- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Poisoning is considered a common ailment. Many people have experienced this condition at least once in their lives. Intoxication can be caused by the presence of bacteria in foods. It offers information on microbial food poisoning, its symptoms, treatment and prevention.
Main types of intoxication
According to the International Classification of Diseases, these conditions are caused by the ingestion of foods that contain bacteria or other toxic substances into the digestive system. Experts distinguish the following types of poisoning:
- Intoxications not caused by exposure to pathogenic organisms.
- Food poisoning of microbial origin.
- Pathologies, the cause of which has not been established.
Most intoxications are caused by harmful bacteria (clostridium, staphylococcus, salmonella) entering the digestive system.
Common features of all types of pathologies
No matterwhat types of microbes provoke the disease, all such conditions are characterized by the following features:
- Infection starts suddenly.
- The disease can be widespread. This is due to the fact that several people use a product at the same time.
- The course of the disease is acute, but not long.
When do symptoms of intoxication begin to appear? The answer to this question depends on the type of poisoning. For example, signs of salmonellosis, as a rule, begin to disturb the patient after 6-12 hours. With botulism, the incubation period can be from 7 to 10 days.
Factors contributing to the occurrence of pathology
How do bacteria that provoke intoxication get into food and into the gastrointestinal tract? Organisms that cause microbial food poisoning are found in soil, fish, shellfish, river and sea water.

In some cases, they get into food through dirty hands in case of non-compliance with hygiene rules, cooking by people suffering from purulent skin pathologies, as well as violation of the shelf life of products and the technology of their preparation. Often, intoxication occurs due to the use of eggs of geese and ducks, infected products of animal origin. Microbes can be on the surface of fruits, berries, vegetables.
They get there with particles of dirt, dust. Bacteria are carried by rodents, arthropods.
Varieties of intoxication caused by microbes
These pathologiesare divided into several types. Depending on which bacteria penetrate the human gastrointestinal tract, the following categories of ailments are distinguished:
- Salmonella poisoning.
- Staphylococcal intoxication.
- A disease caused by clostridia (botulism).
- E. coli ailments.
- Mycotoxicoses - mold poisoning.
This group of pathologies is also divided into food toxicosis and toxic infections. The first type of disease occurs as a result of the entry of poisons of harmful bacteria into the gastrointestinal tract in the absence of microbes that secrete these substances.
The second category develops due to the penetration of food into the gastrointestinal tract, in which there are pathogenic organisms that have multiplied in large numbers. Of course, in the course of their life, they also release toxins. There are general signs that are observed in any type of such intoxication.
Characteristic manifestations

The disease usually starts suddenly. Most intoxications make themselves felt within 3-4 hours after eating infected foods. The disease is characterized by an acute course, pronounced manifestations are observed during the first two days. Signs of microbial food poisoning are as follows:
- Occurrence of nausea, bouts of vomiting.
- Presence of discomfort in the peritoneum.
- Frequent, loose stools.
- Pathological manifestations of the central nervous system (pain in the head,visual disturbances, seizures).
- Fever.
E. coli infection. Ways to prevent it
This microorganism forms many strains, among which there are harmless and pathogenic. Harmless people inhabit the intestines of a person already in the first hours after his birth. They are very important for a person, as they contribute to the normal functioning of the digestive tract. Only in cases where good E. coli enter other organs (prostate, vagina, etc.) can they cause inflammation.
Pathogenic Escherichia coli are absent in the intestines of a he althy person. They get there if a person consumes dirty foods, insufficiently processed meat, milk. These microorganisms can cause severe infectious diseases. Some strains produce toxins so poisonous that they cause death in elderly patients, children and those with weak immunity.
The disease caused by pathogenic Escherichia coli appears as a result of contaminated food entering the digestive tract, as well as as a result of non-compliance with personal hygiene while eating or cooking. In addition, if the food was stored incorrectly, these bacteria can also multiply in them. In order not to pick up pathogenic E. coli, you need to remember the following recommendations:
- Carry out thorough heat treatment of food products (meat, raw milk).
- Follow food storage rules.
- Wash fruits, berries, herbs, vegetables.
- Respect personalhygiene.
Salmonella poisoning

