- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Tonsils or tonsils (lat. tonsillae) are accumulations in the pharynx of areas of lymphoid tissue on the border of the nasal cavity and mouth. They form the so-called lymphoid ring (Waldeyer-Pirogov) and are the central link of immunity. When breathing, this ring becomes the first barrier to microbes, neutralizing them. In addition, the tonsils produce macrophages and lymphocytes - protective cells of the immune system.
This lymphoid ring also contains paired palatine tonsils, inflammation of which is called tonsillitis. If such inflammation is repeated more than 3 times during the year, the process becomes chronic.
In medicine, purulent tonsillitis is a follicular or lacunar tonsillitis, in which a film appears on the lacunae. Pirogov's ring contains only 6 tonsils: pharyngeal, lingual, a pair of tubal and palatine. It is fully formed only in 5 years. Related to this is thatangina is not diagnosed in infants.
Structure of tonsils

They have a mesh connective tissue structure, which is permeated through with ducts (lacunae). In each gland, there are about 20 such lacunae. Follicles open in the lacunae, which are engaged in the destruction of pathogenic pathogens. Follicles are collections of lymphocytes. The tonsils contain a lot of nerve endings, so when they become inflamed, the throat hurts.
Causes of inflammation
Infection can be:
- external - contact with the sick or household, alimentary route of infection;
- auto-infection - associated with a drop in immunity, when opportunistic bacteria that are always and everywhere wake up and begin to activate, multiply and release toxins.
Provoking factors most often include hypothermia, soaked feet, SARS and other inflammation in the nasopharynx, carious teeth, sinusitis, swimming in cold water, overheating followed by drinking cold water, eating a lot of ice cream, too dry air, damp climate, drafts.
Lack of sleep, overwork, smoking, chronic pathologies, hypovitaminosis can also contribute to weakening the immune system.
In 90% of cases, the main culprit of angina today is beta-hemolytic streptococcus group A (GABHS). Then comes Staphylococcus aureus, pneumococci, rinaviruses, adenoviruses, fungi, chlamydia, etc.
Angina often occurs in the off-season - in spring and autumn. Children get sickmore often and harder.
Chronic tonsillitis

If acute tonsillitis has not been treated correctly and completely, then the process becomes chronic. At the same time, the tonsils are constantly inflamed, plugs with pus can accumulate in the lacunae. Bacteria are always present here and also constantly reduce immunity. Tonsillitis becomes an "uncontrollable" source of infection, constantly exacerbating. Moreover, exacerbations of chronic tonsillitis are most often purulent. Often, to avoid the negative impact, the tonsils have to be removed.
Symptomatic manifestations
Purulent tonsillitis begins with a sore throat, then intense pain during swallowing, fever and chills join. The temperature reaches 39 degrees and above. There is lymphadenitis of the mandibular nodes with general intoxication with headaches, myalgia, lack of appetite, weakness and malaise. In the pharynx, swollen red tonsils and the appearance of purulent plugs are visible, which can be removed with pressure. With pus from the mouth, there is a putrid smell, cough. Rhinitis, otitis can often develop.
Important! Chronic purulent tonsillitis remains contagious from the first day and while there is a purulent process in the tonsils. If a person has had a sore throat on his legs, he becomes a carrier.
Manifestations in adults and children
In adults, tonsillitis occurs without fever, even in the presence of purulent plugs. Other symptoms: swelling and redness of the tonsils, sore throat.
Such cases in recent yearshave become more frequent. This usually indicates a weakened immune system, which cannot actively fight the infection. Bacteria can only die at high temperatures. In addition, such a course of tonsillitis can be with: autoimmune diseases, heart failure, obesity, frequent use of antibiotics, vasoconstrictors, and exhaustion of the body.
Treatment of purulent tonsillitis in adults without fever is also carried out with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory therapy.
In children, the peculiarity of purulent tonsillitis is the possibility of starting the process, for example, with otitis media, with seizures in babies, hypersalivation, vomiting, diarrhea and abdominal pain. Children under 3 years of age are subject to hospitalization.
