- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Syphilis is considered one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases. The infection is transmitted mainly during unprotected intercourse, although other ways of spread are also possible. Syphilis in women is accompanied by a very characteristic set of symptoms, the appearance of which should not be ignored.
Of course, many people are interested in more information about this disease. How can you get an infection? How long is the incubation period? What are the symptoms of syphilis in men and women? What methods of treatment does modern medicine offer? What are the consequences of the lack of therapy? The answers to these questions are important to many readers.
Description and features of the pathogen

To begin with, it is worth understanding the causes of the development of syphilis in women and men. The causative agent is a bacterium - pale treponema. The habitat of this microbe is the human or animal body.
This is a type of gram-negative spirochetes. The bacterium was discovered in1905 by German scientists F. Schaudin and E. Hoffmann. Its genome is represented by a double-stranded DNA molecule. The cell is surrounded by a structureless substance, which plays the role of a protective capsule. The bacterium is stained by the Romanovsky method in a pale, pinkish hue.
How is the infection transmitted?
Many people are interested in questions about how syphilis manifests itself in women and what complications it can lead to. But first, it's worth learning more about how the infection spreads. There are several ways of transmitting treponema:
- According to statistics, in more than 90% of cases, infection occurs during unprotected intercourse. Not only vaginal but also oral and anal contact are dangerous.
- A household transmission route is also possible, for example, by sharing cutlery, toothbrushes, lipstick and other items that may contain the saliva of an infected person.
- Of course, the infection is also transmitted through the blood, for example, during a transfusion or when sharing a syringe.
- Medical personnel are also at risk. A doctor can easily catch an infection through contact with patients (if masks, medical gloves were not used).
- Treponema also crosses the placenta. Pregnant women with syphilis can pass the infection to the developing fetus.
That is why it is so important to use the appropriate protective measures and not to miss scheduled examinations at the venereologist.
Incubation period
As already mentioned,pathogenic bacterium enters the body through lesions on the mucous membranes and skin. Immediately after entering the tissues, microorganisms begin to divide approximately every 30 hours.
Gradually the number of bacteria increases. A chancre is formed at the site of invasion - this is the first manifestation of syphilis in women (as well as men). Such a neoplasm, as a rule, appears a month after the invasion. On the other hand, in some patients the incubation period lasts 1-2 weeks, while in others it takes 6 months - a lot here depends on the state of the immune system.
Primary syphilis in women: features of the clinical picture
It is worth noting that this disease develops in three stages. Sexual syphilis in women is accompanied by the appearance of the so-called hard chancre. This is a solid subcutaneous formation of a rounded shape with clear, pronounced edges. A similar structure appears at the site of infection, for example, on the tissues of the genital organs, in the anus, less often on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity or fingers. Palpation of the neoplasm is not accompanied by pain. In most cases, only one chancre appears.

The second characteristic symptom is an increase in lymph nodes, which are located close to the site of infection. For example, if a chancre is formed in the tissues of the external genital organs, then the lymph nodes in the inguinal zone increase.
The appearance of uncharacteristic discharge with syphilis in women is also possible, but this is not the main symptom. Slime,released from the vagina becomes thicker. If the chancre is located on the cervix, then streaks of blood may appear. By the way, a change in the chemical composition of mucus affects the genitals. Syphilis in women is often accompanied by burning, itching, irritation of the skin and mucous membranes of the external structures of the reproductive system.
In addition, there are signs of general intoxication. Perhaps a slight, temporary increase in body temperature, dizziness, weakness, fatigue. However, the patient usually chalks these up to normal fatigue.
This is how the first signs of syphilis look in women. Unfortunately, the disease is not always accompanied by the appearance of a chancre. Moreover, if the neoplasm appeared on the inner surface of the vagina or cervix, the patient simply cannot detect it on her own. That is why the disease becomes either secondary or latent.
What does syphilis look like in women? Symptoms of the secondary stage