This disease also applies to food poisoning of microbial origin. Pathology occurs as a result of the consumption of poultry meat, as well as unheated milk and raw eggs. The hidden period is six to twelve hours. In rare cases, signs of intoxication begin to appear on the second day. The sick person has a feeling of nausea, there is a liquid and mucous stool, a feeling of weakness, spasms in the peritoneum.
Pathology caused by botulinum toxin
This condition in medical practice is considered one of the most severe types of poisoning. It is characterized by a high probability of death in patients due to damage to the organs of the central nervous system and the respiratory system. It is known that it is not the bacterium itself that poses a he alth hazard, but the substances that are released during its vital activity. The habitat of the microbe is the body of birds, mammals, and fish. Reproduction occurs in food.
The main danger is represented by canned vegetables, berries and fruits, as well as home-cooked fish. With botulism, the incubation period is approximately 4-6 hours. In some patients, symptoms of pathology occur 10 days after eating infected food.
Signs of the disease include discomfort in the peritoneum, vomiting, the appearance of fog before the eyes, respiratory and swallowing disorders, dry mouth. The temperature with botulism may not rise. In case of severe intoxication, there is pain in the head, loss of voice, a person cannot eat or drink. With this form of poisoning, you should immediately seek medical help.
Therapy includes cleansing the stomach, introducing a special serum and drinking plenty of fluids. In case of respiratory disorders, patients are provided with mechanical ventilation.
Staphylococcal intoxication
This is a pathology that is characterized by an acute course. It occurs as a result of eating contaminated foods.

Food poisoning of microbial origin caused by staphylococcus aureus appears 2-4 hours after bacteria enter the body. They are accompanied by symptoms such as pain in the abdomen, intense vomiting, pain in the head, feeling of weakness, pain in the eyes. The malaise lasts from one to three days. Staph food poisoning is not fatal.
Bacteria multiply in products prepared by the hands of people suffering from sore throats, purulent skin lesions. To avoid poisoning, food workers should be screened for these ailments. It is necessary to boil milk, observe the norms of heat treatment and storage of products.
Mold intoxication
These organisms pose a he alth hazard as they release highly toxic toxins. Once in the body with food, they cause severe damage to organs. For example, some poisonscause malignant neoplasms in the liver. Food mycotoxicoses include ergot poisoning, fusariotoxicosis and aflotoxicosis. Diseases result from the following factors:
- Eating bread that was made from grain contaminated with molds.
- Eating wheat or rye products that have been in the field for a long time in the winter and exposed to moisture.
- The source of infection can be peanuts, coffee and cocoa beans contaminated with these organisms.
Careful observance of the rules for harvesting, harvesting and processing grain and other products helps to avoid the appearance of intoxication.
Methods of therapy
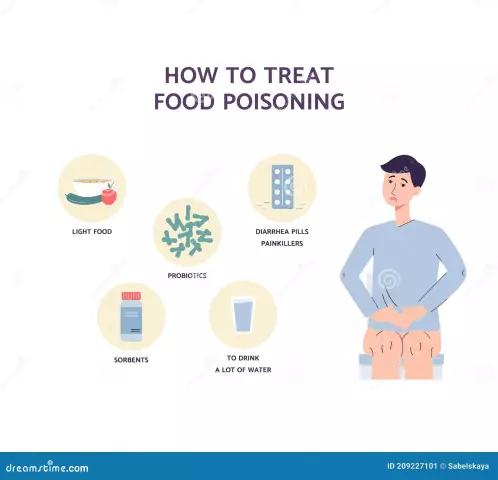
Poisoning caused by microbes, accompanied by bouts of vomiting and loose stools. As a result, a person loses a large amount of water, his condition worsens even more. Therefore, with this ailment, help should be provided to the patient immediately. First, you need to call a doctor. Secondly, before the doctor arrives, give the victim plenty of water to drink and clear the stomach.
Taking funds that restore the balance of fluid in the body (for example, Regidron) helps to avoid dehydration. In some cases, the patient needs hospital treatment, which includes drugs that eliminate inflammation, antibiotics, injections and drips.
How to prevent the development of pathology

Prevention of microbial food poisoning is as follows:
- Strictquality control of meat, fish, milk, confectionery and sausage products, smoked meats, canned food.
- Compliance with the conditions of processing and storage of food, checking the timing of implementation.
- Perform regular medical examinations of food industry employees.
- Refuse to make canned mushrooms at home.
- Compliance with hygiene standards.
- Storing jars of jam and pickles in the refrigerator.
Examination of goods

The procedure is carried out by Rospotrebnadzor. Food products must be tested if the buyer suspects that a food or drink contains pathogenic bacteria or a large amount of chemicals. After all, such circumstances can cause serious he alth problems. There are several types of goods, the examination of which is usually carried out by employees of Rospotrebnadzor. Food items that are checked quite frequently include:
- Sea delicacies.
- Milk products.
- Meat and convenience foods.
- Fruits and vegetables.
The presence of chemicals and harmful microorganisms in products indicates the potential danger of food for the he alth of buyers.