- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
When a woman is expecting a baby, she has to take multiple tests and undergo scheduled examinations. Each expectant mother may be given different recommendations. The screening test is the same for everyone. It is about him that will be discussed in this article.

Screening study
This analysis is assigned to all expectant mothers, regardless of age and social status. Screening examination is carried out three times during the entire pregnancy. At the same time, it is necessary to observe certain deadlines for taking tests.
Medicine knows screening research methods, which are divided into two types. The first of these is a blood test from a vein. It determines the possibility of various pathologies in the fetus. The second analysis is an ultrasound screening study. The evaluation should take into account the results of both methods.

What diseases does the analysis reveal?
Pregnancy screening is not an accurate waydiagnosis. This analysis can only reveal the predisposition and establish the percentage of risk. To obtain a more detailed result, it is necessary to conduct a screening study of the fetus. It is prescribed only when the risks of a possible pathology are very high. So, this analysis can reveal the possibility of the following diseases:
- Down and Edwards syndromes.
- Cornelia and Patau Syndrome.
- Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome.
- Possible defects or abnormal development of the neural tube.

When is the test scheduled?
As already mentioned, the screening test is carried out three times during pregnancy. In this case, a blood test is done only twice. There are certain deadlines in which it is necessary to undergo an examination.
First trimester screening is scheduled from the eleventh to the fourteenth week of fetal development. The second examination must be completed between the twentieth and twenty-second weeks. The third screening ultrasound should be performed between the thirty-second and thirty-fourth weeks of pregnancy.
Any deviation from the established deadlines may give a false result. That is why it is better not to shift the dates of the tests yourself, but to trust the doctor in carrying out the calculations.
First examination
The most exciting moment for the expectant mother is precisely the first protocol of screening ultrasound and receiving the result of a blood test. It should be noted that prior to this, it is not normalan additional ultrasound. This means that a woman will see her baby on the screen for the first time.

Blood test
As already noted, the period of the first examination can be carried out from 11 to 14 weeks of pregnancy, but it is preferable to conduct this analysis from 12 to 13. First, the woman will have to donate blood. The analysis is carried out strictly on an empty stomach. The material is taken from a vein. Previously, the expectant mother fills out a questionnaire, where she indicates her age, the characteristics of the course of pregnancy and previous births (if any).
Next, the laboratory assistant examines the material obtained and notes possible malformations of the fetus. After that, the computer processes all the received data and produces the final result. It is worth noting that risks can vary greatly for different ages.

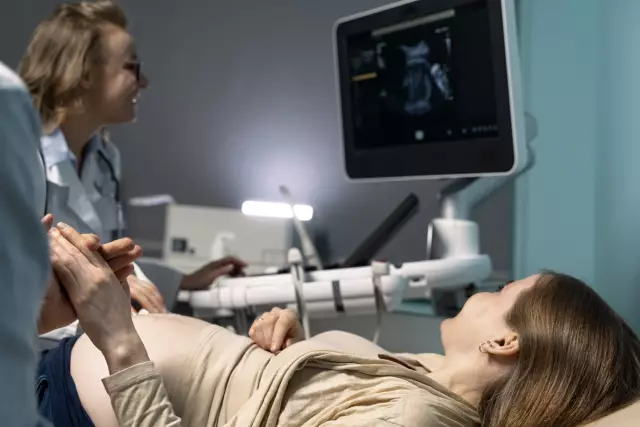
Ultrasound diagnostics
After donating blood, a woman needs to undergo an ultrasound. The procedure can be carried out in two ways: with a vaginal probe or through the abdominal wall. It all depends on the ultrasound machine, the qualifications of the doctor and the gestational age.
During the examination, the doctor measures the growth of the fetus, notes the location of the placenta. Also, the doctor must make sure that the child has all the limbs. One of the important points is the presence of the nasal bone and the thickness of the collar space. It is on these points that the doctor will subsequently rely when deciphering the result.
Secondsurvey
Screening during pregnancy in this case is also carried out in two ways. First, a woman needs to take a blood test from a vein and only after that undergo an ultrasound scan. It is worth noting that the deadlines for this diagnosis are somewhat different.

Blood test for second screening
In some regions of the country, this study is not carried out at all. The only exceptions are those women whose first analysis gave disappointing results. In this case, the most favorable time for blood donation is in the range of 16 to 18 weeks of fetal development.
The test is carried out in the same way as in the first case. The computer processes the data and produces the result.

Ultrasound examination
This checkup is recommended between 20 and 22 weeks. It is worth noting that, unlike a blood test, this study is carried out in all medical institutions in the country. At this stage, the height and weight of the fetus are measured. The doctor also examines the organs: the heart, brain, stomach of the unborn baby. The specialist counts the fingers and toes of the crumbs. It is also very important to note the condition of the placenta and cervix. In addition, dopplerography can be performed. During this examination, the doctor monitors the blood flow and notes possible defects.
During the second ultrasound screening, it is necessary to inspect the water. They should be normal for a given period of time. Inside the fetalshells should be free of suspensions and impurities.

Third examination
This type of diagnosis is carried out after 30 weeks of pregnancy. The most suitable period is 32-34 weeks. It is worth noting that at this stage, blood is no longer examined for defects, but only ultrasound diagnostics are carried out.
During the manipulation, the doctor carefully examines the organs of the future baby and notes their features. The height and weight of the baby is also measured. An important point is the normal physical activity during the study. The specialist notes the amount of amniotic fluid and its purity. Be sure to indicate the condition, location and maturity of the placenta in the protocol.
This ultrasound is the last one in most cases. Only in some cases, re-diagnosis is prescribed before childbirth. That is why it is so important to note the position of the fetus (head or pelvic) and the absence of cord entanglement.

Deviations from the norm
If during the examination various deviations and errors were revealed, the doctor recommends seeing a geneticist. At the appointment, the specialist must take into account all the data (ultrasound, blood and pregnancy features) when making a specific diagnosis.
In most cases, the possible risks are not a guarantee that the child will be born sick. Often such studies are erroneous, but despite this, doctors may recommend additional studies.
Morea detailed analysis is a screening study of the microflora of the amniotic fluid or blood from the umbilical cord. It should be noted that this analysis entails negative consequences. Quite often, after such a study, there is a threat of termination of pregnancy. Each woman has the right to refuse such a diagnosis, but in this case, the entire responsibility falls on her shoulders. When bad results are confirmed, doctors suggest abortion and give the woman time to make a decision.
Conclusion
Pregnancy screening is a very important test. However, we must not forget that it is not always accurate.
After birth, the baby will undergo neonatal screening, which will absolutely accurately show the presence or absence of any disease.