- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
In many diseases, when it is necessary to take a biochemical blood test, among the indicators you can see creatinine and urea. Their values for the most part show the state of the kidneys in the human body.
Both indicators are products of nitrogen metabolism. Based on the results of the tests, in conjunction with a survey, examination, and other methods of examination, the doctor draws conclusions about the functional state of the kidneys.
Definition
Urea is the end product of the breakdown of protein molecules. In the liver, proteins break down first into amino acids and then into smaller nitrogen compounds, which are toxic to the body. They must be taken out. For this, urea is formed by complex chemical reactions. It is removed from the body by filtering the blood in the tubules of the kidneys.

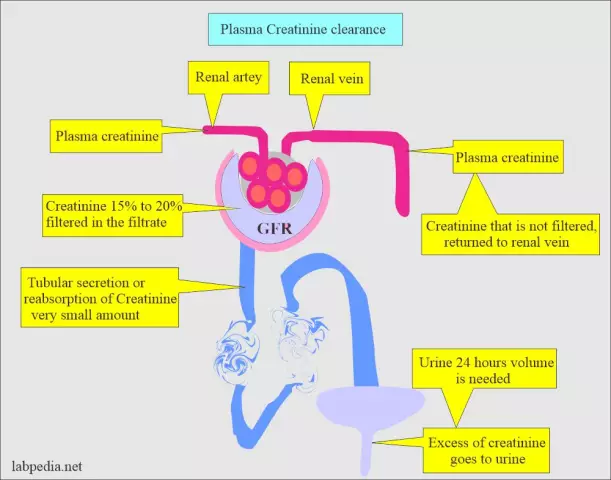
Creatinine is one of the end products of the breakdown of creatine. It is formed in the liver and enters the muscle and other tissues, directly participating in energy metabolism. This protein undergoes some transformation and transfersenergy inside the cell between its structures.
Creatinine is completely excreted by the kidneys and is not absorbed back into the blood. This property has found particular application in laboratory diagnostics.

Meaning
Creatinine and blood urea are the main indicators of kidney he alth. Since some of the pathological processes occurring in these organs disrupt the filtration process, doctors can most quickly suspect something is wrong with a simple analysis.
Examination to determine the concentration of these products of protein metabolism refers to screening, that is, mass. Upon medical examination or admission to a hospital, an analysis is assigned to everyone. This is necessary, first of all, for the early detection of kidney disease. In addition, with increased creatinine and urea, approaches to treatment will be slightly changed, drugs that have the least effect on the kidneys will be selected.

Norma
In each test form, so-called reference values are written opposite certain items. This is the range of normal values of this or that indicator.
Shifts in the concentration of substances depend on the ratio of the processes of their formation and excretion. From external causes, excessive meat consumption, increased physical activity can affect the result.
A blood test is taken from a vein in the morning on an empty stomach, after 8-14 hours of fasting. On the eve, it is better to avoid stressful situations and excessive physical exertion. The latter are allowed only with the permission of the doctor andif necessary, check the function during such loads. This is used mainly by professional athletes.

Norms of creatinine and urea in the blood can vary widely. For urea, the indicators are basically the same and equal to 2.5-8.3 mmol / l.
Creatinine has different norms in certain age categories. Newborns are characterized by values of 27-88 µmol / l, children under one year old - 18-35, children 1-12 years old - 27-62, adolescents - 44 - 88, adult men - 62-132, women - 44-97.
Decrease in performance
Decrease in serum creatinine and urea, as a rule, has no diagnostic value. This change in creatinine is not affected by extrarenal causes, unlike urea. Fasting, liver failure, a decrease in catabolism, that is, destruction, of proteins, as well as increased diuresis usually lead to its reduced indicators.
But more often you can see an increase in urea and creatinine in the analysis. The reason often lies in kidney disease. This will be written below.
Increase in blood creatinine
The concentration of a substance in the blood of he althy people is usually a constant value and rarely depends on extrarenal causes. Reducing its content is of no importance in clinical practice.

If an increase in the rate is detected, then first of all they think about kidney failure. This diagnosis is made when a level of 200-500 µmol / l is reached. However, an increase in creatinine and urea are among the later signs of the disease. Such values appear when about 50% of the kidney substance is affected.
Also, an increase in creatinine can be detected in diabetes mellitus, hyperthyroidism, intestinal obstruction, muscle atrophy, gigantism, acromegaly, extensive trauma and burns. Therefore, to make a correct diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct a full examination.
Changes in blood urea
Increasing the concentration of a substance is much more important. Among the reasons, 3 groups are distinguished:
- Adrenal are caused by increased formation of nitrogen metabolism products in the body. Such reasons include extremely high protein intake, severe dehydration caused by vomiting or diarrhea, severe inflammatory processes in the body, which are accompanied by increased protein breakdown.
- Renal. In this case, as a result of the pathological process that affected the organ, the kidney substance responsible for filtration dies. If this important function is impaired, then urea remains in the blood, and its level gradually rises. Diseases leading to such consequences include glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, nephrosclerosis, malignant arterial hypertension, amyloidosis, polycystic or tuberculosis of the kidney. In such cases, a donor kidney and an artificial kidney machine, or hemodialysis in another way, can help.
- Subrenal, that is, preventing outflow. If a hazardous substance does not find an exit through the urinary tract, then it is absorbed back intoblood, increasing the concentration there. This outcome is caused by blockage of the pelvis of the kidney and ureter or compression from the outside, for example, stones in the lumen, adenoma, prostate cancer.

Transcript of analyzes
Knowing the rate of urea and creatinine in the blood serum, with an increase in indicators, one can judge the degree of renal failure. It is worth considering in more detail the gradation of this state.
The criteria for RFI are:
- serum creatinine level 200-55 µmol/ml;
- increase in its level by 45 µmol/ml from the previous value below 170 µmol/ml;
- increase in the indicator by more than 2 times compared to the original.
Severe AKI is diagnosed when a creatinine concentration of more than 500 µmol/ml is detected. But in the practice of a doctor, there are results above 1000 µmol / ml.

If the analysis revealed an increase in urea more than 10 mmol / l, then this always indicates kidney damage, in this case they also put kidney failure, and an increase in creatinine and urea always go hand in hand. At the same time, the concentration of the latter in the range of 6.5 - 10.0 mmol / l can also indicate other diseases. This condition of patients in clinical practice is called uremia.
Where to go?
If the attending physician has prescribed a test for creatinine and blood urea, then the patient should go to him with the results. If there are minor changes, they will most likely offerretake the analysis, since errors in the calculations are not excluded.
If the concentration is repeatedly changed or greatly increased, the doctor will refer the patient to a nephrologist, a specialist in kidney disease. He will figure out the reasons for what is happening, conduct an additional examination and prescribe the necessary treatment, and give recommendations.