- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Hepatitis, the classification of which is presented in this article, is a very relevant topic in modern medicine, since the disease is very widespread among the population. Often the disease does not manifest itself and develops latently. There is a high risk of infection. This applies to the infectious form. In addition, a long-term disease can provoke irreversible fibrotic changes in the liver and severe liver failure, which is usually incurable.

Varieties of hepatitis
What is hepatitis? The classification assumes the following varieties of the disease: an ailment of an infectious or viral nature. Medicine distinguishes its five main types A, B, C, D, E, which can cause inflammation of the liver. In addition, hepatitis can become a complication of infectious diseases such as cytomegalovirus, mumps, rubella, etc.
What is toxic hepatitis? This category includes pathologiesdeveloping under the influence of drugs, alcohol and poisons. Among the drugs, drugs used in the treatment of tuberculosis, antiviral drugs, sulfonamides, antibiotics that lower the temperature, drugs against convulsions and oncological neoplasms have a high degree of toxicity. Autoimmune forms of hepatitis often have an unexplained etiology. The immune system starts attacking its own liver cells. Depending on the course of the disease, it is customary to distinguish two forms of the disease:
- Hepatitis in acute form. It manifests itself suddenly and is expressed in intoxication, fever, jaundice of the skin, but not in all cases. This scenario has most hepatitis of a viral and toxic nature. If the patient turns to a specialist in a timely manner, then after the acute form, in most cases, a complete recovery occurs.
- Chronic form. It can be the result of an acute lesion, autoimmune processes, the result of the use of alcoholic beverages and drugs, as well as long-term treatment with hepatotoxic drugs. In addition, viral etiology hepatitis B and C can develop immediately as a primary chronic disease. The course of a chronic disease is characterized by erased symptoms. Therefore, diagnosis sometimes occurs late, when the liver has undergone serious damage.
Main transmission channels
Only the viral form is contagious. In this case, the infection is transmitted in different ways:
- through dirty hands;
- through contaminated dishes and foodproducts.
Hepatitis A and E are spread in this way. Transmission also occurs through contact with the blood of an infected person. In this regard, manicures, pedicures, tattoos, piercings, drug use by injection, etc. are a threat. This type of transmission is inherent in viral hepatitis B, C, D. Viruses B, C, D can also be transmitted sexually.

Hepatitis symptoms
How does hepatitis manifest itself? The main symptoms include:
- high body temperature;
- pain in the hypochondrium on the right side;
- icteric color of skin and eyes;
- colorless feces;
- itchy skin;
- nausea;
- dark urine color;
- asthenia.
However, it should be noted that such signs do not always appear. In some cases, the disease is hidden and is perceived by a person as a slight malaise.
Hepatitis A
If a person complains of feeling unwell, his body temperature is elevated, and the urine becomes dark (the color looks like strong tea leaves), then you can suspect the development of a disease such as hepatitis A. In this form, chills may be observed, accompanied by disorder of the gastrointestinal tract, nausea, vomiting, heaviness in the stomach and hypochondrium on the right. After a while, the urine darkens, the sclera and skin become icteric, the feces become colorless. After the appearance of jaundice, the general condition of a person improves.
Type B
Viral hepatitis B is contagiousdisease. Its appearance provokes a virus. It is ubiquitous and can affect anyone. Hepatitis virus Mostly carried by the blood. The chronic form of this disease can cause severe complications and lead to death. Therefore, timely diagnosis and treatment of the disease is very important. Signs of hepatitis B may appear on the 12th week of the incubation period. Against the B virus, there are even vaccines that can reliably protect against the development of the disease.

