- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Gingival fibromatosis is a pathological increase in the volume of connective tissue. This pathology is considered to be genetically determined, but the exact causes that could contribute to the onset of the disease have not yet been clarified.
General information about pathology
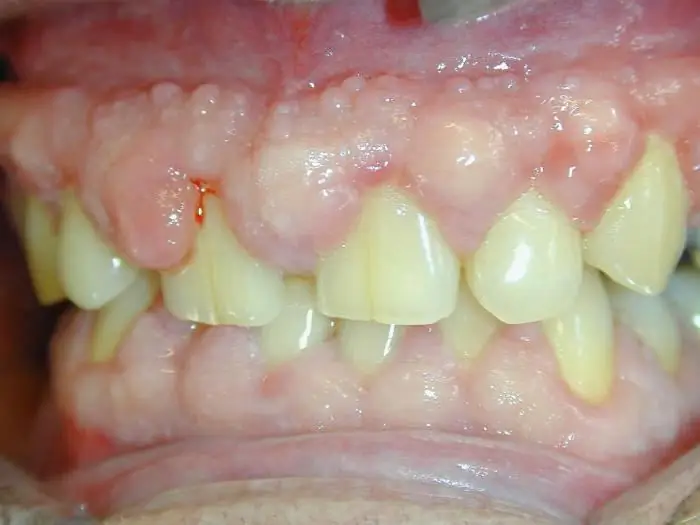
It is slowly progressive and not very common. If a person has a genetic predisposition to it, then the first signs of pathology appear already at the stage of teething in an infant. In the absence of a hereditary factor, the disease can develop in young people, as well as middle-aged patients.
Most often, patients are diagnosed with generalized fibromatosis. In this case, the connective tissue grows throughout the gum and its volume gradually increases further. This form of the disease subsequently leads to the fact that the teeth are completely hidden (even the cutting part).
Sometimes the patient has focal fibromatosis. Here growth is limited in size. They are several hearths that are not interconnected.
Causes of disease

There are only a few reasons for the development of pathology:
- Hereditary predisposition. In this case, the disease manifests itself already in the first year of life. The reaction of the body to teething or a violation of the hormonal background can provoke the development of the disease. In adults, generalized fibromatosis appears due to blood diseases, pregnancy.
- The use of drugs. The disease in this case is caused by drugs such as "Phenytoin" (to eliminate epileptic seizures), "Cyclosporine" (depressant immunity), as well as oral contraceptives. Calcium channel blockers can be dangerous: Nifedipine, Verapamil. Drugs for the treatment of hypertension also contribute to the development of fibromatosis.
The occurrence of a dosage form of pathology does not depend on a person's gender or age. That is, it appears at any stage of life.
Main symptoms
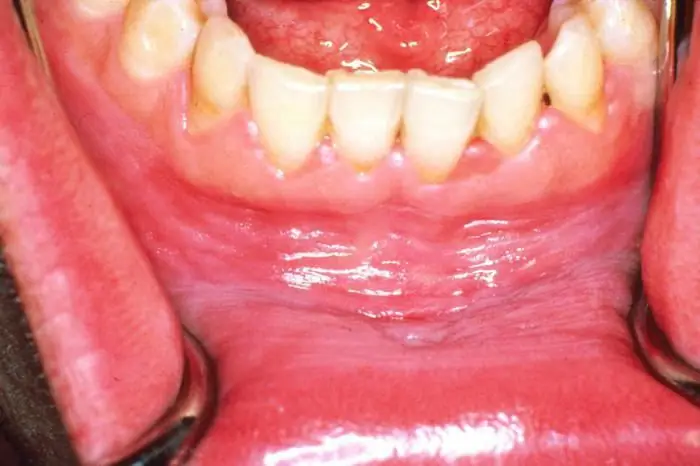
Gingival fibromatosis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Swelling of the interdental papillae, as well as the edges of the gums.
- Uniform shade of soft tissues - they acquire a uniform pink color.
- Changing the shape of the gums, which become like rollers.
- Condensation growths.
- Difficulty in eruption of crowns, both dairy and permanent.
- Closing the teeth with at least half of the overgrown tissue.
If the patient hassuch symptoms, it means that he develops gingival hyperplasia. It is necessary to treat the pathology while it does not yet cause severe discomfort.
Degrees of development of fibromatosis
Gum fibromatosis progresses slowly. In total, there are 3 stages of the development of the disease:
- First. The thickening of the gums becomes like a roller, and the overgrown tissue covers the teeth by 1/3 of the height. The structure of the fabric is very dense.
- Second. This is characterized by the closure of half of the crown. When brushing your teeth or eating, your gums bleed.
- Third. The interdental papillae, as well as the surrounding soft tissues, are enlarged to such an extent that they can completely cover the tooth. The edge of the gum becomes uneven, covered with granulation tissue. It bleeds intermittently, even if it has not yielded to mechanical stress.
It is advisable to start therapy at the first stage of the development of the disease in order to avoid complications. The most common treatment is surgery.
Complications and comorbidities
Gingival fibromatosis must be treated, as it causes a lot of discomfort. First of all, the patient's gums form deep gingival canals into which food enters. Its accumulation leads to the development of an inflammatory process, accompanied by suppuration.
