- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Eggs are one of the strongest allergens and often cause a specific reaction not only in adults, but also in young children.
Signs of allergy usually appear within minutes (sometimes hours) after eating eggs or foods containing them (including egg powder). Symptoms of intolerance can range from mild to severe: skin rash, hives, nasal congestion, vomiting, or other indigestion. Rarely, eggs cause anaphylaxis, a life-threatening reaction.

Egg allergy often begins in infancy, during the introduction of new complementary foods. Most children outgrow it by adolescence.
Symptoms
The reaction of the body depends entirely on its individual characteristics and manifests itself shortly after eating the allergen. Considering what an egg allergy implies, the symptoms are as follows:
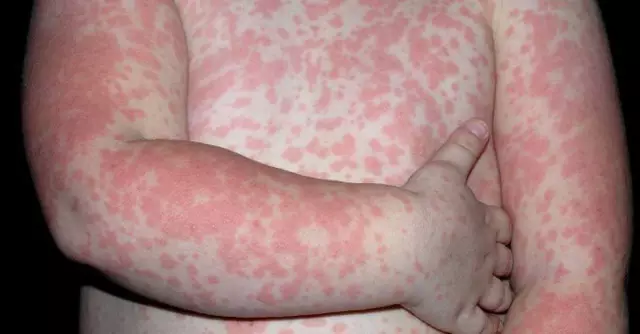
- Skin inflammation, or hives, is the most common allergic reaction.
- Nasal congestion, runny nose and sneezing(allergic rhinitis).
- Signs of indigestion: colic, nausea, vomiting.
- Signs and symptoms of asthma: coughing, sneezing, chest tightness or shortness of breath.
Anaphylaxis
A severe egg allergy in adults or children can lead to anaphylaxis, a potentially fatal condition that requires immediate epinephrine (adrenaline) administration and emergency care. Signs and symptoms of anaphylaxis include the following conditions:
- Narrowing of the airways, including swelling or feeling of a lump in the throat along with shortness of breath.
- Colic and chest pain.
- Increased heart rate.
- A state of shock with a sharp drop in blood pressure, manifested as a deterioration in well-being, dizziness or loss of consciousness.
It is advisable to discuss any reaction (even if it seems minor) with your doctor if you or your child has an egg allergy. The severity of symptoms can vary from time to time, so even with a small initial reaction, more severe symptoms can be expected later.

If the doctor thinks your child may have a severe reaction, they will prescribe an immediate epinephrine shot for anaphylaxis. Such injections are made using a syringe pen, which provides emergency administration of the drug.
When to see a doctor?
Make an appointment with an allergist if you or your child has symptomsfood allergies immediately after eating eggs or products containing eggs. If possible, it is better to see a doctor right during an atypical reaction to a product - this way a specialist will make a diagnosis faster and more accurately.
If there are signs of anaphylaxis, you should immediately call an ambulance and use a single dose of epinephrine in a special syringe if an egg allergy is diagnosed and the drug is officially prescribed by a doctor.
Reasons
Intolerance to certain foods is not quite an adequate response of the immune system to a new food. In this case, the immune system mistakenly perceives some proteins contained in eggs as harmful substances. When you or your child come into contact with these proteins, immune system cells (antibodies) recognize the perceived danger and signal the body to release histamine and other chemicals into the bloodstream that cause signs and symptoms of allergies.

Proteins, which are potential allergens, are found in both protein and yolk, but the most common individual intolerance to egg white. Egg allergy (photo of which is presented in many medical reference books) can also occur in a breastfed infant if his mother eats yolks and proteins.
Risk factors
The following circumstances increase the risk of developing egg intolerance:
- Atopic dermatitis. Children with similar skin rashes are more likely to be allergic to chickeneggs than their he althy-skinned peers.
- Family history. You are at risk if one or both of your parents has been diagnosed with asthma, a food allergy, or an individual intolerance that manifests as allergic rhinitis, hives, or eczema.
- Age. Egg allergy is most common in children. With age, the digestive system finally matures, and cases of food allergies are recorded less and less.
Treatment
The only way to prevent an abnormal reaction is to stop eating eggs and their derivatives. However, some people with this type of allergy react normally to foods containing processed eggs, such as baked goods.
Drugs - antihistamines - reduce the intensity of symptoms of mild food allergies. These drugs can be drunk after exposure to the allergen on the body. However, it should be remembered that they are not able to completely prevent an abnormal reaction and are ineffective in the treatment of severe conditions.
You may need to carry an epinephrine pen with you at all times. An injection will be required for anaphylaxis.

Egg allergy in a child is rarely serious, as most children gradually outgrow this ailment. Discuss with your doctor the possibility of monitoring whether signs of individual intolerance to egg proteins persist over time. You should not give your child eggs as an experiment, as it is impossiblepredict how a child's body will react to repeated eating of a potentially harmful food.
Prevention
You can take steps to prevent an allergic reaction or make it worse. For example:
- Carefully read the food information on the package. Some people cannot tolerate even trace amounts of eggs (as indicated by the label on product packaging: "May contain traces of eggs").
- Be careful in catering establishments. Not only waiters - sometimes even chefs are not entirely sure about the presence or absence of egg proteins in a particular dish.
- Tell any adults you leave your child with that they have an intolerance. Babysitters, teachers, relatives should remember that the child is allergic to eggs (show them a photo of what can happen if he eats an egg), and not give him potentially dangerous foods. Make sure adults know how to handle an emergency.
- If you are breastfeeding, avoid eating eggs. Egg proteins pass into breast milk and may cause food allergy symptoms in an infant.
Products with hidden egg content
Unfortunately, even if a product does not list eggs or egg derivatives, it may still contain some egg proteins. Only the manufacturer can dispel all doubts in this case.

For convenience, you canuse the list of hidden egg foods below, but be aware that it is far from complete:
- marshmallow and marshmallow;
- mayonnaise;
- meringue;
- baked goods;
- breadcrumbs;
- marzipan;
- icing;
- processed meat, meatloaf and meatballs;
- puddings and custard;
- salad dressings;
- pasta;
- foam on gourmet coffees with alcohol added;
- drying.
If egg proteins were used in the production of certain food products, the following substances can be found in the composition:
- albumin;
- globulin;
- lecithin;
- livetin;
- lysozyme;
- vitellin;
- names beginning with "ova" or "ovo", such as ovalbumin (egg albumin) or ovoglobulin.

An allergy to eggs can also occur when treating home-cooked meals in someone else's house, where small amounts of eggs may be found in food due to the peculiarities of preparing a set menu. If you cannot completely avoid allergies, you should prepare as much as possible for possible symptoms.