Signs of disease
What are the signs of hepatitis B? The latency period for the disease lasts up to six months. The first signs appear at the 12th week. Patients complain of asthenia, lack of appetite, nausea, heaviness in the right hypochondrium. Urine darkens and foams, feces lighten. There are pain in the joints, disruption of the digestive tract. Body temperature is elevated.
Hepatitis C
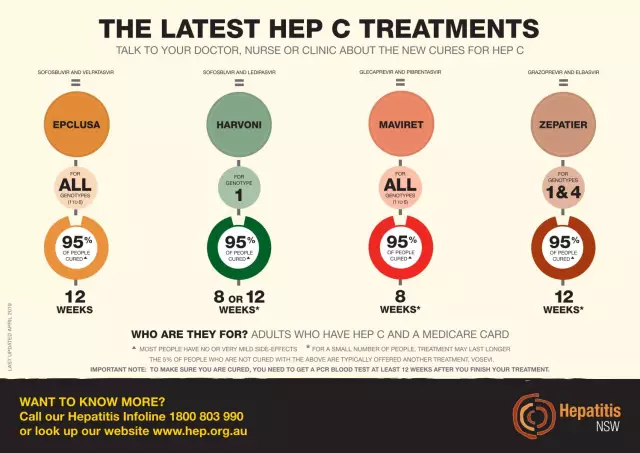
How dangerous is hepatitis C? This is an infectious disease of the liver that is caused by a virus. Anyone can get infected. It usually occurs in young patients. The incidence rate has been steadily increasing over the past decades. The hepatitis C virus is transmitted through the blood. Are there clear signs of hepatitis C? In most cases, the disease develops gradually and becomes chronic. However, it is asymptomatic.
What are the consequences of a disease like hepatitis C? The disease can disrupt the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and liver and become chronic. By the way, she responds well to treatment.modern medicines. Why is hepatitis C dangerous? It can cause cirrhosis of the liver. In addition, a valid vaccine against the disease has not yet been invented, but infection can be prevented.
How does this type of disease manifest itself?
What are the signs of hepatitis C? In general, the disease can be classified as asymptomatic. It appears by chance. Most often, patients complain of asthenia, but the symptoms are blurred. There are pains in the joints. There is an increase in the size of the liver and spleen. What can cause hepatitis C? The consequences are the most serious. One of the most severe is cirrhosis of the liver. With it, yellowness of the skin and eyes appears, the abdomen swells, spider veins are visible, and asthenia increases.

Varieties of D
This disease is caused by the hepatitis D virus. The causative agent of the disease cannot develop in the body on its own. To do this, he needs the participation of a so-called assistant. This is the hepatitis B virus. The symbiosis of two viruses can cause a disease that is characterized by a severe course. Infection, as a rule, occurs during blood transfusion and through syringes of drug addicts. It is not excluded and the sexual way, as well as the spread of the virus from mother to fetus. All patients affected by virus B are susceptible to hepatitis D.
Symptoms
How does hepatitis D manifest itself? The patient is febrile. There are pains in the liver, in the area of the knees and other large joints. There are complaints of nausea. Man lacksappetite. He is lethargic and inactive.
Hepatitis E
Earlier, before the identification of this variety, the disease did not belong to either group A or group B. The mechanism of transmission is the feces of a sick person. The virus enters the body through contaminated water, less often through unwashed hands. Young people aged 15-29 get sick with this type of hepatitis. In particular, this form has become widespread in countries with a hot climate and poor water supply. The prognosis of the disease is favorable. The exception is women who are in the last three months of pregnancy.

Main signs
The disease manifests itself in steps. The period preceding jaundice is characterized by asthenia, dizziness, loss of appetite. Nausea and vomiting are rare. Hepatitis E may present with heaviness in the right hypochondrium or upper abdomen. Pain can be both moderate and acute. Body temperature remains within normal limits. Incubation lasts 9 days.
Further there is a malfunction in the liver, which marks the beginning of the icteric stage. Urine darkens, feces lightens. The skin and sclera of the eyes turn yellow. A complete blood count shows an increase in bilirubin. The patient suffers from itching of the skin. Weakness and nausea persist. The liver increases in size. The duration of the disease is 1-3 weeks.
Hepatitis G
This kind of disease has become widespread. In Russia, the frequency of the pathogen is 2%, in the capital of Russia it is 8%. According to doctors, hepatitis Gis the younger brother of hepatitis C. It is transmitted in the same way as the latter - through the blood. The disease has become widespread among people who use drugs. Sexual transmission of the disease, as well as the transfer of the virus from mother to fetus, is not excluded.
Symptomatics
The patient complains of lack of appetite, pain in the right hypochondrium. Urine darkens and feces lightens. Nausea and vomiting are often noted. Jaundice begins to appear. Yellow mouth and eyes. The skin also gives off yellowness. The level of bilirubin in the blood increases. The liver increases in size. Sometimes the same process occurs with the spleen. The disease can become chronic. When combined with hepatitis C, the disease can provoke the development of cirrhosis of the liver.
Botkin's disease
This is one of the mild forms of hepatitis A. The duration of the incubation of this disease is one and a half months. The person is easily susceptible to this disease. The virus that got into his body causes mandatory infection. This infection is 20% among the adult population. The disease often affects people in the autumn. Half of all infections fall at this time of year.