And in these pockets, tartar is formed, contributing to injury to soft tissues. Growths do not allow a person to bite off and chew food normally, which provokes the developmentpathologies of the gastrointestinal tract. The patient is unable to properly brush his teeth. In babies, the crowns cannot erupt, so the jawbone can be deformed.
A rather dangerous complication of the disease is the destruction of the partitions between the teeth, as well as a decrease in bone density. Gingival hyperplasia leads to loosening and loss of crowns. A very serious complication is the degeneration of overgrown tissue into a malignant one. After its removal, relapses of the disease may occur, which entails a second operation.
Disease diagnosis
If a person has swollen gums, treatment should be done only after an accurate diagnosis has been made. It must be differential, as fibromatosis can be confused with other pathologies of the oral cavity: hypertrophic gingivitis.
The doctor prescribes the following examinations to the patient:
- External examination of the gums and fixation of complaints. The patient should describe his feelings in as much detail as possible.
- Histological analysis of overgrown tissue.
- X-ray examination.
In some cases, a biopsy of the cells taken for analysis can be done, which will help confirm or refute the presence of a malignant pathological process.
Treatment of disease
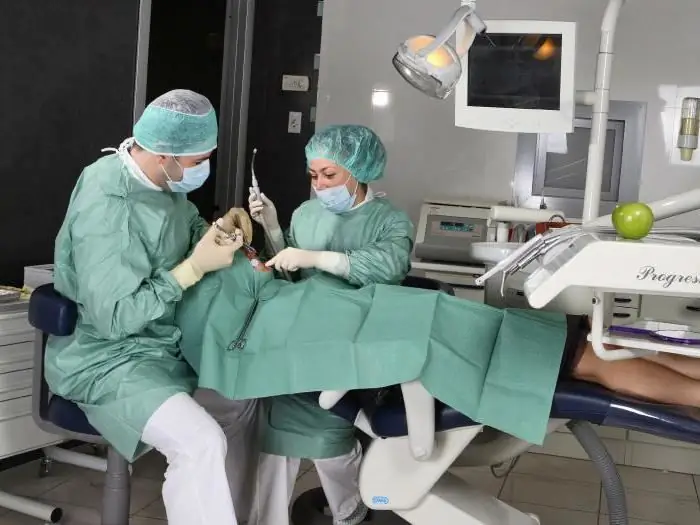
If a person has swollen gums, treatment depends on the underlying cause. For example, to eliminate the dosage form of a pathology, you simply need to cancel the drug thatcaused tissue growth. In this case, the disease passes without a trace on its own.
As for a genetically determined disease, then, apart from surgery, no more methods of therapy are used, since they will simply be ineffective. Folk remedies will not be able to stop tissue growth. There is currently no medical alternative to surgery.
Surgery lasts only half an hour. The operation involves the removal of the affected edge of the gums. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. After the intervention, a special orthodontic bandage is applied to the gum. Thanks to her, the infection will not be able to get into the wound.
During the operation, the oral cavity is also sanitized. That is, plaque must be removed from the surface of the teeth, and the depth of the gum canals should also be measured. After the intervention, the patient will need to be periodically shown to the doctor to monitor recovery.
Since the presented disease can recur, after surgery, a person will need to carefully monitor their he alth and try to prevent the resumption of tissue growth.
Prevention of fibromatosis
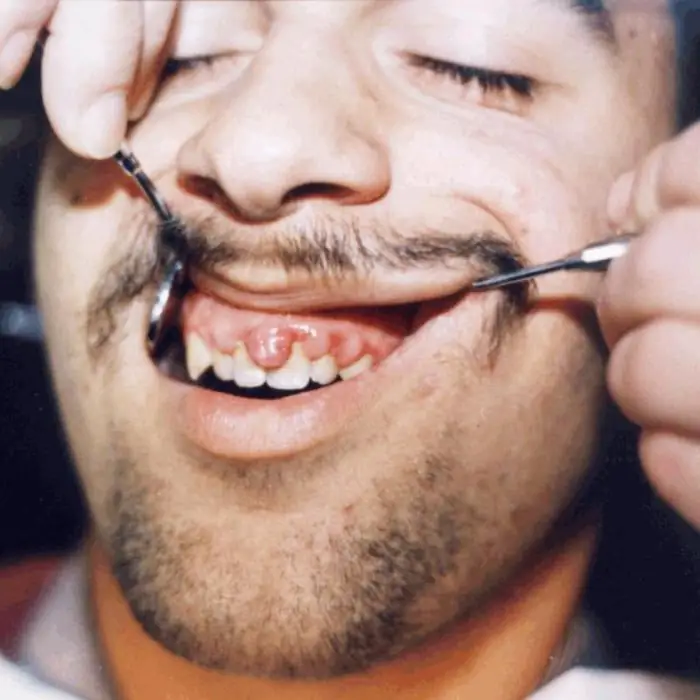
If a person has previously been diagnosed with gingival fibromatosis, treatment cannot guarantee that it will not reappear. Therefore, the patient should follow these recommendations:
- Keep daily oral hygiene.
- Try to avoid the appearance of dentaldiseases or treat them immediately at the first signs.
- It is important to choose the right toothbrush and toothpaste so as not to injure the gums.
- If medications have been prescribed for the treatment of any inflammatory or infectious disease, then they should be taken with extreme caution.
Fibromatosis is a very unpleasant and painful pathological condition, which not everyone manages to get rid of completely. However, it cannot be left without treatment. Stay he althy!






