- Author Curtis Blomfield [email protected].
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Increasingly, people suffer from heart problems. Excessive physical and emotional stress, chronic diseases, bad habits - all this cannot but affect the work of the cardiovascular system. One of the dangerous pathologies of the organ is heart block - a disease that occurs either as an independent or against the background of other diseases. So, a condition in which the transmission of an impulse through the heart muscle slows down or stops is called heart block. What is this disease, what are the causes of its development, symptoms, signs, how to protect yourself from it?

Reasons
Pathology can occur on its own or as a result or complication of other diseases. In the first case, hereditary predisposition plays a role. If a person in the family has someone suffering from heart problems, then they are much more likely to be stricken with a disease called heart block. That this is a serious risk, not everyone knows, and in many casespatients are not even aware of possible malfunctions in the cardiovascular system, continuing to lead their usual lifestyle. Congenital pathologies are another factor that contributes to the development of human heart problems.
Heart block can also develop against the background of diseases such as myocarditis, angina pectoris, cardiosclerosis, myocardial infarction, thickening of the heart muscle, etc. Another reason is an overdose of drugs or improper medication. From this it follows that you should always follow the doctor's recommendations or carefully reread the instructions for use.
Views
Blockade can be localized in different parts of the organ, which determines its classification and treatment.

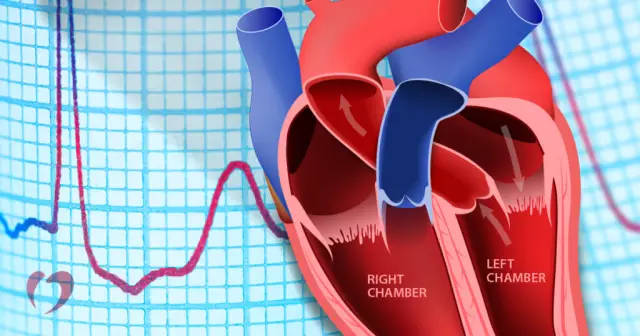
With atrial (sinotrial) blockade at the level of the atrial muscle, the conduction of the nerve impulse slows down. If the atrium is left, then this condition is also called left heart block, if right, then right. This pathology is very easy to confuse with bradycardia - a slow heart rate. Sometimes a he althy person may experience this type of blockade. A pronounced degree is accompanied by convulsions and fainting.
Atrial-gastric or atrioventricular blockade develops due to disturbances in the conduction of an impulse on the way from the atria to the ventricles. Blockade of the ventricle of the heart is a condition in which conduction is disturbed in the bundle of His. Problems such as cardiomyopathy, coronary heart disease, infective endocarditis, myocarditis,myocardial infarction. Another condition is heart block. Another common name for the disease is bundle branch disease. If only a blockade of the right leg of the heart (or left) is found, then it does not pose a danger to life. It is much worse when the patient has a blockade of both legs, then immediate hospitalization and adequate treatment are required.

Atrioventricular block I and II degree
If a patient is diagnosed with atrioventricular heart block (which is well shown by an electrocardiogram), then the condition and prognosis depend on the degree, of which there are three. At the first degree, delayed conduction of impulses is noted. The most common causes of development are electrolyte disturbances, acute myocardial infarction, myocarditis, increased vagal tone, and an overdose of cardiac drugs. Ignoring the disease can lead to an increase in the degree or progression of the blockade.
The second degree is characterized by the receipt of not all impulses into the ventricles. Clinical signs of the condition: chest pain, dizziness, hypoperfusion, bradycardia, low blood pressure, irregular pulse. Professional sports, acute myocarditis, valve surgery, heart defects, vagotonia can provoke the development of the disease.

Atrioventricular block ІІІ degree
Third-degree blockade, or complete blockade, is a condition in which an impulse is not conducted at all. ventricular contractions andatrial events occur independently of each other. The patient may experience the following symptoms: chest pain, nausea, vomiting, shortness of breath, weakness, dizziness, sweating, impaired consciousness, sudden death may occur.
The causes of acquired blockade are metabolic disorders, acute rheumatic fever, myocarditis, myocardial infarction, complications after surgery, drug overdose.

Incomplete heart block
This disease is often found in young people and is even considered a variant of the norm. The only danger that an incomplete heart block carries is that this condition can develop into a complete one. In most cases, the development of the disease is associated with organic heart disorders: cardiomyopathy, aortic valve dysfunction, hypertension, coronary artery disease. Diagnosis of incomplete blockade is carried out using an electrocardiogram.
Sometimes patients are diagnosed with "incomplete blockade of the right leg of the heart" (bundle of His). This disease can be congenital or acquired, and is associated with a partial violation of the passage of an electrical impulse through the right leg of His. It proceeds benignly, does not require special treatment, and can rarely turn into a complete blockade. Incomplete blockade of the ventricle of the heart is also not dangerous, but it is necessary to monitor it to prevent progression.
Children's heart block
When conductor cages of the second and third types,responsible for the transmission of impulses to the contractile myocardium through the entire conduction system, function poorly, heart block develops in children. By localization, it can be ventricular block (left and right heart block), atrioventricular or sinoatrial block, by completeness - complete and incomplete, in relation to the bundle of His - transverse or longitudinal.
Heart problems in a child can be congenital or acquired. If a heart pathology of any nature is found in children, it is necessary to immediately consult a doctor (pediatrician, cardiologist) and begin treatment. The occurrence of heart block in childhood will deprive the child of the opportunity to lead a normal life, he will constantly be haunted by symptoms, and life expectancy will be significantly reduced. Therefore, it is important to prevent the development of complications of heart disease, monitor the child's he alth, and fight for his life by any means.

Diagnosis
Diagnosing heart block at an early stage can be a successful step towards recovery. Therefore, it is recommended to seek help when the minimum symptoms are disturbing, and not when the ambulance is already picking up. The danger of the disease depends on each specific case. And if, with an incomplete patient, the patient can continue a normal lifestyle, then full forms can result in serious complications, even death.
You can diagnose a pathology based on the results of an electrocardiogram, which at the time of the study allows you to assess the state of the organ. Butit is worth considering the fact that the occurrence of blockades can be periodic. Transient blockades are examined using a treadmill test, Holter monitoring, and echocardiography can also be prescribed to confirm the diagnosis.

Treatment
The treatment of blockades is divided into several important steps. Firstly, this is a timely diagnosis, then - the establishment of the nature and cause. Further, most of the actions should be aimed at eliminating the cause (if it is acquired). In some cases (incomplete blockade), only observation is carried out. Only then proceed to the direct treatment of blockades, which, depending on the severity, can be medical or surgical.
When treating with medications, drugs such as Orciprenaline sulfate, Isoprenarine hydrochloride, Atropine are most often prescribed. The severe condition of the patient and the ineffectiveness of medications can be a signal for temporary or permanent pacing. Implantation of a pacemaker is carried out mainly in patients aged 60-70.