Autoimmune hepatitis
Hepatitis, the classification of which involves five main types, is also autoimmune. Let's talk about it in more detail. Autoimmune hepatitis is a progressive form of inflammation of the liver tissue. The disease is characterized by a high level of antibodies in the blood and hypergammaglobulinemia. With histologicalstudy of liver tissue can be diagnosed with periportal hepatitis. It is characterized by the presence of stepped or partial necrosis. This hepatitis is of unknown etiology. The disease progresses quite quickly. It can cause liver cancer, portal hypertension, liver failure and even death.
Since pathognomonic symptoms are observed in autumn, when making a diagnosis such as autoimmune hepatitis, it is necessary to exclude the chronic form of viral hepatitis, Wilson's disease, hemochromatosis, drug-induced and alcoholic hepatitis, non-alcoholic liver degeneration, diseases of immune origin, the presence of biliary cirrhosis and primary sclerosing cholangitis.
The disease can develop in patients of different ages: from 9 months to 77 years. But, as a rule, it is diagnosed in patients younger than 40 years. Autoimmune hepatitis can be misdiagnosed. One third of patients have comorbidities. Among them, it should be noted Hashimoto's thyroiditis, ulcerative colitis, synovitis, thyrotoxicosis. Unfortunately, the autoimmune form of hepatitis is diagnosed in 25% of cases in the later stages, when the disease causes cirrhosis of the liver.
Classification of disease according to ICD
How are varieties of a disease such as hepatitis subdivided in medicine? The ICD classification suggests the following list with its conditional codes:
- B15 - acute form of hepatitis A.
- B16 - acute form of hepatitis B.
- B17 - other types of acute viral hepatitis.
- B18 - viralchronic hepatitis.
- B19 - viral hepatitis of unknown origin.
What are the consequences of hepatitis?
Infection with hepatitis involves an incubation period: the time from the beginning of the penetration of the virus into the blood until the first symptoms of the disease. This process leads to the degeneration of liver cells. With hepatitis forms A, B, C, the duration of this period can be from 10-20 to 100-200 days, which is determined by many factors.
The development of hepatitis proceeds in the acute phase. The first manifestations of the disease can be severe and noticeable. Sometimes there are lightning-fast development that can lead the patient to death. Recovery may also occur. This happens when the virus leaves the body, and the liver cells return to normal.
What are the characteristics of hepatitis? Recovery occurs in all cases of damage to the body with an acute form of hepatitis A and in most cases of hepatitis B. If this does not happen, then a chronic form develops. The reason why the acute form degenerates into a chronic one is the weakened state of the immune system. However, it is very difficult to give an unambiguous definition of who will recover and who will not.
The chronic form develops in 20% of cases of infection with the hepatitis virus and in at least more than half of cases of hepatitis C. The most dangerous form of the disease is the fulminant form. It is extremely rare (in 1% of cases of hepatitis A or B). It can be fatal.
To dangerousthe consequences of chronic hepatitis include cirrhosis of the liver and a cancerous tumor (hepatocellular carcinoma). A complication such as cirrhosis of the liver is noted in 20% of cases of chronic hepatitis B and C. Viral forms of the disease often provoke cancer and become the main reason for liver transplantation.
The risk of death in the presence of chronic hepatitis is 15-50%. With cirrhosis of the liver, up to 50% of patients affected by the chronic form die within 5 years. The disease is one of the top ten causes of death for males in developing countries.
As for treatment, the acute form does not require antiviral therapy. At the same time, it is prescribed for chronic. Combined treatment includes the patient taking interferons, which at the cellular level enhance the body's fight against the virus, and nucleosides, which replace the molecules of the genetic material of the virus.
Are there vaccines against the disease?
At the moment in Russia, as in other Western countries, the process of immunity prevention is widely known. In other words, vaccination. It provides the human body with immunity to infection even when in contact with a source of infection. Many are interested in whether it is possible to be vaccinated against hepatitis? To date, vaccines against type A have been developed. The drugs have a high degree of effectiveness.
Vaccination against hepatitis A is indicated for both children and adults who have not previously had this disease, and almost all people who have variousliver disease. Such a vaccination does not cause side effects and does not pose any danger. This vaccine is administered twice at intervals of six months or a year. Antibodies appear after the first dose of the drug after about 14 days. Thanks to this, a person can be protected from such an infection for 10 years.
The hepatitis vaccine is genetically engineered. It contains an immunogenic protein. Such a vaccination is given intramuscularly to infants three times with an interval of one month after the first vaccination carried out in the maternity hospital, and five months after the secondary vaccination. In this case, certain antibodies appear that suppress the development of the disease in 99%. This vaccine provides reliable protection for 8 years and more. Sometimes it protects the body for life.
Hepatitis B vaccine should be given to all people, especially those at risk. Their work is related to blood (surgeons, doctors, laboratory assistants). Vaccination against forms A and B is done on the recommendation of a doctor. It is not planned. Many people refuse it altogether. Although this vaccination for children, by order of the Russian Ministry of He alth, has become mandatory since 2002.
For hepatitis C, unfortunately, there is no vaccine yet. Scientists have not been able to find a stable virus protein for which neutralizing antibodies could be developed. Many scientists are looking for ways to create such a drug, ongoing research in this area. Clinical trials are regularly carried out in Europe.

