- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Until recently, the hepatitis virus was considered the only virus of the genus Hepacivirus. But it turned out that horses, dogs, rodents and bats are also susceptible to this disease. Let's try to figure out how dangerous hepatitis C is for a person, how to detect and treat it, since timely diagnosis of the disease greatly simplifies therapy. In addition, young children are susceptible to the disease, and the sooner it is detected, the greater the chance of a favorable outcome.
What is hepatitis C virus
When a person is diagnosed with this disease, he immediately begins to be tormented by many questions about hepatitis C: what is it (photo of the manifestations of the disease), which doctor to seek help, and so on. The hepatitis or jaundice virus is a particle consisting of genetic material (RNA) in a core surrounded by an icosahedral protective protein shell and enclosed in a lipid (orfatty) membrane of cellular origin.

Hepatitis C is one of several viruses that cause severe, diffuse inflammation of the liver. Up to 85% of people who have had an acute form of the disease remain chronically infected for the rest of their lives. Infection most often occurs through the blood (intravenous injection with non-sterile needles, scratches, wounds). The risk of sexual transmission of this virus is considered low, but still occurs.
Causes of hepatitis in adults
Hepatitis C is a disease caused by a virus that attacks the liver. The functions of the liver include removing harmful chemicals from the body, improving digestion, processing vitamins and nutrients from food, and participating in the processes of blood clotting in cuts and wounds. Hepatitis C in women poses a great danger to infants, since a newborn can be infected from a sick mother during childbirth. That is why it is important for a woman to monitor her he alth when planning a pregnancy.
The jaundice virus in an adult can be spread in the following ways:
- When using non-sterile instruments for the introduction of intravenous or intramuscular infections (including narcotic drugs).
- When tattooing, piercing, acupuncture procedures with non-sterile needles.
- During unprotected sex with an infected partner, if at that time there is contact through blood (ulcers, cuts, sores on the genitals or duringtime of menstruation). This method is referred to as unusual methods of infection.
- During a blood transfusion procedure.
- During treatment in dental clinics.

Hepatitis does not spread through sneezing, coughing, sharing food, sharing cutlery or other casual touch.
Causes of hepatitis in children
The symptoms and treatment of hepatitis C in children are somewhat different from the signs of the disease in adults. Childhood hepatitis is spread in two ways: from mother to fetus (vertical route of infection) and through direct contact with the blood of an infected person (parenteral route of infection). The virus can be transmitted from an infected mother to a newborn during childbirth, the frequency of such cases is about 4-5%. If this situation arises, then the woman is offered a caesarean section, which slightly reduces the risk of transmitting the hepatitis virus to the newborn. Infection of children by the second route usually occurs during various medical interventions, dental treatment, the introduction of drugs through non-sterile instruments, hemodialysis, blood transfusion and other medical procedures.

Adolescents, like adults, have an increased chance of getting hepatitis when using drugs. In addition, the risk of infection in adolescent children increases if the rules of skin hygiene are violated when applying tattoos, piercings and other things. When shaving with common hygiene items through cuts and abrasions onViruses can also enter the body through the skin.
Hepatitis symptoms in adults
Often, many people who become infected with hepatitis C do not have symptoms characteristic of the disease. Signs of chronic infection do not appear until scarring (cirrhosis develops) on the liver. In this case, the disease is usually accompanied by general weakness, increased fatigue and has non-specific symptoms even in the absence of cirrhosis.
Signs of the disease usually appear much later than infection, as the incubation period for hepatitis is 15 to 150 days. An infected person without symptoms of the disease poses a threat to others, as he acts as a carrier of the virus and can transmit it to other people in the above ways. The main symptoms of the disease include the following:
- loss of appetite;
- malaise, weakness;
- nausea, bouts of vomiting;
- diarrhea;
- sudden dramatic weight loss for no apparent reason;
- yellowing of the skin, sclera of the eyeballs (therefore, the people call the disease jaundice);
- discoloration of urine (to dark brown) and feces (whitish feces).
Hepatitis symptoms in children
On average, the incubation period of childhood hepatitis can last from 15 days to 6 months. Symptoms of jaundice in children occur in less than 50% of cases and are expressed mainly by yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes. The icteric period usually lasts up to 3 weeks. Since hepatitis is characterized by inflammation of the liver, the child has a generalintoxication of the body, which is accompanied by nausea, vomiting, diarrhea. The acute form of the disease begins slowly, the symptoms increase gradually, with the development of dyspeptic disorders and asthenovegetative syndrome. Symptoms of jaundice in children may be accompanied by fever, headache. The stool becomes discolored, while the urine, on the contrary, acquires a dark brownish tint.

