- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
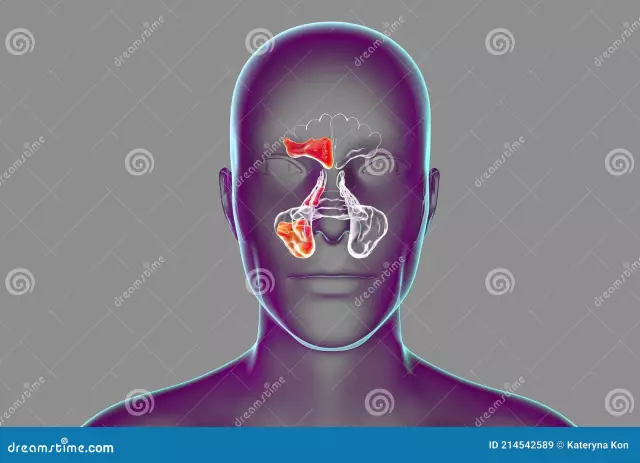
Paranasal sinuses are appendages of the nasal cavity, represented by bony recesses in the skull, covered from the inside with a mucous membrane. They are connected to the oral cavity and serve to moisten, clean and warm the inhaled air. The paranasal sinuses are also directly involved in the formation of sounds.
In this material I would like to describe the anatomy of such appendages. Let's find out what the paranasal sinuses are for. Their meaning, variants and anomalies will be discussed further. We also highlight the diseases that these appendages are susceptible to.
Paranasal sinuses: anatomy

The following sinuses adjoin the nasal cavity on the sides:
- maxillary;
- frontal;
- wedge;
- lattice maze.
Let's take a look at how the paranasal sinuses work one by one.
Maxillary sinus
The maxillary sinus is located in the thickest bone of the upper jaw. This is the most massive paranasal sinus. In a mature adulta person, its average volume is from 10 to 12 cm3.
The shape of the maxillary sinus resembles a tetrahedral pyramid. Its apex is located near the zygomatic process. The lower wall forms the so-called alveolar process, which separates the upper jaw from the oral cavity.
Frontal sinus
Let's continue to find out how the nose and paranasal sinuses are formed. Next, consider the anatomy of the frontal sinus. The latter is located between the lamellar bone bodies of the frontal zone. It is divided into equal halves by a special partition.
The size of the frontal sinus varies greatly among individuals. Its average volume can be from 3 to 5 cm3. The development of the presented appendage of the nasal cavity begins from the first years of life and ends by the age of 25.
Sphenoid sinus

The sphenoid sinus, which is also called the main sinus, is located in the thickness of the sphenoid bone of the upper jaw, immediately above the nasopharyngeal arch. It is divided by a bony septum into two unequal parts, each of which has an exit to the upper nasal passage.
The sphenoid sinus borders on the cranial fossa, carotid artery, nerves that are responsible for eye movement. Therefore, the development of pathological processes in the presented area poses a serious danger not only to he alth, but also to human life.
The sphenoid sinus begins to develop immediately after birth. Its formation ends around the age of 20.
Grid Maze
Describing the paranasal sinuses (the photos presented in the article clearly demonstrate their location), it is worth considering the anatomy of the so-called ethmoid labyrinth. This sinus is formed by a network of air chambers of various shapes and sizes. They are located in the area between the nasal cavity and the eye sockets. In the upper part, the ethmoid labyrinth borders on the orbital grid and the anterior cranial fossa.
In babies, the presented paranasal sinus develops most actively. The final formation of the network of air cells ends at about 14-16 years of age.
Next, find out what pathologies and diseases of the paranasal sinuses exist.
Rhinitis

The most common ailment that affects the paranasal sinuses. The disease is acute infectious nature, has a viral origin. It is characterized by the appearance of copious mucous discharge from the nasal cavity, difficulty in breathing.
For rhinitis, drug therapy is used. In the most difficult, advanced cases, doctors resort to surgical intervention. The need for such treatment arises in the presence of deformity of the nasal septum, as well as pneumatization of the middle and hypertrophy of the upper bone shells.
Sinusitis

Under this definition, tissue inflammation is known, in which the paranasal sinuses hurt. The causative agent of the disease are allergies and infections. Main symptoms: persistent feverbody, constant nasal congestion, headaches, loss of smell, feeling of pressure on the eye sockets. In the most severe cases, there is an acute toothache, as well as swelling of the face.
In the treatment of sinusitis, the use of immunomodulating drugs, dilating blood vessels drops, antibiotics, drainage of the paranasal sinuses is indicated. Without timely therapy, sinusitis can turn into more acute forms, known as frontal sinusitis, sinusitis, ethmoiditis. These complications lead to inflammation of the bone walls and mucous membranes of the respiratory tract.
With severe sinusitis, an abundance of purulent masses is released from the affected sinuses. Without quality treatment, the infection can spread to the tissues adjacent to the sinuses, in particular to reach the brain, which threatens with the most serious consequences.
Polyposis of the paranasal sinuses

Polyps are neoplasms of tissues that gradually grow on the mucous membranes of the nose. They occur against the background of a variety of ailments. Most often, chronic tissue inflammation leads to their formation.
Among the main symptoms of polyposis, it is worth noting:
- obstruction of free breathing;
- periodic bouts of complete nasal congestion;
- tissue inflammation;
- changing the timbre of the voice to a more nasal;
- impaired sense of smell and then hearing.
Polyp growth is stopped by surgery. If the pathology is detected in the early stages of formation, it is possible to useconservative methods of therapy, in particular, taking antihistamines and anti-inflammatory drugs, vitamin complexes.
Deformation of the nasal septum
At the root of the pathology lies the deviation of the nasal septum from its midline in both or any one direction. The disease can be acquired or hereditary. If the nasal septum is deformed, a person may experience breathing problems, regularly suffer from sinusitis and rhinitis.
Treatment is by surgical intervention. To restore he alth, an operation is performed to correct the nasal septum - the so-called septoplasty. The main purpose of the procedure is to improve nasal breathing.
In closing

As you can see, the paranasal sinuses actually form a single network of air-conducting cavities. It is not surprising that all the pathologies covering the presented area are similar in etymology. It is extremely difficult to independently determine which disease affected the paranasal sinuses. Methods that give results in some pathologies may be completely ineffective in others. If you have symptoms of the above ailments, it is better to immediately seek a diagnosis from a qualified doctor, which will avoid complications.