- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
What can it mean when the tendon of the quadriceps femoris hurts?
Types of damage
Injuries to the tendons of the quadriceps femoris are divided into open (violation of their integrity due to injury by a variety of sharp objects) and ruptures under the skin, which, in turn, can be divided into direct and indirect according to the mechanism of their occurrence.
Depending on the time that has passed since such damage, fresh (up to six weeks) and chronic tears (more than six weeks) stand out.
Symptoms
Pain is noted along the front surface of the thigh and in the knee joint,instability of the injured limb, which, as it were, gives way as a result of the loss of the function of this thigh muscle. Active extension of the knee joint with such a pathology is impossible. When pressing with your fingers along the extensor apparatus, you can feel a drop below or above the patella (especially with strong tension in the quadriceps muscle).
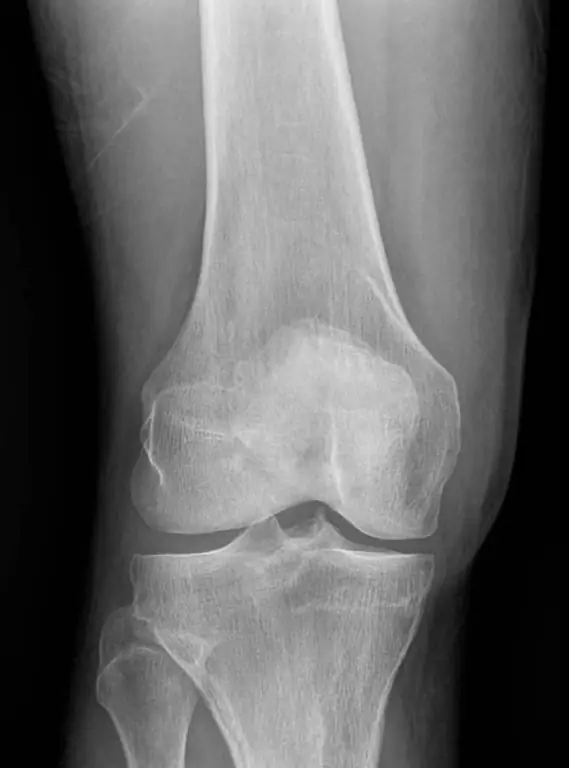
What can be seen on the x-ray?
On the radiograph of the knee joint, in case of violation of the integrity of the knee tendons of the quadriceps femoris, the patella is in its place or slightly shifts down, and in the case of a complete damage to the patellar ligament, it shifts significantly upwards.
Additional data that are needed to confirm this diagnosis can be obtained by ultrasound or MRI. These techniques allow you to track the course and integrity of the tendon fibers or ligaments along their length, and in case of damage, by changing the received signal, determine the location and depth of the rupture, the amount of diastasis between the tendon fibers or ligaments.
Tendinosis and tendonitis
Tendinosis or, as it is also called, tendonitis is a degenerative and dystrophic process that affects the tendon of the quadriceps femoris where they attach to the bones, although secondary inflammation can reach the muscles. The name of this pathology comes from tendo - "tendons". Theoretically, this disease can develop on any part of the body where there are tendons. However, most oftentendinitis of the tendon of the quadriceps femoris. Disease of the shoulder and hip joints may also occur
Reasons
The main cause of this ailment of the tendons of the quadriceps femoris is their excessive functional load. Due to the constant increased motor activity in any part of the body, which is associated with the type of professional occupation of people or with a passion for sports, microtraumas begin to develop in the tendons.
If the load on the limb is stopped during this period, then such injuries are healed quite quickly and without a trace, without causing the patient any particular inconvenience and pain.
However, in cases where damage to the tendon of the quadriceps femoris muscle is repeated regularly, the body does not have time to heal the injury, as a result of which an aseptic inflammatory process begins to develop in this place. Over time, there is a violation of the normal structure of the tendons, their degeneration develops, which gradually leads to the loss of the main qualities - strength and elasticity. As a result of the movement of a sore leg, a person is hurt. At the same time, the functions of the affected joint also suffer.
Risk group
High risk of tendinosis of the tendon of the quadriceps femoris have:
- people involved in heavy types of physical work (builders, movers);
- professional athletes (there are also some nosological forms of tendonitis, for example, "jumper's knee" and "elbowtennis player");
- people who, due to professional duties, systematically overload the joints (computer operators, turners, seamstresses, people working with various levers, wrenches and mechanisms);
In other situations, the main primary link in the pathogenesis of this disease can be an inflammatory process. It is in these cases that it is recommended to use the term "tendonitis", which indicates the main cause of the pathology - inflammatory disorders in the tendons. However, tendinosis also has an inflammatory nature, but it is already secondary.
Provoking factors
Tendinitis of the tendon of the quadriceps femoris can occur under the influence of the following diseases and conditions:
- inflammatory autoimmune pathologies (systemic connective tissue diseases, rheumatoid arthritis);
- infection of soft tissues near the joint;
- reactive arthritis (Reiter's syndrome);
- secondary changes in other pathologies of the musculoskeletal system (osteoarthritis, poor posture, flat feet, etc.).
- allergic reactions.

In order to effectively treat tendinitis/tendinosis, it is necessary to know what caused it, since the methods of treatment will differ significantly. For example, in the case of a bacterial infection, antibiotics are prescribed, in case of autoimmune disorders, anti-inflammatory and cytostatic drugs are prescribed, and in the case of professional stress, inFirst of all, it is necessary to eliminate provoking factors. Therefore, the study of the cause is extremely important in each individual case.
