- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
If we turn to WHO statistics, we can see that among all kidney diseases, pyelonephritis occupies a dominant position. Almost every second person is diagnosed with latent chronic pyelonephritis. The direct danger of this disease is that it can lead to kidney failure. The latter significantly reduces the quality of life and sometimes leads to death.
In the article we will present the main classification of pyelonephritis adopted by the WHO (World He alth Organization). Consider the characteristics of the disease, statistical data. Let us describe the forms of the disease distinguished in the classification.
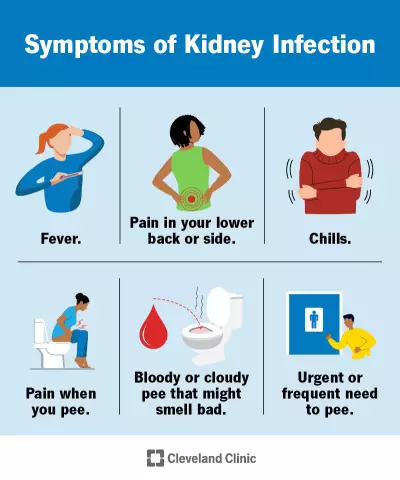
What is this?
Before considering the classification of pyelonephritis, let's present a description of this disease. This is the name of the inflammatory process of an infectious nature that develops in the interstitial tissues and tubules of the kidneys. At the same time or later, it can also affect the parenchyma and pelvis of the kidney. At its final stage, the diseaseextends to the glomeruli and blood vessels of the organ.
Pyelonephritis is also often referred to as a bacterial variety of interstitial nephritis.
Statistics data
Next, we will present the WHO classification of pyelonephritis. But first, let's announce the statistics of the World He alth Organization on this disease:
- The most common kidney disease in all age groups. As for children, pyelonephritis occupies the 2nd-3rd place in terms of prevalence, second only to respiratory diseases.
- Among the adult population, pyelonephritis is diagnosed in 100 out of 100,000 people. Among children - 480-560 people out of 100 thousand.
- 60-75% of cases are young, middle-aged people (30-40 years old). The disease often develops in them after defloration, pregnancy, in the postpartum period.
- In children, the peak incidence of pyelonephritis occurs at the age of 2-3 years.
- As for the "sex" of the disease, it is mostly female. Pyelonephritis is diagnosed more often in girls than in boys. This trend continues with age. Young women suffer from the disease 4-5 times more often than men. This is explained by the anatomical features of the genitourinary system.
- Provokes pyelonephritis mainly urolithiasis, urethral stricture, chronic prostatitis, abnormal development of the kidneys and urinary tract. As for older men, the disease can provoke an enlarged prostate gland in them, which makes it difficult for urine to drain from both the kidneys and the urinary tract.bubble.

International Classifier of Diseases
If we turn to the classification of pyelonephritis in the ICD-10, we will notice that this disease is not singled out in the reference book as a separate disease. It belongs to a subclass of pathologies of the tubulointerstitial renal apparatus. Pyelonephritis in ICD-10 can be found under codes N10-N13.
Let's imagine special cases:
- N10. Tubulointerstitial acute nephritis. There are infectious interstitial nephritis, pyelonephritis and pyelitis.
- N11. Tubulointerstitial chronic nephritis. The category includes the same interstitial nephritis, pyelonephritis and pyelitis. There are additional subcategories of the listed diseases: N11.0 - non-obstructive origin, associated with reflux, N11.1 - obstructive forms (except pyelonephritis, which are associated with urolithiasis), N11.2 - other forms of diseases, N11.3 - serious data forms chronic pathologies.
- N12. Tubulointerstitial disease, in which case it is impossible to specify its form - acute or chronic.
- N13. A number of obstructive disorders, among which both obstructive pyelonephritis and urolithiasis stand out.

Clinical classification of pyelonephritis
This disease is characterized by several ways of infection, forms, nature of the course and other important features for specialists. Therefore, nephrologists decided to introduce a single gradation. It was announced in 1974 at the First All-Union Congress of Nephrologists.
This is the classification of pyelonephritis according to Lopatkin N. A., Rodman V. E. The following types of the disease are distinguished:
- Single-sided and double-sided.
- Acute and chronic.
- Primary and secondary.
- Serous and purulent.
- Hematogenous and urinogenic.
- Obstructive and non-obstructive.
There is a separate classification of acute pyelonephritis:
- Primary acute.
- Secondary acute.
- Acute pyelonephritis in pregnant women.
- Apostematous pyelonephritis.
- Kidney carbuncle.
- Kidney abscess.
Classification of chronic pyelonephritis is as follows:
- Actually chronic form.
- Pyonephrosis.
- Paranephritis.
- Necrosis of the renal papilla.
Let's get acquainted with the presented categories of the disease in detail.

Number of affected kidneys
According to the number of affected kidneys, the classification of pyelonephritis is as follows:
- Single-sided.
- Double-sided.
In the first case, one kidney is affected, in the second - two. This gradation is typical for both acute and chronic forms of pyelonephritis.
Of course, with a unilateral course of the disease, its prognosis is more favorable, since one he althy kidney is able to provide a relatively high-quality cleansing of the body of toxins during the illness. Otherwise, pyelonephritis is oftenturns into complications.
Occurrence conditions
Classification of pyelonephritis according to the conditions of occurrence:
- Primary.
- Secondary.
In the primary form, the pathogenic factor has a negative impact on the renal system immediately after it enters the body. In the case of secondary pyelonephritis, an infectious inflammatory process has already developed in some location of the body. Consequently, pathogens from it, by migration, got into the former he althy kidneys, provoked their inflammation.

