- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-06-01 06:18.
Cross-allergy is a variation, or rather, a property of ordinary allergies. As you know, many stimuli have their counterparts. For example, if one allergen causes any negative reactions in a person, then it is likely that his existing counterpart or even a group consisting of them will also provoke them.

The essence of the relationship
Cross-allergy occurs due to the similarity of the structure of allergens in a set of amino acids. To understand how such a deviation manifests itself in real life, consider an example.
A person is allergic to dust. But one day he observes similar negative reactions in himself after eating shrimp. Thus, he has a cross-food allergy similar to that caused by ordinary house dust. So why is this phenomenon possible? The fact is that the body of this person simply mixed up dust cells and shrimp because of their incredible similarity. The complexity of these situations lies in the fact that it is not always possiblefind out what is the allergen-double of the pathogen you already know. However, the most common such relationships have already been calculated. Thanks to them, a special table of cross-allergy was compiled. Let's look at some of its parts in more detail.
Pollen allergy
As a rule, such a cross-allergy makes itself felt in the spring-summer season, when there is an active flowering of various plants and herbs. So, consider the allergen counterparts of ordinary pollen.

- Cross allergy to birch (leaves, buds) and alder pollen, hazel, apple and alder cones.
- Pollen intolerance of all grasses and food grains (oats, barley, wheat, etc.).
- Cross allergy to wormwood, sunflower, dahlias, chamomile, dandelions, calendula, elecampane, string, coltsfoot.
Food Allergy - Food Twins of Pollen
Cross-allergy to birch and other plants can occasionally occur if a person develops adverse reactions after exposure to common pollen. But this deviation extends not only to grasses and trees. After all, often such a person is allergic to fungal spores, as well as some types of food products. The biggest mistake patients make is that very often, due to their ignorance, they do not connect these seemingly distant allergens.
- Birch, hazel and alder pollen allergy crosses over with hazelnut allergy,apricots, almonds, cherries, peaches, potatoes, kiwi fruit and celery.
- Mugwort Pollen - Potatoes, red peppers, celery, chamomile, fennel, dill, cumin, coriander, and all beverages containing this plant (vermouths and balsams).
- Sunflower pollen - halva, sunflower oil, mustard and mayonnaise.
- Agbrosia pollen - banana, melon.
- Grass pollen - tomatoes, peanuts and melon.
- Fragrant herbs - celery, various spices.
- Latex - potato, banana, papaya, pineapple, avocado, chestnut, tomato, fig, spinach.
- Meadow weed pollen - flower honey.

Food allergens and their counterparts
What types of allergies do you know? Food, vegetable, medicinal, etc. But such a division is only conditional. After all, a person often has only one of the above deviations, and the rest are all types of cross-reactions.
Thus, if a patient is allergic to any food product, then often he cannot consume those ingredients that contain even a small proportion of similar irritants.
- If a person is allergic to cow's milk, then, most likely, he will also have the same negative reactions as a result of the consumption of products containing its proteins, as well as goat's milk, beef, veal and meat products from them, enzyme preparations made on the basis of the pancreas of cattle, as well as after contact withcow hair.
- Kefir or kefir yeast - yeast dough, mold fungi, penicillin antibiotics, mold cheeses, kvass and ordinary mushrooms.
- Sea and river fish - seafood (shrimps, crabs, mussels, caviar, lobsters, lobsters, etc.), as well as fish food.
- Chicken eggs - duck meat, chicken broth and chicken meat, quail eggs, sauces, creams, mayonnaise, pillow feathers, etc.
- Carrots - vitamin A, celery, parsley and beta-carotene.
- Strawberries - cranberries, raspberries, currants and blackberries.
- Apples - pear, peach, quince and plum.
- Potatoes - tomatoes, eggplant, green and red peppers, tobacco and paprika.
- Nuts - rice flour, kiwi, sesame, mango, poppy, buckwheat and oatmeal.
- Peanuts - soybeans, green peas, bananas, tomatoes, stone berries and fruits.
- Bananas - melon, wheat gluten, latex, kiwi and avocado.
- Tangerines - grapefruit, orange and lemon.
- Red beets - white beets, sugar and spinach.
- Beans - mango, peanuts, beans, soybeans, lentils and peas.
- Plum - apples, almonds, nectarines, apricots, cherries, cherries, prunes, peaches, etc.
- Kiwi - nuts, bananas, avocados, sesame, flour (buckwheat, rice, oatmeal), cereals, etc.

