- Author Curtis Blomfield [email protected].
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
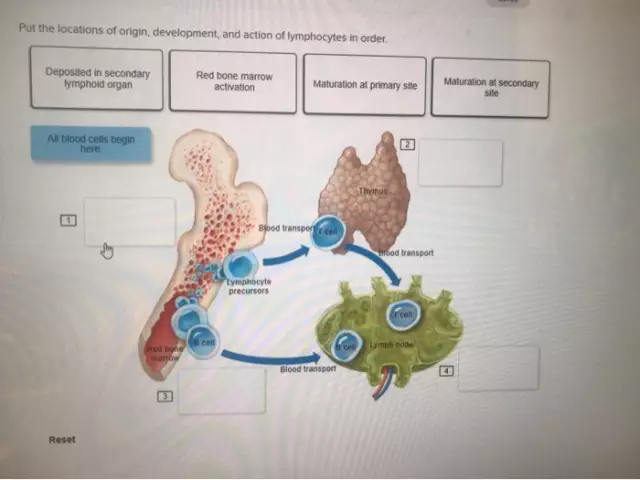
Lymphocytes are the basic cellular elements that are part of the human immune system, which are formed in the bone marrow and distributed in the tissues of the lymphoid type. Their main function is to detect a foreign antigen and provide a complex immunological forced response of the body to the threat that has arisen. Very often, tests reveal an increase in the level of lymphocytes in the collected blood. This may be the result of some physiological or pathogenic condition that can be caused by various causes.
Norm of lymphocytes in an adult
In medicine, there are norms for the permissible level of lymphocytes in the blood. Deviations from these norms in one direction or another are the reason for additional diagnostic measures in order to find the cause of the violation.
The relative norm of the content of lymphocytes in the blood of an adult is in the range of 20-30%. In absolute terms, the number of lymphocytes should not go beyond 1-4.5x109/liter.
Tolerable amount in children
Varying the norm of the content of lymphocytes in the blood of a child directly depends on his age, so the limits of the range are very wide.
The following norms are generally accepted:
- for a child up to a year - 55-75% or 4-10, 5 x 109/liter;
- from 1 to 4 years - 45-65% or 2-8 x 109/litre;
- 4 to 6 years - 35-55% or 1.5-7 x 109/litre;
- 6 to 10 years - 30-50% or 1, 5-6, 5 x 109/liter;
- from 10 to 21 years old - 30-45% or 1-4, 8 x 109/litre.
Thus, it can be seen that the absolute and relative indicators of the number of lymphocytes in children's blood gradually decrease as the child grows.

Among physicians, elevated lymphocytes are usually called lymphocytosis. Such a condition is not considered a disease, since it is caused by a protective reaction of the body and is an indicator that any pathological processes begin to develop in the human body. When conducting a blood test, both relative and absolute indicators are necessarily studied, since both of them play an important role in the analysis of the patient's condition. After receiving its results and, if necessary, conducting additional studies, the doctor will be able to determine what elevated lymphocytes are talking about.
Increase in the level of lymphocytes
Not only diseases, but also physiological features can cause an increase in the level of lymphocytes - for example,for example, a woman's blood test during the menstrual cycle gives very controversial results. In addition, in people whose immune system is of the reactive type, any malfunction in the functioning of the body (even the common cold) most often shows an increased level of concentration of these cells.
Causes of growth of lymphocytes in an adult
As mentioned above, there can be many reasons for increased lymphocytes in adults, and they all have a different nature. Here are some of them:

- Long-term diet based on the complete rejection of food.
- Viral diseases of the liver that cause it to enlarge, as well as similar problems with the spleen.
- Having a person with tuberculosis, the type of which can be different, even asymptomatic.
- Infection with various bacterial infections, including syphilis and brucellosis.
- The beginning of the development of infectious mononucleosis.
- The occurrence of various allergic manifestations.
- Hypertrophic thyroid function.
- Bad habits, in particular, alcoholism and smoking, in combination with constant stress.
- Development of pathogenic autoimmune processes (rheumatoid-type arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, dermatomyositis, etc.).
- Benign chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
- Lymphosarcoma at the stage of progression.
- Direct poisoning with hazardous chemicals including arsenic, chlorine and lead.
- Crohn's disease.
- Multiple typemyeloma.
- Diseases related to the endocrine system.
- Side effects and reactions to various medications.
- Broad spectrum neurasthenia.
- Moment of transition in acute disease from illness to recovery and in chronic disease from relapse to remission.
Symptomatics in adults
Increased lymphocytes in adults may not give absolutely no symptoms and proceed in a latent form. Such lymphocytosis is detected by chance, during a blood test, which can be either planned or carried out as a diagnostic study for any disease. However, they can also cause a range of symptoms. Clinical signs of lymphocytosis in adults:

