- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
X-ray of the paranasal sinuses is performed in two projections: chin and nasopharynx. Each x-ray allows visualization of a specific anatomical structure. Due to the many different nuances and subtleties, the appointment of the attending physician before performing an x-ray must necessarily be analyzed by a radiologist. This specialist can prescribe an alternative projection or even cancel the appointment of the main doctor.

What does an x-ray show?
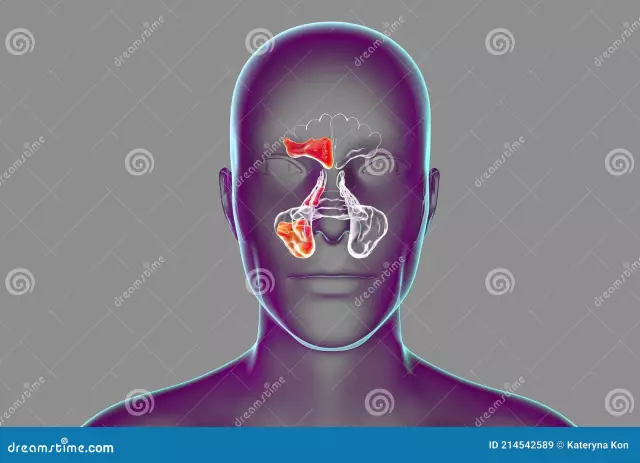
X-ray of the paranasal sinuses in the frontal projection shows the following anatomical structures:
- The structure of the lattice labyrinth.
- Display of the right and left half of the sphenoid sinus.
It should be noted that, unfortunately, it is impossible to determine sinusitis with such radiography. This is actually so, so the frontalprojection in the study of pneumatization of the nasal sinuses is rarely used. The chin projection in the study of sinusitis is the most preferred. She displays the sinuses as accessible and open as possible.
A description of the sinus x-ray procedure will be provided below.
When using the nasal chin stacking, the pyramids of the temporal bone are superimposed on the region of the maxillary sinuses. Against the background of poor performance of the naso-chin projection, the structures of the temporal bones can almost completely block the view.
To eliminate the above defect, sometimes the patient is asked to open his mouth. With such laying, the temporal bones can fall down. The beam can be directed vertically at an angle of thirty degrees to the vertical. On such radiographs, it is possible to clearly trace the state of the sinus of the sphenoid bone.

What can be added?
In the event that the above projection is not enough, then the x-ray of the paranasal sinuses can be supplemented with genyantrography or tomography. Tomography is a layered study. It allows you to study the anatomical structures that lie deep in the tissue. Gymorography involves the introduction of a contrast agent to the patient in the region of the paranasal sinuses. This technique is often used in case of detection of an annular shadow that resembles a cyst.
How the study is done and the description of the procedure
X-ray of the paranasal sinuses as part of the chin projection can be performed invertical position. Or this is done in a horizontal version, that is, when the patient is laid down. Most often, during the procedure, a person sits or stands near the radiographic vertical stand. This laying makes it possible to obtain optimal images in case of suspected development of sinusitis. How is an x-ray of the paranasal sinuses performed?
- The patient should stand along the counter, equipped with a fixed grid.
- The person's head is positioned so that the chin can touch the bar and the nose is two centimeters away from it.
- The midline of the head is positioned sagittally.
- The exposure is made on a cassette 13 by 18.
- This maintains a focal length of one hundred centimeters.

Using contrast agent
X-ray of the paranasal sinuses using a contrast agent allows you to fully explore the structure of the anatomical formations, and in addition, this manipulation makes it possible to identify additional plus-shadows, which often turn out to be formed by a cyst, tumors or polyps.
Additional nuances of the procedure
There is no need to carry out any additional preparatory procedures before x-rays of the paranasal sinuses. You just need to come to the x-ray room, providing the diagnostician with a referral. Next, the patient takes off all his metal jewelry with clothes that have iron inserts, then puts onspecial apron. Actually, this is the whole basic preparation for the x-ray of the paranasal sinuses.
What does the algorithm depend on?
The algorithm for X-ray manipulation largely depends on the indications:
- For the purpose of examining the sinuses, images are taken from the occipital chin view, and also from the frontal side.
- As part of the study of the presence of a bone formation, an image is taken in three planes at once, namely: in the left, in the straight line and in the right, sometimes even the fourth projection (naso-chin) is made by diagnosticians.

From the radiologist during the procedure, as a rule, accurate recommendations and instructions regarding the proper position of the patient are received. While taking the picture, be sure to take a deep breath, and then hold your breath. The examination can last from one to several minutes.
The results of the procedure, as a rule, are transmitted directly to the attending physician (usually this nuance is indicated in the referral) or thirty minutes later directly to the patient himself. The doctor evaluates the images and makes a conclusion with a subsequent treatment schedule and recommendations. It is worth noting that this type of examination is strictly contraindicated to be carried out more often than once every six months.
Contraindications for the procedure
It is categorically not recommended to carry out an x-ray of the paranasal sinuses of the nose for women in position, since the extremely negative effects of rays have been known for a very long timefor the development of the embryo. It is also necessary to refuse this manipulation if the patient has facial, dental or cranial metal prostheses.
It is necessary to refuse this type of research even if the patient has been diagnosed with an oncological disease. Otherwise, this type of X-ray does not have any other contraindications, however, it is still recommended to consult a doctor.

