- Author Curtis Blomfield [email protected].
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
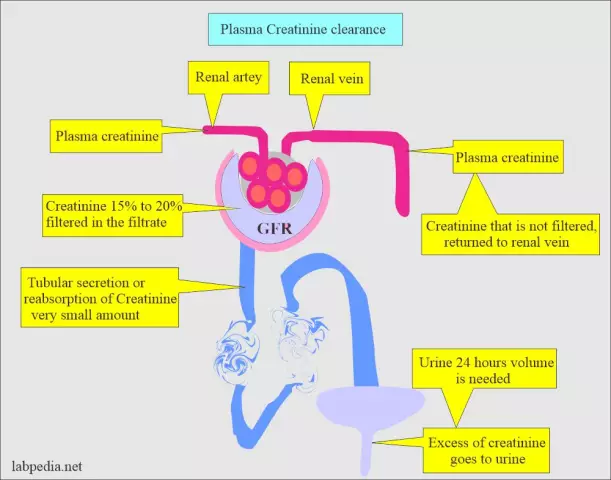
Creatinine is the end product of the creatine-phosphate reaction, formed as a result of the breakdown of protein molecules and amino acids. It belongs to the so-called "non-threshold" substances that are filtered by the renal glomeruli (glomeruli) and are not reabsorbed or secreted in the tubules. An increase in blood creatinine is of great diagnostic value for nephrological ailments, pathologies of the muscular system, and suspected dehydration.
Indications for testing
Creatinine is produced by non-enzymatic dehydration and dephosphorylation of creatine phosphate. From muscle tissue, the metabolite enters the bloodstream and is almost completely excreted from the body through the kidneys. An increase in the level of creatinine indicates a dysfunction of one or another internal organ.

Biochemical analysis is the most accessible and informative method of blood testing. It is indispensable for patients with obvious signs of hypercreatininemia, urolithiasisdiseases, with damage to skeletal muscles, as well as potential kidney donors. In order for the data on the concentration of creatinine not to be distorted, it is necessary to exclude physical loads 48 hours before going to the laboratory. On the eve of blood sampling, give up alcohol and caffeinated drinks, do not lean on protein foods. It is optimal to take the test in the morning on an empty stomach.
Norm and pathology
Reference values of creatinine in the blood depend on the age, gender, physique and culinary preferences of the person. The concentration of a substance is determined by the individual muscle volume, so its level in the blood of men is usually higher than that of women. He althy kidneys excrete up to 2 g of creatinine per day, thereby preventing intoxication of the body.

The limits of the norm in different laboratories may differ slightly from the indicated average values. Creatinine is not the most sensitive bioindicator of kidney, liver, or musculoskeletal disease. To detect hypercreatininemia at an early stage, it is recommended to donate blood twice a year.
Etiological factors
The physiological causes of elevated blood creatinine include hormonal failure during pregnancy, lactation, intense physical activity, prolonged malnutrition, or an exclusively protein diet. In some cases, the level of the metabolite increases not due to an excess of its production, but due to a decrease in plasma volume due to dehydration or blood loss. Please note that if you donate blood for biochemistry in the secondnoon, the result will be higher than the morning.
Hypercreatininemia is often associated with the following ailments and conditions:
- Renal failure.
- Toxic, inflammatory or cirrhotic lesions of the liver.
- Diabetic Nephropathy.
- Hyperadrenal function.
- Traumatic injury to muscle tissue, bones.
- Extensive skin burns.
- Acromegaly or gigantism.
Radiation sickness or autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, myasthenia gravis, lupus erythematosus accelerate the breakdown of proteins. Drugs that have a nephrotoxic effect, as well as protein-containing supplements, increase blood creatinine. In order to correctly evaluate the results of a biochemical analysis, the doctor needs to know all the circumstances and features of the patient's lifestyle.

Due to the high reserve capacity of the renal circulation and insufficient sensitivity of the metabolite, an additional blood test for urea is taken. The nitrogenous compound, along with creatinine, illustrates the productivity of renal function. An increase in urea in the blood is said when its level goes beyond the maximum permissible range (8.3 mmol / l).
Clinical picture
Creatinine is a slightly toxic substance, but the body reacts to a significant deviation from the norm with headache, nausea, an unusual taste in the mouth and other signs of intoxication. Suspicion of hypercreatininemia falls if the patient complains of edema, shortness of breath,muscle weakness, decrease or increase in the volume of daily urine. There are drops in blood pressure, pulling pain in the lumbar region, in severe cases, convulsions may occur.
Medicated approach
Having determined the nature of the disease and the cause of increased creatinine in the blood, the appropriate treatment is selected. So, if the patient suffers from diabetic nephropathy, hypoglycemic drugs are prescribed. Basic therapy for autoimmune diseases includes corticosteroids and immunosuppressants. Kidney failure is treated with loop diuretics, which speed up the excretion of urine from the body.