Where can I get testedhepatitis?
Many are interested in where to donate blood for hepatitis. Analyzes can be done in any city or center of regional significance. If a disease is suspected, the therapist sends the person to the laboratory. To diagnose the disease, as a rule, they resort to a blood test. For viral types of diseases, hepatitis D antigen or antibodies to virus C are determined. Antibodies of other types of hepatitis are also determined.
For forms with non-infectious etiology, it is advised to conduct a general and biochemical blood test, as well as liver tests. For patients, such an analysis is carried out free of charge and is paid for by the CHI policy. The results are received by the doctor who gave the referral to the laboratory. He communicates them to the patient.
Usually, tests are carried out in district clinics or medical centers with which an agreement has been concluded for such a manipulation. Also, a laboratory examination for the presence of hepatitis B or C can be done in special rooms that exist in large cities. They usually function together with AIDS centers. Testing for HIV infection is often indicated. These centers provide diagnostics free of charge and anonymously.
It happens that an urgent analysis is required. In this case, the examination is carried out in the laboratories of private clinics or diagnostic centers. Analyzes are carried out for 1-2 days, the conclusion is given to the patient in his hands. Upon receipt of a positive result during a free examination in order to clarify the diagnosis, a secondary examination can be carried out on a paid basis. It may also beproposed passing quantitative tests. Private clinics also guarantee the accuracy, anonymity and speed of research.

How is the analysis done?
In order for the analysis to be as accurate as possible, blood is taken from a vein. The procedure is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach. The last meal should be no later than 8-10 hours before blood donation. For a day, you should stop the consumption of fatty foods, spicy foods and alcoholic beverages. The analysis is carried out by laboratory assistants. At the same time, all hygiene rules are observed. Usually 10 ml of blood is taken. In the laboratory, you can clarify information about when you can get an answer.
Conclusion
Hepatitis, the classification of which has been presented in this article, is a serious lesion of the liver. It can cause complications, and in case of untimely treatment, go into a chronic form. In some cases, it can even lead to death.