Diagnostic measures

The throat is examined with a pharyngoscope, a picture of a chronic inflammatory process is revealed. A smear on Leffler is required to rule out diphtheria. In the blood test, leukocytosis and accelerated ESR are detected. It is advisable to take a swab from the throat for culture and identification of the pathogen, as well as to determine its sensitivity to antibiotics. This will take at least 4 days. Therefore, when visiting a doctor, he chooses an antibiotic empirically, based on his experience.
Complications and consequences of purulent chronic tonsillitis
Chronic tonsillitis itself is already a complication of an acute process due to improper treatment or amateur parents. The most unpleasant consequence of chronic purulent tonsillitis is a rheumatic process with damage to the joints, heart andkidney.
When streptococci enter the heart valves, they lead to heart defects, infectious-allergic myocarditis, etc. can also develop. The kidneys are silent at first, and then a chronic inflammatory process is detected in them.
Complications of angina also include:
- collagenoses like systemic lupus erythematosus;
- vascular pathologies like Raynaud's disease;
- Ménière's syndrome (pathology of the inner ear);
- retropharyngeal abscess;
- otitis media;
- laryngitis;
- sinusitis;
- pharyngitis;
- bronchitis;
- nervous system damage;
- septicemia (rare but fatal).
Principles of Therapy
Treatment of purulent tonsillitis should always be comprehensive and carried out in a full course without interruption. Antibacterial therapy is mandatory, prescribed for at least 10 days.
It helps avoid complications and speeds up recovery.
Principles of antibiotic treatment
Antibiotics for purulent tonsillitis should only be given and taken as a continuous course. Reception should always be observed, even if there is clinical improvement. Antibiotics are not prescribed for prevention; they are ineffective for viruses. If there is severe intoxication, the patient may be hospitalized.
All other cases are treated at home. The decision to take antibiotics for the treatment of chronic purulent tonsillitis is made by the doctor.
Man alone canchoose an inadequate dose or the wrong antibiotics, which will lead to generalization of the infection.
General Requirements

General requirements include the following activities:
- Compliance with bed rest for a week.
- Drinking plenty of warm fluids to flush and flush out toxins.
- Eating only when warm.
- You can’t squeeze out purulent plugs yourself, they will burst during treatment themselves. Why you shouldn't squeeze plugs yourself: you can damage the protective film of the lacunae, and the infection can easily penetrate into the bloodstream.
- Do not give analgesics at temperatures below 38.5 degrees.
Antibiotics in the treatment of purulent tonsillitis are divided into drugs of the 1st and 2nd row. GABHS are sensitive to penicillins cephalosporins.
First row
These are penicillin drugs. They are valuable in that they treat sore throats and prevent the development of complications in the form of rheumatism.
But natural penicillins have now faded into the background, synthetic penicillins are used more often. These include Ampicillin, Oxacillin, Ampiox.
Inhibitor-protected penicillins lead the way. They contain clavulanic acid and remain resistant to microbial enzymes. These funds include: "Klavunat", "Sulbaktam", "Augmentin", "Amoxiclav", etc.
Second row
These are macrolides ("Azithromycin", "Sumamed", etc.) and cephalosporins 2, 3, 4generations ("Cefalexin", "Ceftriaxone", "Cefamisin", etc.).
Macrolides are taken for 5 days, but their concentration in the blood lasts 10 days.
Antibiotics don't stop even if you feel noticeably better. And one more thing: the effectiveness of antibiotics in the treatment of purulent tonsillitis is evaluated after 3 days: if the temperature persists, the antibiotic is changed.
Therefore, the first 3 days the doctor must visit the patient daily. This is especially true in the treatment of purulent tonsillitis in children.
Symptomatic treatment

So, systematic treatment includes taking the following groups of drugs:
- Antipyretics - Nurofen, Ibuklin, Paracetamol, Panadol.
