- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Medications that are taken directly from the blood itself are called blood products. The obtained fractions allow to significantly expand the boundaries of hemotherapy, and most importantly - make it possible to use specific components of blood and plasma, which have a targeted effect. Blood products are divided into three groups: complex action, immunoglobulins (immunologically active) and hemostatic.

Preparations of complex action. Plasma
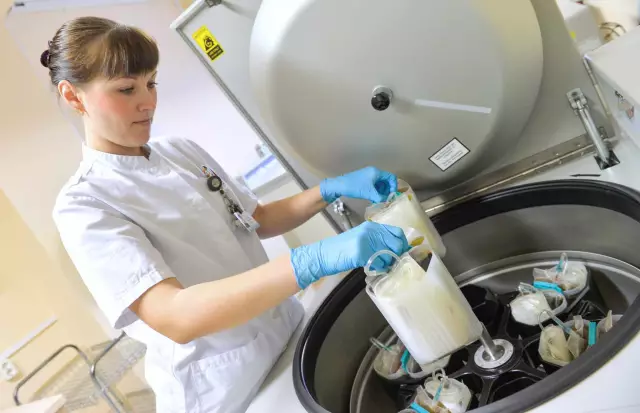
Preparations of complex action include blood plasma and albumin. Their effect is to provide both anti-shock and hemodynamic action. Fresh frozen plasma completely retains all functions, so its use is most appropriate. There are other types of plasma: dry (lyophilized) and liquid (native). In the manufacturing process, they significantly lose their medicinal properties, so their use is not as effective. Fresh frozen is obtained by plasmapheresis or whole blood centrifugation, freezing is performed from the moment blood is taken from the donor in the first 1-2 hours. Freshly frozen blood products can be stored for up to one year at temperatures from 1 to 25 degrees and below. During this period, all plasma coagulation factors, fibrinolysis components, anticoagulants are preserved.

Preparing for a plasma transfusion
The blood product is fresh frozen plasma. Before you start the transfusion, you need to prepare the drug. The plasma is thawed in warm water, the temperature of which is no more than 37-38 degrees. The plastic bag with biomaterial can be kneaded by hand to speed up the process. The thawed plasma must be transfused within the next hour according to the instructions provided. After preparation, fibrin flakes may appear in it, but this does not prevent it from being transfused through plastic standard systems that are equipped with filters.
Plasma should not be transfused if massive clots are found in it, significant turbidity is evidence that the drug is of poor quality. Do not refreeze and thaw fresh frozen plasma.
A human blood product should not be transfused from the same bag to multiple patients. Also, plasma should not be left for the subsequent procedure after the plastic bag has been depressurized. If the patient is sensitized to parenteral protein administration, it is contraindicatedtransfuse fresh frozen plasma. Biological samples are taken to avoid pathological reactions, just as in whole blood transfusions.
Transfusion
Fresh frozen plasma that is transfused to the patient must be taken from a person with the same blood type as the patient, according to the AB0 system. In emergency cases, if there is no one-group plasma, the following combinations are allowed:
- Plasma: group A(II) - patient: blood type 0(I)
- Plasma: group B(III) - patient: blood type 0(I)
- Plasma: group AB(IV) - patient: any blood type.
No group compatibility tests. Blood products (plasma transfusions) are indicated for:
- thrombotic hemorrhagic syndromes,
- burn diseases,
- purulent-septic processes,
- hemorrhagic diathesis: including hemophilia types A and B,
- prolonged compression syndromes,
- with massive blood loss (over 25%), plasma is combined with red blood cells during transfusion.
Fresh frozen plasma is also used to treat patients with recurrent thrombosis of blood vessels, more often against the background of the use of streptokinase or other fibrinolytic drugs.
Albumin
Blood medicines such as albumin are available in 5%, 10% and 20% solutions. The protein is also used along with purified albumin, while containing alpha and beta globulins. The albumin solution after the introduction of stabilizers into it is able to withstand pasteurization. BUTit helps inactivation of HIV and hepatitis viruses. Albumin is used for various types of shock - surgical, traumatic, burn. It is administered for edema, which is caused by disturbances in the protein composition of the blood, with a large loss of albumin in the liver (ascites, cirrhosis, burns). Albumin in concentrated solutions is used when it is necessary to limit the amount of fluid introduced into the body (for heart failure, cerebral edema).
5% concentration of a blood product (albumin) is used for blood loss when normalization of blood pressure is required. When introducing albumin with significant blood loss, it must be combined with the transfusion of erythrocyte masses. In pediatric practice, albumin is most often used in the form of a 10% solution.