Deciphering the x-ray of the paranasal sinuses
A good x-ray of the sinuses, unfortunately, does not show additional shadows (so-called artifacts). But at the same time, anatomical structures, as a rule, are symmetrical and clearly visible. In the presence of sinusitis, a fluid level can be visualized, which is located from the medial to lateral walls. Chronic inflammatory process in the sinuses (for example, with hypertrophic sinusitis) is usually accompanied by thickening of the mucous membranes with concave outer contours (according to the principle of a parabolic curve).
Why do x-rays of the paranasal sinuses are interesting to many.
In order to distinguish acute processes from chronic symptoms, it is advisable to shift the patient's head to the right or left when conducting a re-examination. In the event that the inflammatory process is fresh, then the fluid level will certainly shift. With a chronic change, the x-ray symptoms of the pathology will not change. The criteria by which the quality of an image is judgedthe following:
- The presence of a clear structure of the bone walls.
- Presence of symmetrical styling.
- The presence of a white-gray shadow. This criterion determines the technical features of the exposure.
Why do x-rays of the paranasal sinuses? In the resulting picture, you can always see various neoplasms and cysts along with the presence of foreign bodies, the formation of cracks, debris and fractures. In addition, the doctor may notice all kinds of eclipses that demonstrate the inflammatory process.

In the absence of disease
In the absence of any diseases, all the structures of the nose will be distinguished by smooth, and at the same time, clear contours, and the sinuses will appear as semi-oval even niches. The sinuses, as a rule, should be completely darkened. In the event that there are light blotches, then this is an indicator of the presence of one or another inflammatory process.
In situations where the doctor cannot reliably establish a diagnosis from x-rays, patients are advised to undergo magnetic resonance and computed tomography. Of course, such studies will cost the patient a little more, but the information content, and at the same time, the safety will be an order of magnitude higher.
How is an x-ray of the paranasal sinuses done with maxillary sinusography?
Gymorography
Gymorography makes it possible to determine intra-sinus formation. It is also applicable to the diagnosis of cysts and polyps. How genyantrography is performed:
- Immediately after anesthesia, the sinus wall is punctured.
- Through it, the paranasal sinuses of the patient are washed with a solution of furacilin.
- Then, a solution with heated iodlipol is injected through the needle.
- Next, pictures are taken in the naso-chin, nasofrontal and lateral projections.
When performing genyantrography, it is forbidden to take an x-ray at the same time of both sinuses. In this situation, clear visualization of the anatomical structure is excluded due to overlapping exposure from the opposite sinus.
X-ray of the posterior nasal cavity
The posterior paranasal sinuses in anatomy include the following anatomical structures:
- Wedge-shaped structure.
- Structure of lattice cells.
The use of the naso-chin and chin projections is not suitable for the study of these anatomical structures. This is where axial projection comes into play. The rocky part of the temporal bones, along with the foramina of the base of the skull and its fractures, can also be seen using this projection. The sphenoid bone has a wide variety of structures. The radiologist must have a lot of experience in order to correctly decipher the x-ray. On axial x-rays, the wings of the sphenoid bone are always clearly visible along with the basilar apophysis.
In such a projection, a round, posterior torn and oval hole can be traced very well. In the presence of injuries of the skull (against the background of a fall on the head, with blows to the crown or occipital bone),a fracture line occurs. During the review, the lines of the lower jaw and the fracture are visible, and in addition, the bases of the apophysis of the occipital bone. If a disease is detected in one of these anatomical structures, the x-ray is supplemented with an aim x-ray for a clearer display.

It must be emphasized that the X-ray of the skull, as well as the paranasal sinuses, is one of the most difficult areas of radiology. Due to the many formations, it is often possible to see symptoms on the radiograph, formed by overlapping or superimposing different anatomical details with each other. This requires a very large practical experience in order to be able to distinguish the norm from the disease in the images of the skull and paranasal sinuses.
What the x-ray shows, now we know.
Where to perform the procedure?
Usually, absolutely every clinic has its own x-ray room. Also, diagnostics can be performed in specialized otolaryngological centers (this is especially recommended for children) or in other large clinics.
Referral for procedure must only be issued by a doctor. In such a case, self-administration can be fraught with extremely negative consequences for the patient.
After passing each procedure with the use of X-rays, appropriate marks are made in the patient's record. Frequent X-ray diagnostics can adversely affect the state of the entire human body: teeth, hair,nails and the like. This can trigger rapid aging processes.
We looked at what an x-ray of the paranasal sinuses shows. The procedure is also described.