial origin: food infection - toxic infection, intoxication - the result of eating foods saturated with toxins;
- non-bacterial.
You can catch the infection only from infected products. The person himself becomes a carrier. Most microorganisms can survive in air. When they survive, they do not reproduce. Only when they enter a living organism do they become active.
Sources of sickness
Bacteria that cause foodborne infections are inactive in food unless conditions are right. When the temperature rises, bacteria begin to multiply. The following factors contribute to growth:
- constant humidity;
- presence of fungi,yeast, dietary fiber;
- sweet environment is the best provocateur of infection;
- toxins such as botulism can often be found in canned homemade meat, chicken;
- milk and meat products, sausage contain salmonella.
If you carefully check the listed products, you can avoid a dangerous infection. In these products, pathogens develop instantly at warm temperatures. Even an hour under the sun, meat and eggs become sources of infection. Food infections and poisoning occur at the same time.

Intestinal infections have distinctive features:
- pathogenic microorganisms after infection can be transmitted to other people, poisoning occurs due to the accumulation of toxins in food;
- infections are found in any product - spoiled and unspoiled;
- a person can only get poisoned by stale food;
- infections can settle in the human body for a long time, making themselves felt in a few days;
- poisoning is observed immediately, within no more than three hours;
A large number of people can immediately get sick from one product.
General signs of infection
Feeling unwell a few hours after eating may indicate poisoning. A food infection has entered the body. Symptoms of these conditions:
- Dizziness.
- Vomiting.
- Increased blood pressure.
- Abdominal cramps.
- Gas formation inintestines.
- Diarrhea, general weakness of the body.
A patient has a set of such ailments when acute food infections are detected. Diarrhea can occur much later, it all depends on external factors and the concentration of pathogens in the products. The first sign of poisoning is a lack of appetite. The stomach starts to swell. Painful conditions appear, aggravated by walking.
After a few hours, an avalanche-like increase in intestinal spasms occurs. The person gets prolonged diarrhea. During this period, they are struggling with clinical signs of poisoning. After the food infection has receded, they try to fix the symptoms and interview the patient about eating low-quality food.

In most cases, the general signs of illness are the same for all people. To establish the true cause of poisoning, it will be necessary to conduct laboratory studies of the biomaterial. Without such a procedure, no doctor will be able to make a correct diagnosis.
Pathogenic microorganisms in milk
The most frequent cases of foodborne infections are observed in case of poisoning with low-quality milk and its derivatives. The matter is more often related to home products, but periodic control is still carried out at factories. According to the results of the check, an animal is determined in which a change in the physico-chemical composition of milk has occurred:
- In case of tuberculosis, an increase in the amount of fat and a decrease in protein units are observed. It tastes like s alty milk.
- Brucellosis is less noticeable, milk remains the same.
- Complications in leukemia lead to an increase in fat, dry matter. Casein and lactose are reduced. A sick animal has a huge number of leukocytes.
- In case of foot-and-mouth disease, milk does not sit well in yogurt. Grow leukocytes, the amount of fat. The drink tastes bitter, the animal reduces production.
- A disease like mastitis also spoils dairy products. There is an increase in leukocytes in the composition of milk.
Toxic infections give symptoms like poisoning, but they are easily transmitted to other people. Microorganisms multiply inside food and in the human body. It is easy to confuse this ailment and will require a full examination to make an accurate diagnosis.

Distinguish infected milk by the following feature: the shape of fat globules on the surface of the liquid. Rounded features indicate the normal he alth of the pet. Pathological figures from blurs indicate a change in composition. However, the analysis takes into account the seasonality of the measurements taken, as well as the conditions of the cow.
A kind of malaise
Foodborne viral infections can be caused by various viruses. They are contagious not only for others, but also for the sick person. Bacteria spread to internal organs. They enter the stomach, intestines, and settle in the upper respiratory tract.
There may be an ascending infection, when the lungs are affected, and then the bronchial system. Mostrotavirus lesions of internal organs are common. Vivid symptoms are intestinal upset, there is a general malaise. Diarrhea gives way to flatulence and constipation. Often the body temperature rises, while a red throat is observed. Painful sensations when swallowing food are absent. Feverish spasms occur in the body.
The following types of infections are distinguished:
- Listed group A rotaviruses.
- Enteroviruses.
- Reoviruses.
- Adenoviruses.
All groups are established by laboratory research. The principles of treatment are practically the same, but individual therapy is selected for each infection. An important step towards a cure is to determine the source of the disease and its complete exclusion. All of the above types have a special survivability inside watery accumulations. Some species even withstand heat and chemical treatments.
How do they get infected?
Food-borne intestinal infections have common routes of transmission to a he althy person:
- Violation of the terms of production and storage of food products.
- Poor hygiene practices, often seen in young children.
- Lack of control over the state of the body after visiting mass events, before entering school, kindergarten.
- The only way to poison a person is the oral penetration of microbes. Microorganisms enter the intestines only through the mouth. They develop inside the subtle department, constantly descending further.
- In the faeces of the patienthuman contains more than a million pathogenic microbes. Therefore, during the period of exacerbation of infection, it is recommended to focus on sanitary and hygienic procedures.
Dirty hands have always carried foodborne infections. Diseases were more often found in slovenly people, as well as in young children due to their lack of understanding of the importance of the problem or the irresponsible behavior of parents. Less often, the infection is transmitted by airborne droplets.

