- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Forms of oncological diseases, unfortunately, are too diverse. But does hair cancer exist? In principle, this type cannot exist, since hair and wool are dead matter. But there are cancers that affect the scalp. In terms of their danger, they are not inferior to other tumor localizations. In the article we will present the reasons for their formation, alarming symptoms, varieties of the disease, methods of diagnosis and therapy.
What is this?
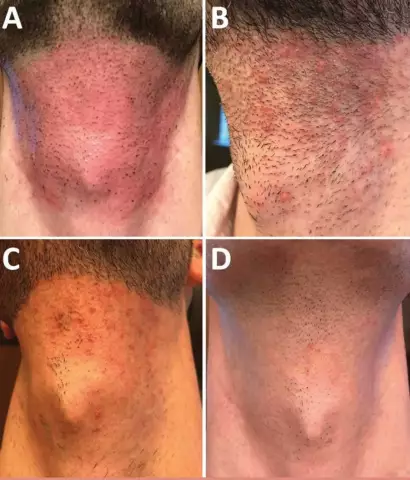
Hair cancer is a simplified name for an oncological process that affects he althy skin cells under the scalp.
I must say that pathology most often affects open areas of the epidermis. Therefore, only about 5% of all identified cases will belong to this species. The risk group here is considered to be people of advanced age (over 50).

Skin cancer types
So, hair cancer is a type of cancer that affects the skin. This type will include several types of tumors:
- Squamous. It develops from keratinocytes (squamous cells). Fortumor character high rate of development and metastasis. It is localized in places where the mucous membranes pass into the skin. This is a homogeneous compacted formation that appears on the surface or in the thickness of the skin. The tumor itches, hurts due to the destruction of the epidermis.
- Basal cell. Speaking of hair cancer, they often mean just the same tumor. It is characterized by slow progression, does not give complications. It develops in the deep layers of the epithelium, as it grows, it also affects the surface integuments. Outwardly - a small flaky seal. In the photo of hair cancer you can see what it looks like.
- Tumor of skin appendages. It develops from damaged blood vessels. It looks like a reddish or bluish rash. As it progresses, it turns into ulcers, inside which the destruction of the skin occurs.
- Melanomas. This is a malignant degeneration of a pigmented spot or mole. Including can be observed on the scalp. A dangerous phenomenon characterized by rapid metastasis and germination inside the skin.
Let's take a closer look at the identified varieties of so-called hair cancer.
Basal cell tumor
Basalioma is a gap between benign and malignant formation. Does not metastasize by itself.
This tumor is divided into several varieties:
- Flat. A distinctive characteristic is the weakly expressed localization of the neoplasm. Can grow on a significant portion of the skin cells under the hair, causing them to die.
- Nodular. It has clear contours and high density. The danger lies in what grows inside the skin.
- Surface. Often this form of cancer is confused with diseases of the skin of the scalp. It affects only the surface of the skin, without causing cell death, without penetrating deep into the epidermis.

Melanoma
Oncologists also divide the neoplasm into several classes:
- Surface. The tumor in the form of a nodule will be above the skin. Outwardly, it looks like a flat circle, a plaque of a yellowish tint. Although it develops slowly, it makes itself felt even in the early stages - a person feels itching, tingling, and other discomfort in its localization. Symptoms increase as cancer develops. In the later stages, melanoma begins to peel off, is affected by erosion.
- Infiltrating. Grows in the deep layers of the skin, has no clear location.
- Papillary. In appearance, such a cancerous tumor is easily confused with papilloma - it looks like a ball (has a wide base), rests on a leg. Characterized by rapid progression.
- Occurring against the background of scars on the skin.
Causes of occurrence
Possible causes of hair cancer (cancer of the skin under the hair) are the following factors:
- Long exposure to direct sunlight (ultraviolet and high temperatures). This is a systematic walking without a headdress under the scorching rays of the sun. Causes both melanoma andbasal cell tumor.
- Ionizing radiation, the influence of direct electromagnetic current. The high probability of developing such education haunts workers in hazardous radioactive industries, survivors of accidents at nuclear reactors, and specialists in the field of radiotherapy.
- Constant exposure to the hair, scalp of aggressive chemical components. The latter can be found in low-quality hair dyes and brighteners, hygiene and cosmetic preparations. Nicotine, arsenic, carcinogens are the causes of cancer.
- Regular injury to the scalp. As we have already mentioned, melanoma often forms on scars. Permanent damage to the skin can provoke the degeneration of epidermal cells into malignant ones.
- Skin diseases. In particular, chronic dermatitis.
- Hereditary factors.
- Reduced immunity.
- Long-term treatment with immunostimulating and hormonal drugs.