Infection pathway
According to this classification, the path of infection causing pyelonephritis can be as follows:
- Urinogenic.
- Homogeneous.
It is important to note that the homogeneous (through the blood) route of infection is more characteristic of acute pyelonephritis. In this case, the inflammatory process will be localized in the cortex, in the vicinity of the intralobular vessels.
Urinogenic (through urine) infection is typical, respectively, for chronic pyelonephritis. Pathogenic microflora migrates here from the lower urinary tract, moving along the wall or lumen of the ureter.
In this case, the location of the inflammation will be fan-shaped. They look like wedges, located with a tip towards the pelvis, and the base - to the outer surface of the kidney. Usually, with urinogenic pyelonephritis, it is preceded by cystitis or urethritis.
Urinary tract patency
Here the disease is alsorepresented in the classification by two forms:
- Obstructive.
- No obstruction.
In most cases, obstruction (obstruction) is diagnosed when infectious agents have migrated into the kidney along the walls of the ureter. This leads to inflammation of the latter, which results in a narrowing of these walls, a decrease in the lumen of the ureter.
Accordingly, with an obstructive form, pyelonephritis develops faster and more severely. The disease may be accompanied by a more pronounced intoxication of the body, since the normal outflow of urine is difficult. It must be said that urostasis (stagnation of urine) creates favorable conditions for the reproduction of pathogenic microflora. And poisoning the body with metabolic products depresses the immune system.

A type of inflammation
There are two types of pyelonephritis in this subcategory:
- Serous.
- Purulent. This type includes apostematous form, renal abscesses and carbuncles.
As for statistics, the first category of the disease is considered more common. Serous pyelonephritis - 70% of all cases of the disease, purulent - the remaining 30%. With serous inflammation, there is a thickening, swelling of the kidney. The body is visibly tense. In the parenchyma, foci of infiltration around the vessels develop. It is important to note that the serous form can turn into a purulent one over time.
Purulent pyelonephritis is characterized by an apostematous course, in which multiple suppurations develop. Leukocytes were noted in the infiltrates,neutrophils, dead cells. This pathological mass compresses the renal tubules.
Carbuncle here is one of the varieties of apostematous pyelonephritis. More precisely, this is its natural final stage. It is an enlarged purulent focus. Even with the complete recovery of the patient, this degree of pyelonephritis is fraught with negative consequences, because the dead kidney cells are replaced by connective tissue. And this provokes further kidney failure.
Classification of the acute form
Classification of chronic pyelonephritis in adults, we will present further. Now consider the gradation of the acute form of the disease:
- Primary spicy. So in the medical environment they call pyelonephritis, which developed without a previous disease of the renal or genitourinary system. With this form of the disease, the pathogenic microflora enters the kidney by the hematogenous route (in other words, through the blood) from any infectious and inflammatory foci localized in the body.
- Secondary acute. This form of pyelonephritis may be preceded by the following: urinary tract abnormalities, bladder stones, pregnancy, strictures of both the urinary canal and ureter, prostate enlargement. In children, hemodynamic disorders are additionally allocated.
- Acute pyelonephritis in pregnant women. It develops approximately in the second half of the gestation period. The disease provokes pressure of the growing uterus on the ureters, asymptomatic bacteriuria, decreased tone of the upper urinary tract, as a result of neurohumoralchanges in the body.
- Apostematous form. This is an inflammation of a purulent nature. Numerous pustules are formed in the renal cortex. This is a stage or complication of acute secondary pyelonephritis. A consequence of a metastatic (spreading) infection with a pyogenic infection.
- Kidney carbuncle. Purulent-necrotic lesion of the organ. A limited infiltrate is formed in the renal cortex. It may also be a primary disease, a consequence of massive bacterial migration from the focus of inflammation.
- Kidney abscess. Quite a rare form.
Classification of the chronic form
Let's imagine the classification of chronic pyelonephritis:
- Actually chronic form. A consequence of acute pyelonephritis. This is facilitated by the causes of obstruction to the outflow of urine that have not been eliminated in time, improper, insufficient treatment of the acute form of the disease, immunodeficiency, serious general diseases, infection with bacteria that are resistant to treatment, being in an inactive form.
- Pyonephrosis. The thermal stage of a purulent-destructive form of the disease, both specific and nonspecific.
- Paranephritis. Spread of inflammation to the perirenal fatty tissue.
- Necrosis of the renal papillae. Consequence of exacerbation of chronic pyelonephritis. A consequence of either embolism of blood vessels by pathogenic microflora, or the result of compression of these vessels by an infiltrate.

Stages of the disease
You are familiar with the WHO classification of chronic pyelonephritis. In its course, this disease takes place inthree stages:
- Spicy.
- Period of latent inflammation.
- Remission (may be complete or incomplete).
The phase of the disease is recognized as acute based on the analysis of the patient's blood and urine, diagnosing pronounced symptoms. As for the latent phase, during its continuation, the disease does not manifest itself in any way. Clinical symptoms are not pronounced, which makes it possible to judge sluggish inflammatory processes.
The options for ending the disease are as follows:
- Recovery of the patient.
- The transition from an acute form to a chronic one.
- Development of secondary nephropathy.
- Diagnosis of secondary kidney shrinkage.
Possible consequences of the disease are as follows:
- Urosepsis.
- Acute onset of kidney failure.
- Chronic occurrence of kidney failure.

Classification for children
There are no differences here. The classification of pyelonephritis in children is similar to that of an adult. The disease is divided into the same categories:
- Primary and secondary.
- Acute and chronic.
- Obstructive and non-obstructive.
You are already familiar with the characteristics of the listed varieties of pyelonephritis.
Pyelonephritis is a serious common kidney disease. You know its main varieties, which have their own characteristics.