- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Treponema pallidum is a very dangerous bacterium that causes syphilis. It rapidly penetrates the human body and multiplies in it at the same speed, while severely affecting the internal organs.
Description of bacteria
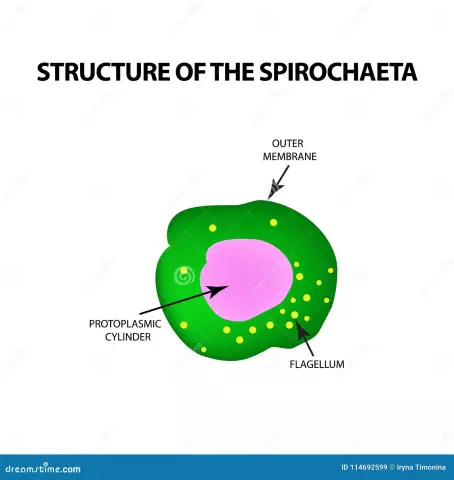
Treponema pallidum is a bacterium with a cell wall. Able to live for some time in the environment. This bacterium belongs to the spirochetes. It looks like a spiral with small curls, which can be from eight to twelve pieces. Just by their number and shape, this bacterium is determined when a smear microscopy is done.

This microorganism hardly stains with dyes that are used in microbiology. In order to see the bacteria, contrast microscopy is used. This is due to the fact that the shell of the microorganism is very thin and is quickly damaged under the influence of alcohol (and it is just used to fix the color). When a bacterium is silvered, it acquires a reddish-black color.
How long does a bacterium live
Treponema pallidum in contact with objects (mainly bed linen and towels) persists until the substrate dries, in whichshe was. Most often it is saliva, liquid secreted from ulcers and erosions, sperm, etc. At a temperature of fifty-five degrees, the bacterium can live for about fifteen minutes. At a higher one, it dies much faster. During boiling, the bacterium dies in seconds, that is, almost instantly.
What is detrimental to bacteria
For treponema pallidum, some environments and substances are detrimental:
- bismuth and arsenic;
- mercury;
- penicillin;
- alkalis and acids;
- antiseptics and disinfectant solutions;
- vinegar and alcohol;
- UV and light.

According to research and experiments conducted by scientists, it turned out that this bacterium can sometimes persist for some time and in unfavorable conditions for it. For example, in a bad environment, under light, in a dried state, or with access to oxygen. If such a specimen of a microorganism comes across, then it can live in an unfavorable environment for up to three years.
Treponema growth and major antigens
Treponema pallidum is poorly grown because of its capriciousness. Cells of chicken embryos and humans are not suitable for growing this microorganism. There are two ways in which culture can be distinguished. The first is to infect laboratory rabbits with the bacterium and wait for the development of specific orchitis in these animals. The second - treponema can be grown on special media under vaseline oil. The presence of these microorganisms is necessary to obtain antigens, which are used to determinesyphilis.

Pathogenicity of treponema pallidum
The pathogenicity of the bacterium Treponema pallidum has its own characteristics:
- due to the presence of the adhesin protein, which interacts with mucosal fibronectin, “sticking” to host cells is ensured;
- the presence of myofibrils and the spiral shape of treponema pallidum contribute to deep penetration and cause migration throughout the body;
- antiphagocytic activity occurs due to the ability of this bacterium to bind fibronectin;
- inflammation starts due to the presence of lipoprotein membranes;
- Treponema pallidum is resistant to antibacterial drugs due to the variability of antigenic properties and the ability to form L-forms, which makes it impossible to create a vaccine;
- these bacteria can not only live in the interstitium, but also multiply there.
Treponema pallidum antibodies
Pale treponemas are mainly collected on the mucous membranes. Therefore, they are easily transmitted not only during sexual intercourse, but also in everyday life. Most often through towels, dishes or kisses. Unfortunately, the human body cannot develop immunity to these bacteria. Therefore, even after a complete cure for syphilis, the disease may return again.
To determine the disease, blood is taken for syphilis. Most infected people have antibodies to treponema pallidum. In primary and recurrent disease - in 88 and 78% of patients, respectively. The rest of them either do not show up, orabsent at all. But the absence of antibodies does not mean that the treatment was successful. In the latent stage of the disease, antibodies are generally found in only 20 percent of patients.

After 1-2 weeks from the onset of the disease, a serum analysis is done. IgM and IgA antibodies to treponema pallidum appear in serum during this period. Over a period of six months to nine months, immunoglobulin titers grow, then a decrease in their number begins. After a while, the level of antibodies also falls below the determined values. Some cannot be passed from mother to child.
IgG antibodies appear 3-4 weeks after infection with syphilis. And by 6-9 weeks they reach their peak. A large concentration of antibodies persists for a long time and decreases very slowly and only after therapy. And the residual titer can remain in the body for life.
Treponemal antibodies can only be produced against treponema pallidum. Therefore, when they are found, it can be precisely stated that syphilis is currently present or has been transferred earlier.
Symptoms of Treponema pallidum infection
There are a number of symptoms indicating the presence of treponema pallidum in the human body. When they appear, it is necessary to donate blood for syphilis. Symptoms may vary depending on the stage of the disease.

On the first:
- painful ulcers appear with a hard chancre located on the mucous membrane of the mouth, rectum or genitals;
- increaselymph nodes;
- ulcers heal on their own after at least three weeks, the process can take up to six months.
On the second:
- a syphilitic symmetrical pale rash appears on the body;
- headaches, general malaise, fever;
- lymph nodes increase;
- sometimes hair can fall out, and wide warts appear on the genitals.
Third is defeated:
- nervous system;
- brain and spinal cord;
- internal organs;
- bones.
In the first and second stages, complex treatment is effective, including antibiotics, physiotherapy, immunostimulants and restorative drugs. But if you do not see a doctor in time, then in a few years the third stage of the disease begins, which can be almost impossible to cure.

How is Treponema pallidum detected?
To determine if there are bacteria that cause syphilis in the body, an appropriate analysis is done. Treponema pallidum by the efforts of modern medicine can be detected in several ways:
- In the first stage of syphilis, the patient is very contagious and releases a lot of bacteria into the outside world. In this case, smear microscopy is used. To get accurate results, ulcers are treated with saline to flush out interfering microflora. Then a scraping is performed and a smear is made.
- Non-treponemal tests. Screening methods are used here. They aregood for primary diagnosis and subsequent monitoring during treatment and medical examination. But these tests often give a false positive result. Treponema pallidum may be absent in the body. This is because antigens (antibodies to antigens) are not taken from the causative agent of the disease.
- Treponemal tests are used specifically to detect treponema pallidum. These methods are used to confirm the diagnosis and rule out syphilis in a false screening test.