Oral intake of the following medications and dietary supplements reduces blood metabolite levels:
- Ketosteril. The composition of the drug includes ketone analogues of amino acids, which affect the glomerular filtration rate and reduce the synthesis of nitrogenous compounds.
- Chitosan. A powerful sorbent fights not only with extra pounds, increased creatinine, urea in the blood, but also prevents the development of gout and osteoporosis. Chitosan has an analgesic effect, regulates the pH balance in the body.
- Supplements with thioctic acid. Used as an anti-toxic and anti-inflammatory agent. Thioctic acid or vitamin N is involved in energy metabolism, reduces insulin resistance, and promotes weight loss.
NSAIDs, ACE inhibitors, tetracycline antibiotics, barbiturates and Cyclosporine can aggravate the coursehypercreatininemia. Be sure to check with your doctor before taking any of these medicines.
Physiotherapeutic procedures can significantly reduce the patient's recovery time. The impact of low-intensity laser radiation on the lumbar region improves the excretory function of the kidneys and microcirculation of muscle tissue, stimulates peripheral lymph flow. With increased creatinine in the blood, in addition to the main therapy, it will not hurt to take a course of professional massage.
Critical indicators
End-stage chronic renal failure, generalized myositis, leptospirosis or other severe infectious diseases lead to severe hypercreatininemia (exceeding the norm by 100 or more mmol / l). High levels of the metabolite are characteristic of a violation of the secretory-excretory function of the kidneys, muscle polytrauma.

If conservative treatment has not brought proper results, they turn to extracorporeal detoxification methods, in particular, hemodialysis. The latter is an extra-renal blood purification apparatus called "artificial kidney". Extracorporeal hemocorrection is carried out in a hospital, the procedure lasts from 3 to 4 hours. The method allows you to quickly bring a person out of a critical state.
Diet
Without vitamins, micro and macro elements, the coordinated work of the muscular, nervous, urinary and other organ systems is not possible. Include complex carbohydrates, unsaturated fatty acids, sufficientthe amount of fiber. Pay due attention to the drinking regimen: 1.5-2 liters of non-carbonated water per day maintains the natural water-s alt balance in the body.

For hypercreatininemia, enrich your diet:
- Fresh fruits and vegetables.
- Nuts, legumes.
- Fermented milk products.
- Dietary chicken or rabbit meat.
- Vegetable and olive oil.
When it comes to a low-protein diet with elevated blood creatinine, it means limiting protein intake, not eliminating it from the diet. Proteins supply the body with energy, are involved in muscle contraction, the formation of hormones, enzymes and antibodies. Thus, high levels of creatinine in blood plasma can be safely associated with debilitating methods of losing weight.
Give up fried and spicy foods, fresh yeast pastries, pure milk, smoked meats, convenience foods and fast food, do not abuse black tea, coffee and strong liquor. Replenish the need for sweets with freshly squeezed juices, honey. Opt for steamed, baked fruits and vegetables.
Recipes of traditional medicine
Means based on diuretic herbs and dietary foods have successfully passed the test of time. They are affordable, easy to use, rarely provoke the development of allergic reactions. To normalize the level of creatinine, liquid dosage forms are usually used: extracts, infusions, decoctions, etc.

Several effective ways to combat hypercreatininemia:
- Diuretic teas. Plants are brewed separately or mixed in equal proportions; you can purchase a ready-made "kidney" collection at a pharmacy. Nettle leaves go well with calendula flowers and knotweed, chamomile with mint, dill seeds. The treatment regimen for elevated creatinine in the blood is selected by the doctor on an individual basis.
- Rice breakfast. In the evening, pour rice with cool water, in the morning put the swollen cereal on low heat and boil a little. Do not s alt the porridge and do not season with butter. Rice cleansing of the body from creatinine and other products of nitrogen metabolism is designed for 14 days.
- Decoction of wild rose. According to the content of vitamin C, the fruits of the shrub "overtook" even lemon and black currant berries. The healing drink has a diuretic and anti-inflammatory effect, cleanses the blood vessels of cholesterol. To prepare a decoction, pour 2 tbsp. l., previously dried and crushed fruits with boiling water (400 ml). Bring the liquid to a boil, after 10 minutes remove from the stove and strain through a 2-3-layer gauze or strainer. Patients with elevated blood creatinine are recommended to drink a decoction three times a day, 0.25 cups before meals.
Preventive measures
Keep a variety of daily diet, keep the optimal mode of sleep and wakefulness. At night, the conversion of creatine to creatinine slows down, metabolic processes enter the active stage only after breakfast. In pursuit of a toned, embossed bodyathletes often use synthetic protein (protein). Most dietary supplements for gaining muscle mass retain fluid in the body, therefore, increase creatinine and urea in the blood. Control blood pressure indicators, because in hypertension, the synthesis of the metabolite is steadily increasing. Power and traumatic sports are strictly prohibited, loads should not exceed the actual capabilities of the body.
Summarize
At the heart of human life are complex biochemical reactions, the totality of which determines our individuality and level of physical he alth. A slight increase in blood creatinine in adults and children is not a cause for concern, but the need to retake the test. Modern medicine has enough knowledge to prevent the accumulation of the metabolite in the blood plasma and activate its utilization from the body. Take care!