- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
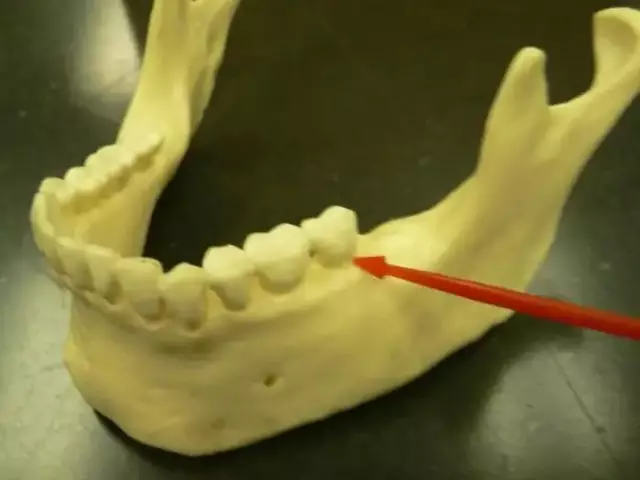
Alveolar process is an anatomical part of the jaw. Such formations are found both on the upper and lower jaws. The appearance of the alveolar process resembles a sponge. Its height may be different, depending on hereditary factors, age, past dental diseases.
Building
The composition of the alveolar process includes the following elements:
- The outer wall that includes the cheeks and lips.
- Internal, including tongue, jaw, teeth.
- The space between both walls is filled with dental sockets from which teeth grow. Interestingly, the alveoli appear along with the growth of the tooth and completely disappear after it falls out. They are part of the jaw, and are covered with a cortical layer on top. On an x-ray, it appears as a dense line that is distinct from spongy tissue.
Process pathology
Correction of the alveolar process may be necessary if this part of the jaw has undergone pathological changes. Among them are the following:
- Atrophy. It happens for various reasons. If the doctor has determined atrophy, then before the correction, he must also perform alveoloplasty, the methods of which can be varied. The need for such a process is to increase the amount of bone tissue in the place where the operation will be performed in the future. Atrophy requires implantation.
- Wrong development. In some patients, doctors observe too large alveolar processes. In this case, their size decreases only during the surgical intervention.
- Fractures of the alveolar process. They can be complete, partial and splintered. Often this phenomenon is associated with a fracture of the teeth. Symptoms of the disease are bleeding, swelling of the affected area, swelling of the cheek, unbearable pain.

Diseases
The alveolar process is exposed to various diseases, as a result of which its correction may be required. Consider diseases for which a doctor can prescribe implantation:
- Partial destruction of the process.
- Defects resulting from various injuries. In addition, they may be the result of the removal of the tumor, if the patient once had one.
How is the correction done?
Correction is carried out in the case when the alveolar process was deformed. It occurs in both the lower and upper jaw. They do it with the help of alveoplasty or other methods.
In some cases, the process is bumpy, narrow and uneven. In this case, the biomaterial used is placed simultaneously on the bone surface and above it. Due to this, the doctor can give the bones the desired shape. During the correction, it may also be necessary to dissect the periosteum and incise the mucous membrane of the process. After that, the doctor prepares the bone (gives it the desired shape), and then places the material used for implantation. The edges of the periosteum are sewn together to get a more regular shape. The entire procedure is performed under local anesthesia. In addition, the doctor can remove excess, strands, overhanging edges. Reconstruction will occur without complications if the patient adheres to all the recommendations of his doctor before and after the operation.

Methods of alveoloplasty
The human jaw is a part of the body that is quite difficult to operate on. Indeed, for a favorable result, it is necessary to expand the patient's mouth as much as possible, so some difficulties may arise in the process of work. Alveoloplasty occurs under the influence of anesthesia, since this process is quite painful. There are four ways to carry out the procedure:
- Performing correction inside the bone. However, the doctor cannot immediately proceed with the plastic surgery, since he must first perform a vertical osteotomy, as well as a transposition of the bone walls.
- Reconstruction by cutting the crest of the process.
- Also, plasty can occur on the surface of the bone clivus. It is done overlay.
- Osteotomy. It is performed by a surgeon by breakingwalls. The resulting space as a result of the operation is filled with a special biomaterial.

Thus, all four methods are implemented differently. However, their common goal is to increase bone tissue in the part of the jaw where surgical treatment will take place in the future.
What is augmentation and what is it for?
Augmentation is a way to build up the jaw bone. First of all, there is an increase in the height of the deformed lower part. This is due to bone blocks, as well as the implantation of artificial bone. This method is applicable in cases where the patient has lost teeth, resulting in bone resorption.
The process is carried out in several stages. First, the surgeon must provide access for the bony socket of the tooth that has been lost. It is filled with a special preparation of artificial bone. After that, the doctor sews up the wound. Bone tissue integration can take from one to several months. All this time, the patient must be under the strict supervision of a doctor. If there are any complications, another operation may be required. If the bone tissue has a height of less than 10 mm, then during implantation, the nerve, which is located in the lower socket, may atrophy slightly. To prevent this from happening, the doctor must perform a transposition.

What happens after the correction?
After the correction of the alveolar process has taken place, it is not recommended to overload the human jaw. throughout the first week aftersurgery, you need to go to your doctor, who will apply a periodontal bandage. After some time, a kappa is applied. Dental implantation can be carried out at least six months after plastic surgery.

Thus, the correction of the alveolar ridge is an inevitable procedure if there is a need for implantation of teeth. The process takes place quite quickly under local anesthesia. But in order to avoid complications, the patient must be under the supervision of a doctor for some time.