- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-06-01 06:18.
During childbirth, the child undergoes a sharp transition from the sterile environment, which is the womb, to the non-sterile environment.

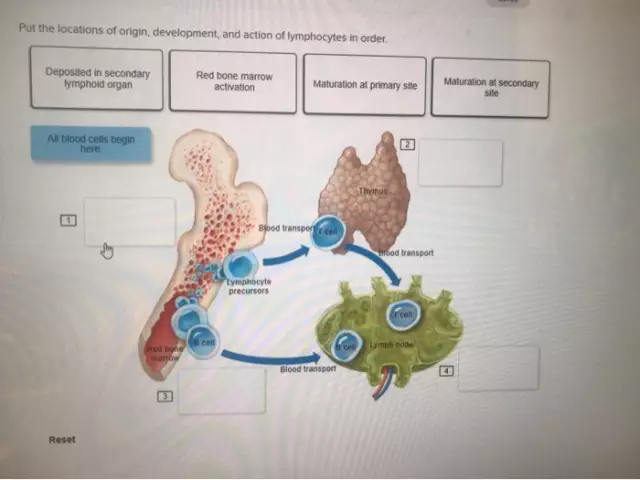
During this period, the child is protected from the hostile factors of the new world around him only by antibodies transferred to him by the mother's body. His own body is not yet able to produce protective antibodies. Gradually, the formation of the immune system. And only by the age of 6 can we talk about mature immunity. Lymphocytes are the main force of good immunity. They specialize in the destruction of viral infections. Lymphocytes are divided into:
- B-lymphocytes are scouts, they are looking for alien, hostile microorganisms;
- T-lymphocytes are controllers, they control the immune response of the body, if you need to strengthen this reaction, then T-hellers come into play, and if you need to suppress it, thenT-suppressors are activated;
- NK-lymphocytes are “natural killers” - they destroy foreign cells.
Lymphocytes in the blood of an adult are normally 20-35%.
In children, this indicator is not constant and varies depending on age:
- from birth to 4 days - 20-22%;
- 4-7 days - 40-45%;
- 8 days - 6 years - 45-67%, and the maximum increase in lymphocytes in the blood of a child at 12-24 months;
- from the age of 6, these figures begin to decline and by the age of 15 they stabilize within 20-35%.
Child's blood lymphocytes are elevated or reduced, the hemogram will show.

Lymphocytosis
A pathological increase in the level of lymphocytes - lymphocytosis - is divided into relative and absolute.
Relative lymphocytosis is an increase in the percentage of lymphocytes in the leukocyte formula while maintaining their normal number.
With absolute lymphocytosis, the total number of lymphocytes in the blood increases.
If it is revealed that the lymphocytes in the blood of a child are increased according to the relative type, this indicates past infectious diseases. The child's body suffers diseases more severely, the immune system reacts very violently, so the tests immediately show an increased level of lymphocytes. But recovery in babies takes less time than in adults. In addition, if the lymphocytes are elevated, the reasons may be the following:
- typhoid;
- some types of beriberi;
- endocrine pathology;
- fasting;
- period after prophylactic vaccinations.

A blood test showing that the absolute type of lymphocytes in the blood of a child is elevated should be the basis for a serious examination, as this can be a symptom of such formidable diseases as tuberculosis, rubella, acute viral hepatitis, chicken pox, cytomegalovirus infection, lymphocytic angina, hyperthyroidism, leukemia of the type of lymphoblastic leukemia, lymphosarcoma. In these cases, the level of lymphocytes can reach up to 90-95%.
Lymphocytopenia
Reducing the level of lymphocytes below normal is called lymphocytopenia. Lymphocytopenia can also be relative and absolute. Relative lymphocytopenia is accompanied by inflammatory-purulent processes, pneumonia. Absolute lymphocytopenia is observed in pathologies of the red bone marrow, with the death of a large number of lymphocytes, for example, with HIV.
It is very important to start treatment in a timely manner, because the consequences can be frightening. Protecting the body (especially children) is the basis of he alth, and you must ensure that the number of lymphocytes is always normal.