What do you need to remember? The first sign of syphilis in women is the appearance of a chancre. But about 1.5 - 2 months after its formation, other symptoms are observed. Bacteria spread throughout the body with the blood, provoking a response from the immune system.
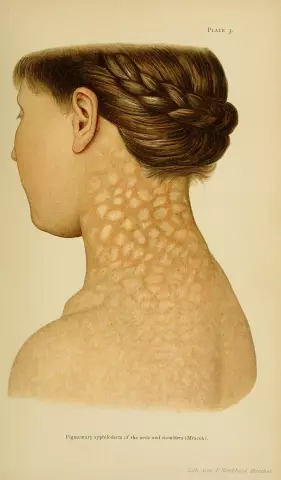
Isolation of specific antibodies and inflammatory mediators leads to the formation of a very characteristic rash. Reddish spots, nodules, papules, purulent sores are formed on the skin. Rashes have a reddish tint - they appear symmetrically throughout the body. This rash is not proneto peeling. Moreover, the elements do not merge with each other at the edges.
This phase is accompanied by fever, chills, body aches. Loss of hair, eyebrows, eyelashes, the formation of wide warts on the body are characteristic signs of syphilis in women at this stage.
In the future, the immune system still manages to suppress the activity of pathogenic bacteria - rashes and other disorders disappear on their own. However, treponema remains in the body. Any weakening of the immune system leads to a relapse - lymph nodes increase again, a rash appears on the skin, however, now it captures a large area.
This stage can last for several years. But, as a rule, in the second year, treponema is already accompanied by lesions of the nervous system, liver and heart. Perhaps inflammation of the walls of blood vessels that carry blood to the brain. Some patients develop meningitis. The infection affects various parts of the central nervous system, which leads to impaired memory, attention, and coordination of movements. Perhaps the emergence of psychotic disorders - such changes are irreversible.

Tertiary syphilis
The secondary stage ends with a latent period. This stage is accompanied by an almost complete absence of symptoms of syphilis in women. On the labia, mucous membranes, skin, there are no rashes, no irritation, or other signs that can alert the patient. This period of relative well-being lasts from 1 to 20 years, after which the disease enters the last stage.
Tertiary syphilis is extremelydangerous. Infection at this stage affects almost all organ systems. So-called gummas are formed on the tissues - purulent tumors that increase in size and open with the formation of scars. Often such formations appear on the skin of the face and neck. Often, gummas become infected with other bacteria and viruses, which leads to the formation of abscesses and even gangrene. Quite often, this stage of the disease ends with disability or death of the patient.
Nervous system damage due to infection
As already mentioned, the infection leads to serious, irreversible changes in brain tissues:
- Infection sometimes leads to the destruction of the walls of blood vessels that feed the structures of the central nervous system. Such a process affects the mental, emotional state of the patient - there are sleep disturbances, changes in personality and behavioral patterns, headaches. Sometimes there are convulsions. The lack of treatment in this case is fraught with a stroke.
- Purulent gummas often form in brain tissues. Their presence leads to increased intracranial pressure and occlusion of nerve tissues.
- Tertiary syphilis is often accompanied by inflammation of the meninges.
- Diseases sometimes affect the spinal cord - dorsal tabes develop. The patient loses the ability to move, and his ability to navigate in space is impaired.
- There is a possibility of optic nerve atrophy.
- Many patients with tertiary syphilis suffer from progressive paralysis.
Atypical chancre
Not in all cases the clinical picture is accompanied by the symptoms described above. Chancres that appear early in development may be atypical:
- Indurative edema most often occurs in the area of the external labia and clitoris in patients. The color of the skin changes, it becomes red or bluish.
- Chancre panaritium is a problem that doctors and staff who care for patients often face. In this case, the infection enters the body through the integument on the hands. The skin on the thumb, index and middle fingers swells and begins to lag behind the deeper tissues, forming extensive bleeding areas (in appearance they resemble second-degree burns). This condition is accompanied by severe pain and is often complicated by a secondary infection. Often, damage to the skin of the palm is supplemented by the formation of a chancre in the tissues of the genital organs.
- Chancre-amygdalitis is manifested by an inflammatory process localized in one tonsil. This structure is rapidly growing in size. Patients complain of severe pain while talking, eating, drinking.
Infection during pregnancy
Pregnant women with syphilis should be treated appropriately. The presence of infection in the mother's body significantly increases the risk of preterm birth. In addition, the infection crosses the placenta, infecting the fetus. Treponema activity can lead to various abnormalities in the development of the child, and also increases the likelihood of stillbirth.
How dangerous is congenital syphilis?