Provoking factors
The following can provoke the development of an oncological tumor under the hairline:
- Sensitive skin type.
- A large number of moles on the body. Injury to these marks often leads to degeneration into malignant melanoma. Combing the hair, it is easy to imperceptibly damage the mole in their midst.
- Disturbances in the endocrine system.
- Permanent injury to the same area of the skin.
- Bowen's disease, Paget's disease.
Initial signs
The initial warning signs of hair cancer are as follows:
- Barely noticeable rashes of a gray-yellow hue. Do not distinguish themselves by other symptoms.
- Itchy skin.
- Moles on the scalp increase, change their shape, begin to crack and peel off. Blood, mucus can be released from them.
- A formation similar to a knot, a plaque appeared on the skin under the hair.
- Unreasonable weight loss.
Does hair fall out with cancer? Such a symptom does not indicate a malignant formation, because in this case the skin under the hair is affected, and not the hair follicles.

Signs of developing pathology
Progression of hair cancer reveals itself like this:
- The affected area of the skin contrasts sharply in color with he althy skin. It may be bluish, yellowish.
- Education aches, hurts.
- With minor damage, the skin cracks and bleeds.
- Sudden unexplained weight loss.

Diagnosis
To diagnose a disease is the prerogative of a qualified oncologist. First of all, the doctor collects an anamnesis - analyzes the patient's complaints, conducts a visual examination, palpates the formation in the thick of the hair.
To clarify the diagnosis, the patient is sent for laboratory diagnostics - a biopsy. This is taking a sample of the affected tissue. The pathology of cells is assessed, the stage of development of education.
Widely applicable alsohardware techniques:
- computed tomography;
- radioisotope diagnostic method;
- ultrasound;
- sonography;
- X-ray examination.

Therapy directions
After making a diagnosis, confirming the malignancy of the formation, the patient is prescribed one of the types of treatment:
- Radiation therapy. Helps remove squamous cell carcinoma. Usually, close-focus irradiation is used for these purposes. Satisfactory effect of the procedure - 97% of cases.
- Surgical removal. Today it is the most effective way to deal with skin neoplasms, as it allows you to completely eliminate them. This is the excision of pathologically altered matter, carried out under general anesthesia.
- Cryoprocedures. The neoplasm is frozen in liquid nitrogen. The field of such influence is destroyed. Effective for superficial tumors.
- Electrocoagulation. In this case, cancer cells are destroyed by applying an electric current to them.
Additionally, as well as preventive and remedial measures, the patient is prescribed the following:
- Vitamin therapy.
- Creating a proper balanced diet.
- Medication taking. In particular, funds that help restore immunity after treatment.
- Recommendations: keep out of direct sunlight, wear hats, use UV filter creams.

Hair loss due to cancer
We also note the fact that with a different form and localization of the disease, alopecia is possible. Why does hair fall out in cancer? It has nothing to do with the disease itself. Alopecia in this case will be a side effect of the treatment - chemotherapy. The patient is injected with highly toxic drugs that can destroy all rapidly multiplying cells in the body. This is exactly what cancers are.
However, cells of hair follicles, mucous membranes of the nasal, oral cavity, gastrointestinal tract, and hematopoietic system are also considered to be rapidly dividing. Accordingly, they also suffer from the effects of chemotherapy drugs. Therefore, with cancer, hair falls out, nails become brittle, a person may develop stomatitis, gastrointestinal diseases. But alopecia will accompany only a course of chemotherapy. As soon as the patient finishes the treatment, his hair after cancer begins to grow and recover.
And another popular question. Can you dye your hair if you have cancer? If the disease does not imply a course of chemotherapy, then such a change in appearance will not affect the patient's condition in any way. With the introduction of highly toxic antitumor drugs, it is better not to disturb the hair once again - wash it with a neutral gentle shampoo, comb it with a soft comb, do not resort to styling and coloring. Dyes and brighteners in themselves are a test for hair. And for those weakened by chemotherapy, they will have the most negative impact.
Even careful attitude, unfortunately, does not always allow you to save the old hairstyle. Hairfall out, thin out, become dull, brittle, dry. Therefore, patients undergoing chemotherapy prefer to have a short haircut or shave their hair altogether. For the recovery period, wigs are prepared, suitable headgear.
I must say that in 95% of cases, hair cancer (epidermis under the hairline) at the initial stage is cured completely. Only 3% of patients relapsed after a few years. Repeated treatment helped to prevent the return of the disease in 86% of cases. If therapy was started with a tumor in the active phase, characterized by rapid metastasis, then the proportion of completely recovered stopped at 25%. The probability of death is 5%.