- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Pets for many people are full members of the family. Dogs and cats are in daily contact with both adults and children. In the villages, almost every family can meet cattle, sheep or pigs. However, any of the pets can cause a dangerous infectious disease - foot and mouth disease. In humans, the disease is severe. In today's article, we will dwell in more detail on the main manifestations and methods of its treatment.
Medical certificate
FMD is an acute infectious pathology that occurs as a result of the penetration of a specific virus into the body. It has been known to science for more than 400 years, but the pathogen was identified only in 1897 by Frotem and Lefleur. Scientists noticed a similar clinical picture in humans and animals, so they became interested in the manifestations of the disease. In both cases it was marked:
- mouth ulcers;
- profuse salivation;
- skeletal muscle and myocardial damage;
- yanimals were also affected by areas of the body devoid of wool.

Infectious agent
The causative agent of foot-and-mouth disease in humans is a virus belonging to the genus Aphtoviruses. It can be safely attributed to the group of microorganisms that are extremely resistant to external factors. The virus cannot be eliminated by disinfectants, drying or freezing. It remains active in soil and water. Destruction occurs only under prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays or when heated with simultaneous treatment with alkali solutions.
Routes of infection
FMD chooses mainly artiodactyl domestic animals (goats, pigs, horses, sheep) as its target. Cases of transmission of the infection through human contact with cats, dogs, rabbits and rats have also been recorded. Outbreaks of the disease occur in the form of an epidemic. Individuals that have already recovered can become carriers of the virus again and transmit it to others.
FMD in people can be called an occupational disease. The chances of contracting it are especially high among workers employed in the agricultural sector and watching cattle. We are talking about veterinarians, milkmaids, cleaning people in pens.
There are several ways in which the virus can be transmitted from animal to human:
- airborne;
- direct (when caring for a sick animal and through abrasions or cuts on the skin);
- through objects contaminated with feces or saliva of sick individuals.
Infection can occur through consumptionraw milk or meat from unhe althy sheep or pigs. This type of infection is recognized as the most common and accounts for up to 65% of all cases.

Features of pathogenesis
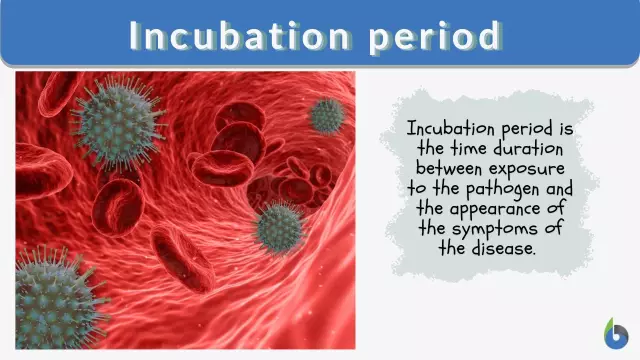
FMD virus enters the human body through mucous tissues or microtraumas on the skin. In the area of the entrance gate, an aphtha is formed - a small sore. The incubation period of foot and mouth disease in humans lasts from 2 to 6 days (in rare cases, this period is extended to 10 days). At the end of it, the virus enters the bloodstream and begins to spread throughout the body.
After a while, it again gets on the oral mucosa, as a result of which aphthae and vesicles appear on it. Cavity formations have a diameter of at least 5 cm and are filled with serous secretions. Vesicles can be found not only in the oral cavity, but also on the skin around the nail, between the fingers and toes.
Clinical picture
The onset of the disease is usually acute. Patients complain of chills. After about 3-4 hours, there is a sharp increase in temperature to 39 degrees. FMD symptoms in humans at this stage are also manifested by headache, decreased appetite, and muscle discomfort.
A little later, the clinical picture changes and is supplemented by the following disorders:
- burning sensation in the mouth;
- severe pain when chewing food;
- aphthous rashes on mucous membranes;
- signs of inflammation in the mouth;
- profuse salivation.
High temperatureusually persists for 5-6 days. When the initial manifestations of fever subside, a blood test shows an increase in the number of eosinophils.
FMD disease in an adult is tolerated quite easily. However, it is very difficult for a child's body to cope with it. Rashes on mucous membranes are much more abundant, and painful sensations are stronger. With a weakened immune system, the gastrointestinal tract is involved in the pathological process, which is accompanied by indigestion.