As already mentioned, if a pregnant woman is infected with a pathogenic bacterium, then the infection can spread to the fetus. Congenital forms of this disease are extremely dangerous. In children, against the background of an illness, severe complications often develop:
- Infection sometimes leads to the development of parenchymal keratitis. This condition is accompanied by inflammation and redness of the epithelial tissues of the eyeball and internal organs. If we are talking about damage to the eyes, then it is possible to reduce visual acuity, the appearance of a walleye.
- Treponema penetrates the fetal nervous system and actively destroys neurons. This can lead to pathological changes in the auditory nerve and congenital deafness.
- There is a possibility of abnormal tooth development. If the tissues are not laid correctly, the teeth may have an irregular shape (there is a rounded notch on the cutting edge of the tooth). Sometimes the teeth are not completely covered with enamel, which leads to their rapid destruction.
- The child may not have any structural anomalies. However, the baby is likely to have a weak immune system.
If a woman becomes infected after childbirth, then breastfeeding is not recommended, as treponema is excreted from the body along with milk. That is why it is necessary to check for the presence of sexually transmitted diseases even at the stage of pregnancy planning.
Diagnostic measures

The appearance of the first symptoms of syphilis in a woman,described above - this is a serious reason to see a doctor. Diagnostics includes several basic procedures:
- Gynecological examination is mandatory. As already mentioned, syphilis in women is accompanied by the appearance of a chancre, mainly on the tissues of the external genitalia, vagina or cervix. In place of the chancre, a very characteristic scar or atrophied area often remains. It is this sign that the doctor can detect.
- A general inspection is also being carried out. The patient's skin is checked for the presence of a characteristic rash. In addition, you need to examine the lymph nodes.
- Cerebrospinal fluid is taken for laboratory analysis, as well as samples obtained during a puncture of the lymph nodes. Informative is PCR diagnostics, as well as ELISA, RIF and the Wasserman reaction.
- Of course, in the future, additional examinations are carried out, the purpose of which is to determine the presence of complications. Patients are sent for electrocardiography, pelvic and abdominal ultrasound, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging.
General scheme of therapy

The appearance of symptoms of syphilis in women is associated with penetration into the body and activation of treponema. That is why antibiotic therapy is carried out in the first place:
- In most cases, patients are prescribed antibiotics from the penicillin group. If a woman has hypersensitivity to penicillin, then it can be replaced with a remedy from a number of tetracyclines or cephalosporins. For secondary and tertiary syphilisuse preparations containing bismuth and iodine (for example, "Biyoquinol"), as well as arsenic ("Novarsenol"). It is necessary to maintain a certain level of antibiotics in the blood for at least 7-10 days.
- The intake of immunomodulators is also mandatory. It is very important to activate the immune system - this will speed up the recovery process, help the body fight the infection on its own. Such drugs as T-Activin and Timalin are considered effective.
- Doctors recommend that patients take pro- and prebiotics, in particular Linex, Hilak, Lacidophila. Such drugs help to restore the natural microflora of the body and create conditions for the active reproduction of beneficial bacteria. Such treatment is necessary to prevent dysbacteriosis, which is often associated with taking antibiotics.
- It will also be useful to take drugs that contain vitamins and minerals. It helps to restore the normal functioning of the body, as well as strengthen the immune system.
- If we are talking about the secondary and tertiary stages of syphilis in women, then symptomatic therapy is also carried out. For example, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, special ointments that help cope with skin rashes, nootropics that improve blood circulation in the brain and activate the central nervous system are used.
Prognosis for female patients
You already know why and how syphilis occurs in women. If we are talking about the primary and secondary stages of the disease, then drug therapy has the desired effect. Already laterdays after the start of treatment, the woman ceases to be contagious.
But tertiary syphilis is accompanied by severe systemic lesions. Of course, antibiotic therapy allows you to get rid of the infection, but it is not always possible to completely restore the functioning of the body. For example, brain damage due to syphilis is irreversible. According to statistics, in 25% of cases the tertiary form of the disease ends in death.
Prevention measures
Unfortunately, there are no specific preventive measures. Patients are only advised to avoid exposure to risk factors. For example, it is worth giving up promiscuity. It is important to use a condom (this also applies to oral and anal acts).
Physicians and medical staff should be aware of masks, protective gloves, proper sterilization of instruments and other precautions.
If, for one reason or another, you still have to contact a person whose body is affected by treponema, then it is important to provide him with an individual set of dishes, towels, and refuse kisses and other contacts (until the course of therapy is completed).