By direct contact with domestic animals in rural areas outbreaks of infectious poisoning are observed. Epidemics occur in the spring-autumn period. Active forms of viruses and bacteria stay inside food for a long time. Improper storage and handling of products leads to the growth of pathogenic microorganisms.
Eating meat from the counters of local markets, dairy products from private yards, you can pick up not only rotavirus or bacterial infections. Dangerous parasites are able to survive in the tissues of a pet, they cause much more dangerous diseases.
Adenoviruses remain after the patient on personal items, dishes, in bed. For inflammation accompanied by acute ailments in the intestines, it is better to adhere to strict sanitation rules.
Explosion phase
Acute periods of the disease are characterized by a decrease in the general well-being of a person. Advanced stages of poisoning even led to death. Medical assistance must be provided in a timely manner. Last resort to save livesthe patient becomes washing the stomach and intestines with special solutions.
After the procedure, pathogenic microorganisms are removed along with useful ones. Therefore, powerful therapy is used throughout the entire recovery period to return a he althy microflora. The most powerful period of complications falls on the first day after infection. If the symptoms do not subside for more than 7 days, then the patient requires mandatory hospitalization and urgent therapy for the destruction of pathogens.
All poisonings pass against the background of a high body temperature of more than 38 degrees. The patient complains of chills, feverish manifestations, rejection of fresh food. He will need to follow a diet, take medications. Vomiting conditions are combined with constant diarrhea. Not everyone is able to withstand this, so most of the victims prefer to experience discomfort in the clinic.
Pain occurs in the head, stomach, lower abdomen. A cough, similar to a sore throat, an allergic attack may form. All inflammatory processes are accompanied by exacerbation in the lymphatic system. The knots visibly swell. At this point, being close to the patient can be dangerous, the infection is easily transmitted through household items.
How to fight: common methods
Prevention of foodborne infections begins with the observance of sanitary and hygienic rules for keeping livestock. Carefully choose food products, trusting only trusted manufacturers. In the warm season, especially carefully pay attention to the change in color of fresh meat to dark tones.

Expired food is not recommended even as ingredients for frying. Boiled meat is the safest to eat, but it cannot be stored for long. Affected products are destroyed by disinfection, simple disposal into the soil will lead to an outbreak of poisoning in the area.
Viruses are not only resistant to chemical methods of meat sterilization, but also persist during frying. According to the statistics of diseases, the peak of infections and food poisoning occurs in the summer. Hot weather promotes the growth of pathogens.
Medicated struggles
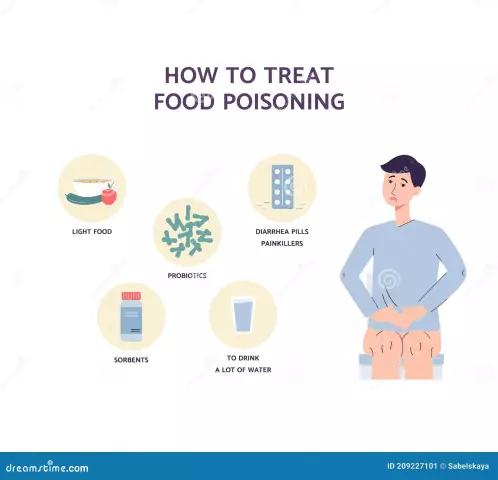
To eliminate acute complications, a food infection is suppressed by drugs. Treatment is prescribed immediately at the first sign of intoxication. Pharmaceutical products are designed to reduce the concentration of pathogens in the intestines. Patients are immediately prescribed a plentiful warm drink and preparations: activated charcoal, "Polysorb", "Enerosgel". They absorb bacteria and viruses, leaving the body naturally.
In case of mild poisoning, it is recommended to induce a gag reflex to remove undigested food. For gastric lavage, a weak solution of potassium permanganate is used. A few glasses of the product contribute to the natural cleansing of the body. Modern drugs have a similar effect: "Gastrolit", "Regidron".
Prescription of powerful antibiotics should be carried out only after a complete examination of the body by laboratorymethods in the clinic. An incorrectly selected remedy will lead to a subsequent outbreak of another inflammation or infection of loved ones. There are symptoms of a food infection, after the appearance of which it is impossible to delay hospitalization. These include blood in the stool, paroxysmal cough, body temperature above 39 degrees, loss of consciousness and delirium.