The identified symptoms and treatment of hepatitis C are closely interrelated, because with late diagnosis or lack of proper treatment in 10-20% of all cases of the disease, the acute form of jaundice becomes chronic. Chronic jaundice, as a rule, is asymptomatic and is usually detected during a random examination of the child, when time is lost and the disease remains with him for life. These children have increased fatigue, asthenia, extrahepatic symptoms (telangiectasias, capillaritis).
Diagnosis
Due to the fact that the acute form of hepatitis C is usually asymptomatic, early diagnosis of the disease is very important. When it becomes chronic, the chances of detecting an infection decrease, the disease remains undiagnosed, and serious complications such as cirrhosis or liver cancer may develop.
Detection of the virus in the body occurs by determining the level of antibodies in the blood, and then confirmed by additional tests to determine viral RNA. The amount of RNA in the blood (an indicator of viral load) does not correlate with the severity of the disease, but can be used to track the responsebody during treatment. A liver biopsy is used to assess the degree of disease (damage to the cells of the organ and scarring), the importance of which is important for planning therapy.

Diagnosis is carried out in 2 stages:
- jaundice virus antibody screening to determine if a person has been infected with the virus;
- If the antibody test is positive, a nucleic acid test for hepatitis C virus RNA is performed to determine the form of the disease (acute or chronic).
After that, with positive tests, the doctor needs to assess the degree of damage to the liver (fibrosis or cirrhosis). This can be done through a biopsy or through various non-invasive tests. In addition, the patient should undergo a laboratory test to determine the genotype of the hepatitis C strain. The degree of liver damage and the genotype of the virus are used to make decisions about the treatment and management of the disease.
Hepatitis C genotypes
In order for the treatment of the disease to be effective, it is important to determine which genotype the virus belongs to. Hepatitis C genotypes are divided into six different types. As a rule, patients are infected with a virus with only one genotype, but each of them is actually a mixture of closely related viruses, referred to as quasi-species. They tend to mutate and become immune to current healing. This explains the difficulty in the treatment of chronic jaundice.
The following is a list of the different genotypes of chronic hepatitis C:
- Genotype 1a.
- Genotype 1b.
- Genotype 2a, 2b, 2c, 2d.
- Genotype 3a, 3b, 3c, 3d, 3e, 3f.
- Genotype 4a, 4b, 4c, 4d, 4e, 4f, 4g, 4h, 4i, 4j.
- Genotype 5a.
- Genotype 6a.
Hepatitis C genotypes are of great importance to physicians when making therapeutic recommendations. For example, genotype 1 is the most difficult to treat, and hepatitis patients with genotype 2 and 3 respond better to therapy using a combination of alpha-interferon with ribavirin. In addition, when using combination therapy, the recommended duration of treatment depends on the genotype.
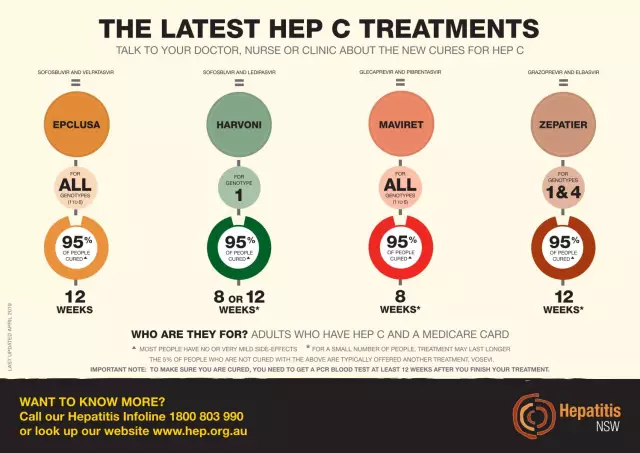
Hepatitis C treatment
Symptoms and treatment of hepatitis C are closely interrelated, since therapy relies, among other things, on the signs of the disease. Before starting treatment, a thorough examination should be carried out in order to determine the optimal approach to the patient and his disease. In addition, based on diagnostic data, the doctor can determine which hepatitis C medicine will be most effective for each specific case. The modern standard of treatment for jaundice is a combination of antiviral therapy with Interferon and Ribavirin, which are effective against all virus genotypes. Unfortunately, "Interferon" is not widely used in medicine, which has a bad effect on the condition of most patients, and in fact the combination of ribavirin with this drug is perhaps the best cure for hepatitis C today.

