- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
In medical practice, there are often cases when it is difficult to evaluate the effectiveness of hypoglycemic drugs and the adequacy of the prescribed treatment in patients with diabetes mellitus. It seems that the person feels satisfactory, and his fasting glucose is within the normal range, but what is the likelihood of complications in this patient? After all, the amount of glucose in the blood is estimated only at the time of the study, this indicator is single.

Sometimes an increase in blood glucose occurs in he althy people, for example, after taking a large amount of carbohydrates or with excessive mental and emotional stress. The intake of certain medications, such as oral contraceptives, some diuretics, psychotropic drugs, can also affect the sugar level. In all difficult cases, an analysis of glycated hemoglobin comes to the aid of the endocrinologist, in the direction for the study it is designated as HbA1c.
Glycated hemoglobin is a combination of glucose and hemoglobin A molecules, normally thisprocess occurs constantly in he althy people. The amount of hemoglobin undergoing glycation is 5-8%. In patients with diabetes, this indicator increases by 2-3 times and persists throughout the life of the erythrocyte, i.e. 120 days. Since both young and mature red cells are present in the blood, therefore, the average age of the erythrocyte is taken, which is equal to its half-life - 60 days.

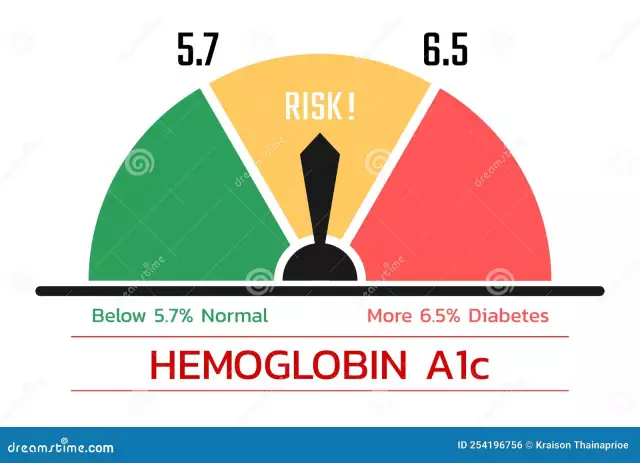
Glycated hemoglobin, the norm of which is 4-6.1% of the total hemoglobin level, shows the average glucose content for two months before the blood test. Therefore, it can be determined whether there was a long-term increase in glucose or within 2 months this indicator was in a normal state. The correlation between HbA1c and blood glucose has been proven by many years of research, it has been empirically established that an increase in blood glucose of 1.59 mmol / l corresponds to 1% glycated hemoglobin.
When is a glycated hemoglobin test prescribed?
- for diagnosing diabetes mellitus and identifying the level of its compensation;
- to control treatment with hypoglycemic drugs;
- to determine the risk of vascular complications in diabetes;
- in all cases of impaired glucose tolerance and diagnosis of prediabetes;
- pregnant women at risk of developing diabetes.
Interpretation of test results for diabetes:
Up to 5.8% - diabetes is well compensated.
From 8up to 10% - partially compensated diabetes.
More than 12% - poorly compensated disease.

Endocrinologists try to select therapy so that glycated hemoglobin is in the range of 7 to 8%. With adequate treatment, elevated HbA1c levels return to normal one month after the adjustment.
The American Diabetes Association recommends testing at least every 6 months. In Russia, an HbA1c test is prescribed for all patients receiving insulin and hypoglycemic drugs once every 3 months. By the level of hemoglobin HbA1c, one can judge whether the patient is likely to develop pathology of microvessels of the retina, kidneys and damage to nerve fibers.
In what cases are possible distortions of the analysis for HbA1c?
False increase in results is observed with an increase in the level of fetal hemoglobin in the blood and with iron deficiency anemia. A false decrease in indicators is detected when red blood cells are destroyed due to hemolysis, after a blood transfusion or massive blood loss.
Analysis for glycated hemoglobin is prescribed somewhat more often (1 time per month) to patients with a non-standard course of the disease, if they have severe concomitant pathology, to pregnant women with diabetes mellitus to prevent the development of pathology in the fetus.