Immunoglobulin
Blood drugs - immunoglobulins - make up a large group of immunological drugs. They actively work against infectious diseases. In clinical practice, gamma globulin is most often used. Specific drugs have high therapeutic effects, they are directed against tetanus, tick-borne encephalitis, influenza and other infectious diseases.
A highly sensitive immunoglobulin is used in the treatment of thrombocytopenic idiopathic purpura. Medicines of this group are administered intramuscularly. Purified immunoglobulins, which are administered intravenously, produce a greater effect. This is due to the fact that the protein immediately enters the bloodstream and does not go through the stagecleavage by tissue proteases.
Hemostatic drugs for blood diseases

Hemostatic drugs are fibrinogen, prothrombized complex, cryoprecipitate. The latter contains a large amount of antihemophilic globulin (otherwise - VIII coagulation factor) and von Willebrand factor, fibrinogen and fibrin-stabilizing factor XIII, as well as other protein impurities. These blood treatments are available in plastic bags, dried or frozen bottles. Used for von Willebrand disease, hemophilia A and other types of bleeding.
What blood products are used for hemorrhagic disease in newborns, hemophilia B, overdose of anticoagulants? In these cases, a prothrombized complex (CSF or PPSB) is used. If not available, fresh frozen plasma is administered.
Fibrinogen has a limited scope, it is used only for bleeding caused by fibrinogen deficiency. In cases of hypofibrinogenemia, which is due to thrombohemorrhagic syndrome, the colorless protein is replaced with fresh frozen plasma. Purified fibrinogen is not balanced with natural coagulants and can coagulate in the bloodstream, which can exacerbate kidney and lung failure. To make up for the deficiency of the mentioned component, it is better to use plasma.
Topically applied haemostatic agents
Thus, blood products are administered mainlyintravenously, although there is a group of hemostatic agents that are applied topically - to stop external bleeding that may occur during surgery. These agents include a hemostatic sponge, fibrin film, thrombin, an antiseptic biological swab, and others. Thrombin has a fundamental action. It causes the formation of clots that thrombose the lumens of blood vessels at the sites of bleeding. The use of hemostatic agents for hemostasis is very effective in case of damage to the surfaces of parenchymal organs.
Fibrin sponges and films due to their mechanical properties are used not only to stop bleeding. As a plastic material, they have found application in the treatment of trophic ulcers and burns. In neurosurgery, fibrin films are successfully used to replace the deficiency of the dura mater.
In addition to the above drugs, there are those that have stimulating and anti-anemic properties. These include the biostimulator "Polybiolin" and "Erigem".
Vascular disease
Pathological conditions of blood vessels occur in cases of loss of flexibility, when they become brittle or compacted due to the accumulation of toxins in them. The following diseases occur: migraine, atherosclerosis, which can provoke a stroke, vegetative-vascular dystonia. At any age, with loss of elasticity of blood vessels and their blockage, the patient experiences the following symptoms:
- deterioration of memory and mental activity;
- sleep disorder;
- depression development, deterioration in morale;
- numbness of limbs;
- chronic fatigue;
- frequent dizziness.
Also, spinal injuries and cervical osteochondrosis can also cause improper functioning of blood vessels. In this case, the vertebral artery, which feeds the brain, may be damaged. First you need to look for and eliminate the cause, that is, treat the spine, and then deal with the vessels: drugs only relieve painful symptoms for a while.
Preparations for blood vessels
Drugs for the treatment of blood vessels of the heart and brain are different, it all depends on the principle of action. Each has its own spectrum of purpose. The most popular group of drugs are drugs to improve cerebral circulation, vasodilation. Such medicines are divided into three groups:
- myotropic (relaxes smooth muscles) - this is "Dibazol", "Eufillin";
- neurotropic (effect on nerve cells) - this is "Reserpine", "Validol";
- nitrates (combination of two principles of action) - this is Nitrosorbitol, Nitroglycerin.