- Local treatment of tonsils: irrigation, lubrication of the tonsils, aerosol application, rinsing, resorption in the mouth of special tablets, lozenges, lozenges - antiseptics are used. Topical treatment does not replace or preclude the use of antibiotics.
- Rinsing and irrigation. They relieve pain and local inflammation. For gargling prescribed: infusions and decoctions of herbs (calendula, chamomile, etc.), ethacridine lactate 0.1%, boric acid solution 1%, "Gramicidin", "Chlorhexidine", "Furacilin". Gargle every 4 hours.
- For irrigation: most often in the treatment of purulent tonsillitis in adults, Furacilin, Iodinol, Chlorophyllipt, Miramistin, Camphomen are used,"Ingalipt", "Yoks", "Kameton", "Tantumverde and others".
- Inhalations. For this purpose, Bioparox has been used for more than 55 years. This is an antibiotic spray containing fusafungin. Its advantage was that it did not penetrate into the blood and had a pronounced effect on pathogens locally. But at present, Bioparox is banned in Russia, allegedly due to the side effects of the antibiotic.
- One of the non-pharmacological methods of treating chronic purulent tonsillitis is the application of compresses to the throat. While purulent plugs remain, inhalations and compresses are not used.
- Lossable tablets - "Falimint", "Strepsils", "Pharingosept", "Septolete", "Gexor altabs" and others.
- Antihistamines. To desensitize the body in severe tonsillitis, Tavegil, Diazolin, Claritin, etc. are prescribed.
- Be sure to drink warm - herbal teas (chamomile, rosehip, sage, oregano), heated still mineral water, compotes, fruit drinks.
- It is mandatory in the treatment of purulent tonsillitis to prescribe vitamins and immunocorrectors, especially in frequently ill children - "IRS-19", "Immunal", "Ribomunil", etc.
- At the end of the course of antibiotics, probiotics are prescribed to restore intestinal microflora: Linex, Bifidumbacterin, Lactobacterin.
- In the treatment of purulent tonsillitis, physiotherapy and rinsing are possible only aftertemperature normalization. More often than others, UHF, electrophoresis, laser, UVI, tube-quartz, ozocerite on lymph nodes, aerosols with ultrasound using lysozyme, hydrocortisone, 10 sessions are used.
How to remove plugs
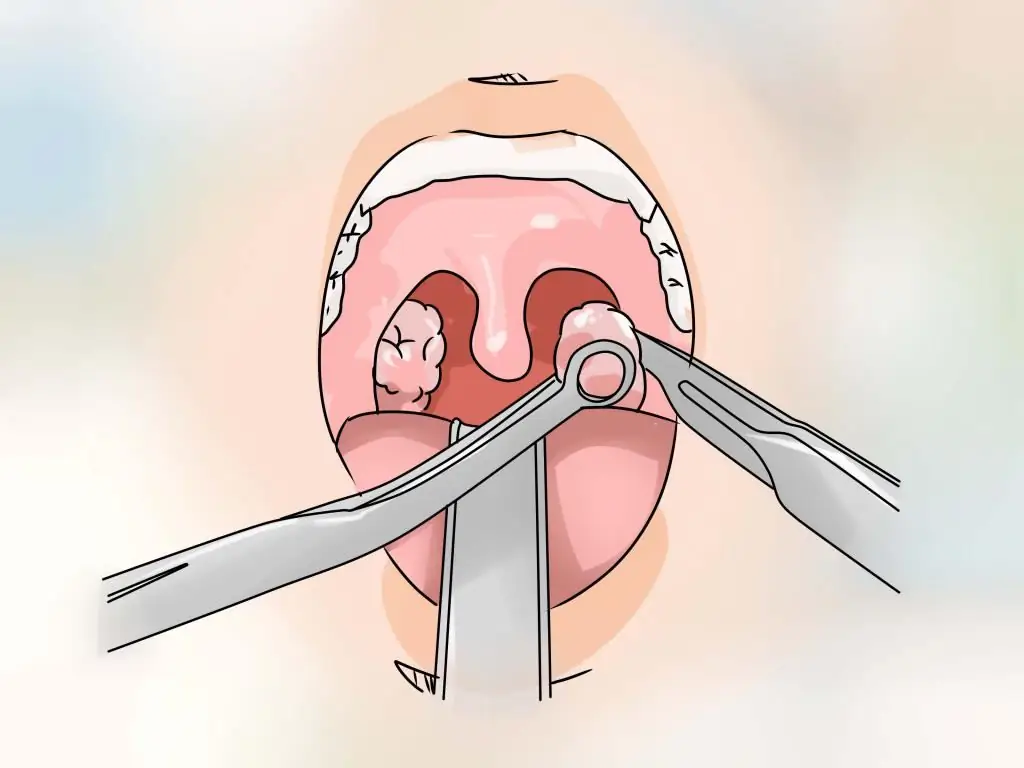
Treatment of chronic tonsillitis with purulent plugs should only be carried out by a doctor. Use manual washing and a special apparatus. With the manual method, one of the solutions is introduced into the lacunae: "Miramistin", "Furacilin", "Iodinol". The course is 7-10 procedures, improvement is noted after 2-3 times.
Treatment of tonsillitis with purulent plugs also implies the removal of plugs by vacuum pumping out pus on the Tonsilor apparatus.