Symptoms of tendinosis (tendinitis)
The clinical signs of this pathology of the tendons of the quadriceps femoris are nonspecific, but they make it possible to suspect a problem. The most common patient complaints are:
- pain in the area of the diseased joint, which occurs with certain movements (it is important to remember that passive movements do not cause pain, unlike a violation of the structures of the joint itself);
- pain when probing the tendon;
- if the patient has ossifying tendinosis, a specific sound (crackling) may be noted during palpation and movements;
- outwardly, usually no pathological changes are observed, however, in the case of acute infectious processes, redness of the skin, its swelling and an increase in local temperature may appear;
- motion in the joint is preserved, however, with severe pain, a person can spare the limb and avoid excessive motor activity.
The constant, and in some cases, the only symptom of tendinosis may be pain during active movements with the involvement of a particular tendon. In addition, the patient may not complain about anything. Often such pain becomes a factor in the impossibility of professional activity.
Therapy of these pathologies
If the pathological process has become chronic,then the treatment of tendinosis / tendinitis is very long and complicated - from 4 to 6 weeks. Therapy begins with conservative methods:
- complete unloading of the affected leg and immobilization (elastic bandage, plaster bandage, orthosis, brace);
- drug therapy - injections, drugs from the NSAID group, glucocorticoids;
- antibacterial drugs are prescribed for infectious varieties of the disease;
- physiotherapy (laser therapy, shock wave therapy, ultrasound with hydrocortisone, magnetotherapy, electrophoresis, UHF, ozocerite and paraffin applications, etc.);
- rehabilitation exercise.
Calcification of the tendon of the quadriceps femoris
In the quadriceps muscle, ossifications and calcifications are sometimes found, the cause of which is still unclear. They cannot be associated with either progressive or traumatic myositis, or with other diseases and disorders of innervation. Such ossifications appear to be formed formations, with a distinct bone structure. The pathological process proceeds asymptomatically and is detected by X-ray examination, often by accident or by examination of palpable seals.
In medical practice, such calcifications and ossifications were found in the shoulder muscles and their tendons, in the tendons of the triceps muscle of the shoulder, piriform pelvis, thigh, in the nuchal ligament, at the lesser trochanter, at the top of the greater trochanter, etc. In a number of cases, ossification data should be classified as independent supernumerary bone elements. Massive lime deposits are less common.
Bone formation in the area of the quadriceps femoris also remains unknown in terms of pathogenesis and etiology. It belongs to the local form of myositis ossificans, and its occurrence is not associated with injuries or any other diseases.
When conducting an x-ray examination, bone formation in the muscles is determined from the knee joint to the buttocks, which appears in a branched dense form in the muscles passing from the femur, has the form of periosteum growth. The bone surface from which such bone formation originates is significantly deformed.
When ossification of the ligaments of the patella in the knee joints is determined by the symmetrical bilateral ossification of the ligaments of the patella, which developed independently. The reason for these ossifications remains unclear. By design and structure, they can be represented as skeletal variants. Similar asymptomatic findings are often found in the ulnar ligament, during examination of the cervical vertebrae and shoulder muscles, in the tendon of the triceps muscle, quadriceps femoris.
Quadriceps tears
Ruptures of the tendons of the quadriceps femoris can occur due to injuries, and may be spontaneous, without a specific cause. The rupture occurs, as a rule, at the place where the tendon is connected to the patella, or at the place where the muscles pass into the tendons. They can be complete, which require surgery and incomplete, which are treated.conservative.
The strength of knee extension is provided by the quadriceps muscle, which belongs to the anterior group of the femoral muscles. It consists of four muscle heads, which in the lower part merge with each other and form one common tendon that captures the patella. Below the patella, the tendons of the quadriceps femoris continue in the form of strong ligaments, which are attached to the tibia.
Injury to this muscle is considered one of the most common injuries. Almost 95% of sports injuries are sprains, bruises and muscle tears.
Types of injury
Quadriceps injuries are:
- direct, for example, a bruise as a result of a blow;
- indirect - due to excessive loading, in which, as a rule, the tendon itself is damaged at the place where it is attached to the bone, while only the abdomen of the muscles suffers with a bruise.
The quadriceps femoris gets bruised more often than any other human muscle.
Muscles work best when they are warm. However, an overheated muscle is more susceptible to injury. Therefore, in order to prevent sports injuries, it is important not only to perform warming exercises, but also to observe a relaxation regimen.

In an indirect injury, a rupture can occur, in which in most cases the wide intermedus femoris muscle is affected. Such ruptures most often occur after the age of 30, when tendons begin to occur.degenerative changes and there is less strength of the tendons, and the physical activity of a person is still quite high. A complete rupture of the tendons of the quadriceps leads to hemarthrosis (bleeding into the knee joint).
There are also bilateral tears - on both thighs. A similar phenomenon is possible when there are concomitant pathologies (diabetes mellitus, kidney disease, lupus erythematosus and other diseases that require steroid medications). In certain cases, rupture may occur spontaneously.
At rupture, severe pain occurs, and knee extension is difficult or impossible. Also, there may be a popping or clicking sensation at the moment of tearing.
Treatment of tendons of the quadriceps femoris
Incomplete rupture is successfully treated conservatively and medically. The leg is immobilized for 3-6 weeks. This is followed by rehabilitation exercises that restore the range of motion. On the first day after receiving a stretch of the tendons of the quadriceps femoris or any other injury, it is recommended to apply cold bandages to the localization site.
A complete tear requires surgery to reattach the tendon to the patella. The operation should be performed as soon as possible, since the muscle after a rupture can be significantly reduced and it will be impossible to restore its length.