Depending on the effect and composition, several more groups are distinguished:
- Calcium blockers. Calcium ions, which make the vessels more fragile, hard and cause constriction. Basically, these drugs to improve cerebral circulation. In heart disease, they can not be used. Calcium blockers are classified into three generations. The first is based on three main components (nifedipine, verapamil, diltiazem). The second generation includes drugs "Klentiazem", "Tiapamil", "Nimodipine". And the third is represented by "Amlodipine", "Norvask". The advantages of the latter are that they have fewer side effects, act selectively and are prolonged.
- Plant based medicines. The main advantage is a minimum of contraindications and side effects. Relieve spasms. Improve blood flow.
- Preparations containing nicotinic acid help lower blood cholesterol, minimize the risk of plaque formation. Ineffective in relation to large vessels, affect small capillaries. These drugs should be taken only as prescribed by a doctor in complex therapy, as they have a bad effect on the liver (nicotinic acid, Enduratin).
- Heart drugs. Such drugs improve the nutrition of the brain and at the same time normalize the function of the cardiac coronary vessels. Produced on the basis of lily of the valley, foxglove, adonis ("Amrinon", "Cardiovalen", "Adonizide").
Other blood medicines
The blood sugar drug is an important component of drug therapy as part of a complex of measures that are carried out in the treatment of diabetes. Not all people are able to maintain normal blood glucose levels with a proper diet and exercise.

Sufferingdiabetics are forced to take medications prescribed by a doctor that lower blood sugar. The doctor describes in detail the course of treatment and the correct dosage. Antidiabetic drugs are divided into three groups:
- Drugs that activate the production of insulin by the pancreas.
- Medications that increase insulin sensitivity.
- Medications that reduce the absorption of carbohydrates.
The most popular are the drugs of the first group, which increase the production of insulin by the pancreas, which leads to a decrease in blood sugar levels. These include "Amarin", "Maninil", "Novonorm", "Diabeton". These medicines should only be prescribed by a doctor. Every body is different and people react differently. Some do not feel a therapeutic effect, blood sugar remains at the same level. In such cases, the doctor should review the treatment and prescribe other drugs or change dosages.

Iron preparations for blood. With a lack of iron in the blood, the required amount of hemoglobin cannot be formed, and this disrupts the process of transporting oxygen from the lungs to all tissues by red blood cells. Oxygen starvation sets in. The result of this is anemia. Modern blood-improving drugs used to treat anemia contain the necessary amount of iron, which can restore normal blood formation. With a mealit is impossible to achieve such a rapid effect. The medicinal dose of iron exceeds the possible absorption of the daily norm of ferrum by the body by 20 times. So attempts to replenish iron in a painful condition only with the help of useful products will not give the desired results. Need special drugs.
1. Means containing ferrous iron in the form of sulfate s alts containing vitamins that can improve the absorption and absorption of the desired substance. Most popular drugs:
- tablets "Tardiferron", "Sorbifer durules";
- capsules "Ferrofolgamma", "Ferretab", "Fenyuls";
- for children capsules, syrup, drops "Aktiferrin";
- combination in solution of iron gluconate, manganese and zinc - "Totem";
- Dragee "Hemofer";
- the well-known he althy delicacy "Hematogen".
2. Medicines that contain ferric iron. A feature of such drugs is the use of iron in the form of polym altose hydroxide:
- tablets "Ferrum Lek", "M altofer", "Biofer";
- syrup, solution, drops "Fenuls", "M altofer", "Ferlatum";
- Solutions for intramuscular administration "Ferrum Lek", "M altofer", "Argeferr", "Venofer", "Cosmofer".
Injections are used if the patient has diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, lesions of small vessels, as well as injectionsindicated for large blood loss. With the intravenous route of administration of the drug, manifestations of thrombophlebitis are possible.