Then, the tonsils are washed with antiseptics and irradiated with low-frequency ultrasound. Course - 8 procedures.
Gland removal
There must be a month period without exacerbations for the operation.
Indications for tonsillectomy:
- development of complications;
- frequency of angina more than 7 times a year;
- failure of conservative therapy;
- decompensated chronic tonsillitis, when it becomes a constant source of infection, etc.
Removing the tonsils is not a guarantee that there will be no more sore throats (remember the lymphoid ring).
Deletion methods:
- ultrasonic tonsil removal;
- electrocoagulation - cauterization of tonsils with electric current;
- radiofrequency ablation (coblation);
- excision with wire loop and scissors -the most common technique.
Another common method is ablation. This is the rejection of tissue by radiation (the tonsils are not completely removed). Ablation is laser and radio wave. Manipulation takes only half an hour.
Anesthesia for tonsillectomy is local, rarely general. The duration of the operation is 1.5 hours. After surgery bed rest - 3 days.
The patient should lie on their side, with a low pillow to prevent mucus and blood from the wound from flowing into the trachea. Drinking is allowed after 6-8 hours. Eat - only after a day, food should be warm and soft.
Folk remedies
Treatment of purulent tonsillitis at home is quite acceptable in compliance with all doctor's recommendations.
To soften the throat, warm milk with soda and butter can be recommended.
Other recipes:
- Morning rinse - add 1 tbsp to 200 ml of water. l. apple cider vinegar.
- It is also good to gargle with fresh beetroot juice, soda solution with s alt and iodine. Rinsing is done at least 3-4 times a day.
- Disinfectants - onions and garlic. They need to be crushed, squeezed juice mixed with honey. You can also mix birch buds and apple cider vinegar with honey.
- Herbal teas - linden with honey, thyme, cranberries. With the severity of intoxication, it is better to drink warm water up to 2 liters per day.
- Tonsils can be lubricated with fir oil, it has a bactericidal effect. Also, fir oil can be added to the solution for gargling. In the case of the permission of the attending physician, fir is first preparedwater - for 200 ml of warm water 1 tsp. honey + 2 drops of oil. The solution is used for rinsing - 3-4 times a day.
Prevention measures
The most important thing in the fight against sore throats is hardening the body and strengthening the immune system. This will be facilitated by a balanced diet, prophylactic intake of vitamins, good sleep and rest. In addition, it is necessary to treat chronic foci of infection in the form of caries, sinusitis and sinusitis, inflammation of the upper respiratory tract. Do not drink ice water from the refrigerator when overheating, hypothermia should be avoided.