Scientific advances have led to the developmentnew antiviral drugs for jaundice that are more effective, safer and more tolerable than existing ones. These are direct-acting antiviral drugs (DAAs), which can not only simplify the treatment of the disease, but also increase the percentage of patients recovering. However, antiviral drugs have serious side effects and often cause the following symptoms in patients:
- headaches;
- flu-like symptoms;
- nausea;
- fatigue;
- body aches;
- depression;
- skin rashes, allergic reactions.
If a child is diagnosed with hepatitis C, treatment should be aimed at preventing the transition from an acute form of the disease to a chronic one. The therapy is also mostly complex and includes such combinations as preparations of recombinant interferon, reaferon in parenteral form and viferon rectal suppositories. Treatment regimens are selected for each child individually.

For children from 7 years old and adolescents, it is possible to prescribe a combination of Interferon and Ribavirin. Also prescribe inductors ("Cycloferon") and immunomodulators ("Taktivin"). The duration of treatment for jaundice in children depends on many factors and ranges from 24 to 48 weeks. If hepatitis C is diagnosed, treatment should be accompanied by diet, he althy eating and lifestyle, smoking cessation, andalcohol. It is important to stay in bed and avoid unnecessary medications.
There are also folk methods for treating jaundice, but when resorting to them, you should definitely consult with your doctor so as not to harm the body and not aggravate the disease.
Forecasts and implications
When patients are diagnosed with hepatitis C, how long they can live with it is probably one of the most important questions they ask the doctor. It should be said right away that the forecasts will directly depend on the timeliness of the detection of the disease and the effectiveness of the prescribed therapy. Timely identified symptoms and treatment of hepatitis C, selected correctly - the key to success. Therapy has a good effect on the general condition of the patient, gives positive dynamics and increases the chances of a favorable outcome of the disease. According to statistics, about 20% of patients who become infected with hepatitis are completely cured, although this does not mean that they are protected from infection in the future. The remaining 80% of patients develop a chronic infection (with the appearance of characteristic symptoms or asymptomatic). These people remain contagious to others for the rest of their lives as they become carriers of the virus.

When a doctor detects hepatitis C in a patient (symptoms), treatment, consequences of the disease - information that should be conveyed to the patient as soon as possible and in an accessible form. If a person lives with hepatitis C for a number of years, they usually develop the following complications:
- chronic hepatitis;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- liver cancer.
Disease prevention
Unfortunately, there is currently no vaccine for jaundice. Patients who have had hepatitis C leave feedback that it is better to prevent the disease than to treat it later. So, to avoid the spread of disease and other blood-borne diseases, people must comply with the following requirements:
- Sharing personal items and using items that may be contaminated with blood (such as razors, toothbrushes, etc.) should be avoided.
- Ear piercings, piercings, acupuncture procedures, tattooing in places of questionable sterility and poor hygiene should be avoided.
- People with the hepatitis C virus are required to tell the doctor when they visit a dental clinic or any other he alth care facility that they are carriers of the virus. Ignoring this requirement puts many visitors to the dental clinic at risk.
- Any cuts and abrasions should be carefully treated with disinfectant solutions and covered with a waterproof bandage.
- People who have multiple sex partners should use barrier methods of contraception, such as condoms, to limit the risk of contracting the hepatitis C virus and other sexually transmitted diseases.
- It is important to carry out preventive measures aimed at the safe use of instruments for injections, injections, tattooing and other things.
It should be understood that the hepatitis C virus is not transmitted through everyday contact. Shaking hands, kissing and hugging are safe and there is no need to use special isolation procedures when dealing with infected patients. Contacts that increase the risk of transmission of infection are necessarily accompanied by the release of blood.