Drug allergy
If a patient is allergic to any drug, then, most likely, he will experience negative effects after using other medicines, which also contain the already knownirritant.

It should be especially noted that drug allergies are the most common of all. And they attribute this to the fact that the production of medicines very often uses synthetic components that are not perceived by the human body.
- The drug "Penicillin" - all its derivatives.
- Levomycetin medication - all its derivatives, including Synthomycin, as well as their antiseptic solutions.
- Sulfanilamides (for example, the drug "Biseptol") - drugs "Novocain", "Anestezin", "Trimekain", "Dikain", etc.
- The drug "Streptomycin" - all its derivatives and aminoglycosides.
- The drug "Tetracycline" - means "Metacycline", "Rondomycin", "Morphocycline", "Olemorphocycline", "Glycocycline", etc.
Cross allergy symptoms
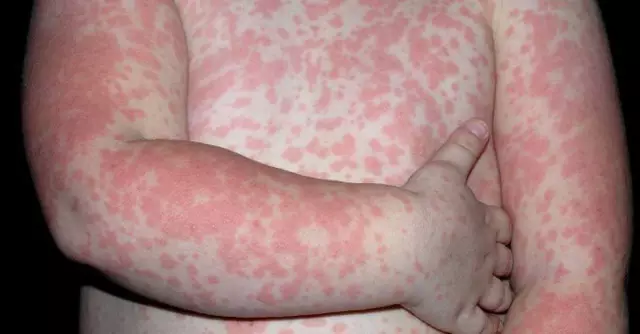
As a rule, cross-allergy in adults and children does not go unnoticed. Its manifestations are very similar to those of a common allergy. Such symptoms include rhinitis, lacrimation, itching and burning on the skin, swelling of mucous membranes, bronchial asthma, urticaria, dermatitis, etc.
Diagnosis
Cross-allergy can be diagnosed using molecular testing. So, using special equipment, doctors detect a person's reaction not to any product or plant, but to a specific protein that is part of them. In this way, the existing twins are determined.
How to treat cross allergies?
Cross Therapyallergies are practically no different from conventional treatment. The only difference between them is that before starting all the necessary measures, the main allergen, which gives impetus to all the others, should be identified.

During the treatment of this type of disease, antihistamine drugs are the main ones. The following medicines are among those that give the best effect: Claritin, Zertek, Cetrin, Erius, etc. The main advantage of these drugs is that they never have a negative effect on the central nervous system, and also practically have no side effects. Although in some cases, the patient may experience drowsiness, dry mouth, constipation, urinary retention, etc.
As practice shows, it takes about one week to eliminate the manifested allergic reactions. In more complex cases, doctors recommend taking these drugs for several months.
Cross Allergy Prevention
What preventive measures to take to prevent the occurrence of cross-allergy depends only on the primary pathogen. For example, if a person has regular allergic reactions to pollen, then when various plants and herbs are flowering, it is recommended to avoid the places where they grow.
It should also be noted that wearing gauze bandages and sunglasses will protect the mucous membranes of a person from possible irritation. In addition, wet cleaning around the house and careful personal hygiene will help reduceminimize the number of likely exposures to allergens.
The use of antihistamines is also a reliable way to prevent allergies, including crossover.
If a patient has a food allergy, then his usual menu should be well thought out. Thus, a person should eliminate all likely irritant foods from their diet.

Among other things, in order to avoid manifestations of allergic reactions, the patient is recommended to purchase only those cosmetics that are marked "hypoallergenic" on their packages.