- reduced or completely absent appetite, resulting in rapid weight loss;
- often dizzy and headache;
- diarrhea or constipation occurs regularly or may alternate;
- skin integuments turn pale and dry;
- skin diseases occur;
- hyperhidrosis develops, that is, sweating increases;
- person often feels chills;
- body temperature stays at 37-38°C;
- general he alth worsens: a person is lethargic, broken, drowsy, efficiency decreases;
- hair begins to fall out or break;
- the tonsils, lymph nodes increase, they hurt, swell and turn red;
- the projection of the spleen and liver increases.
The child has elevated lymphocytes. About whatdoes it say?
Among the factors in this case are the following:
- Anemia disease based on acute vitamin B12 deficiency.
- Development of classic infectious diseases: rubella, measles, encephalitis, chickenpox, whooping cough, smallpox, mumps, malaria.
- Formation of malignant tumors and oncopathology.
- Infectious type of lymphocytosis, also known as Smith's disease.
- Having asthma or other lung disease.
- Problems related to the endocrine system.
- Development of physiological lymphocytosis in a child under 4 years of age, in the absence of manifestations of any other disease and satisfactory he alth.


These are the main factors affecting the increase in lymphocytes in a child
Symptoms of lymphocytosis in children
As in an adult, elevated lymphocytes in a child's body may not cause symptoms. However, if they appear, they look like this:
- child is lethargic and apathetic all the time;
- he is dizzy, sometimes it hurts;
- he is sick or vomiting;
- constipation is replaced by loose stools;
- baby has difficulty breathing;
- there is an enlarged projection of the lymph nodes, spleen, and liver;
- skin covers all over the body covered with a small rash;
- increase in size of tonsils;
- the child often suffers from respiratory diseases (colds, flu);
- body temperature constantly elevated to 38°С.

Diagnostic measures
To determine whether lymphocytes in the blood are low or high in both a child and an adult, you can use a blood test.

If, in addition to the classic symptoms of lymphocytosis, any other symptoms are observed, a specialist may be given referrals for additional diagnostic measures in order to immediately exclude the possibility of an erroneous diagnosis. Among them are the following:
- ultrasound examination of the peritoneum;
- chest x-ray;
- histological and cytological studies of the bone marrow;
- CT scan.
Treatment procedure
Because elevated lymphocytes are not a disease, no specific treatment can be given as it does not exist. In cases where there are no clear symptoms of a particular disease, in addition to a laboratory test, the specialist directs the patient to the above diagnostic methods.
Children and adults are given specific therapy for elevated lymphocytes only after an accurate diagnosis has been obtained. The vast majority of cases involve the appointment of antiviral drugs, antibiotics, antipyretic, anti-allergic and anti-inflammatory drugs. In some cases, corticosteroids, chemotherapy (in the case of myeloma treatment), bone marrow transplantation (in leukemia) and other measures that are developed individually for each patient may be prescribed.taking into account his current condition, the severity of the disease and other indicators.

Therapy for elevated lymphocytes involves, first of all, the elimination of the cause of such a patient's condition. When an increased level of lymphocytes is found in a person, it is necessary to direct treatment not to reduce their number, but to eliminate the root cause of its growth.
Treatment of lymphocytosis can take several days or months. The duration of therapy depends on the disease that caused this condition of the patient. However, after treatment, the level of lymphocytes in the patient's blood will be stabilized.
Possible Complications
Often, the treatment of lymphocytosis ends with a complete recovery and timely treatment will prevent the development of any complications.
If treatment of lymphocytosis is not performed or it is ineffective, the patient's condition may worsen significantly. A patient with an elevated level of lymphocytes in the blood may begin an internal hemorrhage, which can lead to the death of the patient. In addition, the development of immunodeficiency conditions such as HIV or AIDS is possible. Another complication of lymphocytosis can be a decrease in the level of blood clotting, in which case even a minor injury can cause severe bleeding.
It should be remembered that only a doctor should deal with an increase or decrease in blood lymphocytes, and self-medication can lead to serious complications.
Preventive measures
As a preventive measure to prevent an increasethe level of lymphocytes in the blood, are:
- regular hardening;
- carrying out routine vaccinations;

- compliance with the rules of personal hygiene;
- tracking your diet and lifestyle;
- doing moderate physical activity;
- maintaining a state of emotional stability, avoiding excessive stress and stress on the nervous system.
All of the above measures will help to maintain the level of lymphocytes in the normal range.