- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Spirochete (not everyone knows what it is) is a bacterium, a single-celled organism that is pathogenic for humans, that is, capable of causing infectious diseases. The most dangerous type of microbe is Treponema pallidum, which is the causative agent of a sexually transmitted disease - syphilis.
Pale treponema (Treponema Pallidium) was discovered in 1905 by German scientists and microbiologists E. Hoffmann and F. Schaudin.

Features of the spirochete
The bacterium is gram-negative, that is, it does not stain with aniline dyes (methyl violet), but only decolorizes. This is due to the fact that the composition of the bacterial cell wall (shell) is stronger than that of gram-positive organisms. This makes the cell resistant to the action of antibacterial substances, whether it be drugs or contained in saliva and secretions from the nasal passages, lysozyme, an enzyme that can destroy viruses and bacteria.
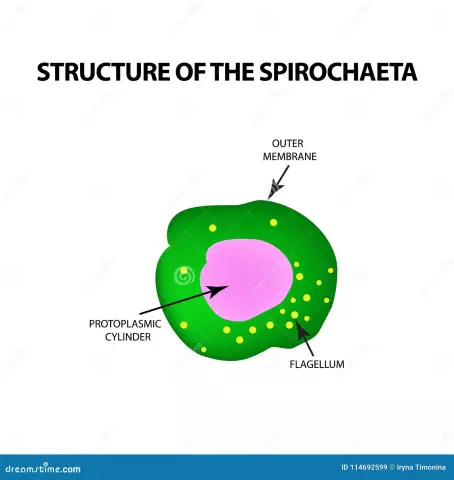
Spirochete pale differs from other bacteria in its length and unusual structure. These cells are twisted in a spiral. The length of the spirochete varies from 8 to 20 µm, whichmakes it different from other bacteria. It is quite mobile, contracting, it moves in a helical manner, bending like a snake. On average, a spirochete has about 10 whorls, similar in appearance to a wine corkscrew.
The cell has fibrils (flagellum-like elements) that allow it to move well, without touching slippery surfaces, to swim. Fibrils rotate, contract, provide movement.
The spirochete cell is covered with an outer membrane, under which there is a cell wall, a cytoplasmic membrane surrounding the protoplasmic cylinder and cytoplasm. The cylinder is covered with flagella, which, being inside the cell, provide its ability to bend and wriggle.
Spirochete pale is an anaerobe. That is, for life, it absolutely does not need oxygen, which makes it a habitat, for example, the human body. Its sources of energy for life are carbohydrates and amino acids.
But she has some peculiarity. The fact is that the spirochete can only reproduce at a temperature of 37 ° C by dividing once every 30 hours.

The causative agent of syphilis
Syphilis is a chronic disease that affects the mucous membranes, internal organs, bones, cartilage, nervous system and skin. Pale spirochete is a parasite, the causative agent of syphilis.
The transmission of the disease occurs mainly through sexual contact, but you can also get sick with close household contact (towels, bath accessories, razors, toothbrushes), with blood transfusions from a person infected with syphilisperson. Also, the fetus becomes infected from a sick mother.
The possibility of transmission of the pathogen through urine and saliva has not been proven, although if there are ulcers in the mouth, theoretically spirochetes can live there. But bacteria live perfectly in mother's breast milk, sperm.

Development of the disease and its periods
Within 3 weeks after the pale spirochete - the causative agent of syphilis, entered the body, the incubation period lasts, which is asymptomatic. It is followed by the primary period, then the secondary and tertiary.
The bacterium is able to secrete endotoxin, poisoning the blood and internal organs of the patient.
After the incubation period, a painless ulcer forms at the site of the introduction of the pathogen, after which the primary period begins, which lasts about 5-6 weeks. Lymph nodes become inflamed.
In the secondary period, the symptoms are numerous rashes of various forms on the palms and feet, the patient's nervous system, internal organs (kidneys, liver, heart) are affected.
The immune system tries to keep the spirochete from multiplying by providing a protective reaction in the form of antibodies, as a result of which the bacterium slows down reproduction. The sickness subsides for a while. But the body itself is not able to overcome all the foci of inflammation, so after a while the disease begins to progress again. This can continue for years, which indicates a chronic course of the disease.
The tertiary stage is characterized by the destruction of tissues and organs,the formation of syphilitic scars, the destruction of cartilage and bone tissue. If the patient does not receive treatment, then the infection leads to the destruction of body systems (damage to blood vessels, heart muscle, valves).

Syphilis during pregnancy
A woman who is not treated before 16 weeks of pregnancy is at risk of losing a fetus, losing a baby in childbirth, or becoming a mother of a baby with congenital syphilis. If children survive after childbirth, then in the first weeks of their life, symptoms of primary and secondary syphilis appear: rash, deformity of the nasal bones, deafness, forehead protrudes.

Adequate treatment
Spirochete pallidum has gradually acquired resistance to many types of antibiotics. It is not affected by conventional penicillins, macrolides. The bacterium can invade the cells lining the inner lining of blood vessels, making it inaccessible to drugs.
Treatment is with benzathine benzylpenicillin, which can be substituted with erythromycin or tetracycline.
Spirochete pallidum in primary or secondary syphilis is successfully eliminated with adequate treatment. The disease is considered cured in case of seronegativity and no symptoms for a year.
Tertiary syphilis is rare these days and develops without treatment. It is difficult to treat, the resulting violations are irreversible, lead to disability, even death.
Infection prevention
Now thatit became clear spirochete - what it is, what danger it poses, it is worth thinking about measures to prevent infection.
First and foremost, you should have a discriminating sex life using protective methods of contraception - condoms.
The use of shared syringes and containers for drug preparation by injecting drug addicts is a global problem that needs to be addressed at the state level. This can lead not only to the spread of syphilis, but also other dangerous diseases (HIV, hepatitis C).
Pregnant women, when registering, must undergo research to exclude the most dangerous disease for the fetus.
Compliance with moral principles, elementary rules of hygiene - these are the main actions that prevent pathogens of sexually transmitted diseases from entering the body. The culture of correct and adequate behavior should be developed from childhood, be an integral part of life in society.