Diagnostic Methods
In humans, the symptoms of foot-and-mouth disease are difficult to confuse with manifestations of other pathologies. The disease has a pronounced clinical picture. On the other hand, the presence of erased forms of the disease and the similarity of its symptoms with other disorders somewhat complicates the diagnosis. For example, foot and mouth disease can be confused with chicken pox, erythema, and herpetic stomatitis. In any case, if you feel unwell, you should seek help from a doctor.
Diagnosis of the disease begins with the examination of the patient and the study of his anamnesis. The specialist can ask a number of clarifying questions to get a complete picture. For example, was there any contact with sick animals in the recent past, did the patient consume raw milk, in what area does he live, etc. Laboratory tests are additionally assigned:
- blood and stool tests;
- serological tests to detect antibodies to the pathogen in the blood.
If the preliminary diagnosis is confirmed, the patient is subject to mandatory hospitalization. In the specialized departmenthe must spend at least 2 weeks in the hospital under the supervision of doctors. Specific treatment of pathology is not provided. The standard course of therapy is aimed at stopping the first signs of foot and mouth disease in humans, preventing the development of complications.

Drug therapy
To normalize the patient's condition and relieve unpleasant symptoms, the following groups of medicines are used:
- Antiviral agents for topical use ("Bonafton", "Vivorax").
- Antiseptic sprays ("Miramistin", "Oracept"). They prevent the addition of a secondary infection.
- Antiviral medicines for internal use ("Acyclovir", "Kagocel", "Ingavirin"). Such drugs are used as part of complex therapy.
- Antihistamines ("Suprastin", "Tavegil"). These drugs are prescribed to prevent allergic reactions.
Additionally, symptomatic therapy can be prescribed, which includes taking antipyretic and analgesic drugs (Panadol, Nurofen). In the event of a bacterial infection, antibiotics are prescribed. For general strengthening purposes, vitamin complexes are used.

Physiotherapy
Various physiotherapy procedures help relieve inflammation and significantly accelerate the healing of affected areas. For example, laser shows excellent results. Treatment of foot and mouth disease in humans with its help is carried out only in a hospital. First on the sickareas, the doctor applies a solution of methylene blue, and then acts with a laser beam for 5 minutes. The standard course of treatment includes up to 10 procedures.
In humans, foot-and-mouth disease is always accompanied by lesions of the mucous membranes. To eliminate this disorder, aerosol therapy is used. Due to early electrification, drugs remain in tissues much longer. The drugs themselves enter the body in the form of aerosols.
Prognosis for recovery
In humans, foot-and-mouth disease has a favorable prognosis for recovery. With proper care and treatment, there are no traces on the skin from wounds. In medical practice, cases of severe pathological processes are also known. They usually occur in young children. Late diagnosis of the disease in patients of this category can lead to complications and even death.
Lack of timely hospitalization and neglect of prescribed therapy is fraught with negative consequences. Foot-and-mouth disease in humans can provoke inflammation of the heart muscle, lungs. In some cases, sepsis develops.
After the infection, the so-called type-specific immunity is formed in the patient. This is a natural immunity to the virus. Its duration depends on many factors, including the presence of antibodies in the body. Typically, this period is up to 1.5 years.

Prevention Methods
Prevention of FMD is reduced to the prevention of epidemiologicalsituations in agriculture. If symptoms of the disease appear in at least one animal, strict quarantine is introduced. This individual must be isolated and a complete disinfection of the premises. Care products, personnel overalls and all work equipment are also subject to processing. This issue is de alt with by a special sanitary service.
To prevent foot-and-mouth disease in people, it is necessary to strictly adhere to safety instructions when working on a farm. Wash your hands at the end of the day and wear protective clothing during working hours.

Since contamination usually occurs through dairy products, doctors strongly recommend that they be consumed only after proper heat treatment. Meat should be cooked with care. It must be well fried. After cooking, it is important to wash the dishes in which the food was cooked and hands thoroughly.