- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
The human body consists of many muscles, the weight of which is about 42% of the total mass. Their shape depends on what they have a working function and where they are located on the skeleton. Nutrients and oxygen are delivered to the muscles through the blood vessels. Due to the ability to contract, they form the elastic tissue of the entire human body, which has increased elasticity.

The muscle strength of various muscle groups, the total number of which is more than 400, depends on the intensity of physical activity. Strength exercises can change the shape and even function of muscles, contributing to their increase in volume and thickening. However, this process is not so fast.
Pectoral anatomy
History of mankind goes back thousands of years. Throughout time, a perfectly formed chest has been considered a symbol of courage. A large amount of muscle during training consumes a large number of calories. Therefore, pumping up muscles, youburn excess fat.
So, the pectoral muscles include: superficial, which go from the ribs to the shoulder and upper limbs, and deep, the location of which is the ribs. With their help, the respiratory process is carried out.
Superficial muscles:
- The pectoralis major is able to rotate the shoulder inward, expand the chest and act as an accessory inspiratory muscle.
- Pectoralis minor is responsible for pulling the scapula up and down, raising the ribs, assists with inhalation.
- The serratus anterior muscle pulls the scapula away from the spine.

Deep muscles:
- External intercostals lift the ribs, thereby expanding the chest. These are the main muscles of inspiration.
- Internal intercostals lower the ribs. These are the main muscles when exhaling.
- The diaphragm is the main respiratory muscle. By contracting, it flattens, promotes inhalation.
In order for the pectoral muscles, the photos of which are presented in the article, to look attractive, they need to be trained. There are many exercises for pumping up muscles.
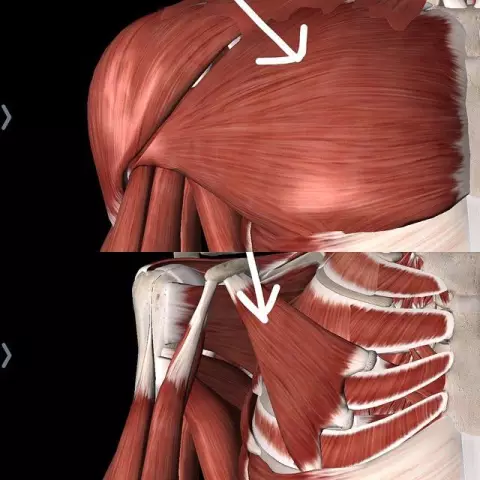
Pectoralis major
It is located on the surface of the chest, in front of it. It covers all the upper ribs. The function of the pectoralis major muscle is to form the anterior walls of the armpit. In shape, it resembles a fan, consists of muscle fibers that are collected in bundles, there are only three of them: clavicular, sternocostal and abdominal. They all join at the tubercle of the shoulder.
The main function of the pectoralis major muscle is the ability to bring the shoulder to the body and turn the arm inward, that is, to pronate. In addition, it is an auxiliary muscle of inhalation, thereby causing the chest to expand. The pectoralis major muscle occupies the entire space from the clavicle to the anterior surface of the sternum, originating from the crest of the large tubercle of the humerus. The arteries and the acromial process of the chest are responsible for the blood supply to the pectoralis major muscle.

The appearance of the upper body, namely its front surface, depends on the shape of the pectoralis major muscle. The peculiarity of the structure of this muscle lies in the location of the lower bundles of fibers: they are located below and behind in relation to the upper and middle bundles, they are attached to the bones of the shoulder above the upper ones. Thanks to this structure, there is a uniform stretching and untwisting of all bundles of muscle fibers. This is well expressed when a person raises his hands up.
Pectoralis minor
It is located under the large muscle of the chest, originates from 2-5 ribs and reaches the beak-shaped process of the scapula, to which it is attached. It has a fan-shaped shape and performs functions similar to the pectoralis major muscle. But its main role is to move the scapula forward and down and rotate it with its lower angle towards the spine. If the scapula is fixed, the muscle will raise the ribs and help expand the chest cells when inhaling.
Workout Features

To stimulate the growth of the pectoral muscles, it is not necessary to pump them every workout. The fact is that if you constantly overload the pectoral muscles, you can not expect good results. For training, it is enough to allocate twice a week and perform 4-8 approaches, and for beginners, 2-3 are enough. To increase the mass of the chest, 10-12 repetitions are enough. The chest gains strength if the number of repetitions is 6-8 times.
Exercises to train the muscles of the lower chest
Dumbbell bench press, lying on your back. To perform the exercise, prepare dumbbells. The lower part of the pectoral muscles is well worked out when performing the following exercise. You need to lie on the bench for the press (it has a back inclined function). Then squeeze and simultaneously lower both dumbbells. If you are training for the first time, the inventory should be small.

The specifics of the exercise is such that the posture when doing the bench press will seem unusual (especially for beginners), the dumbbells may initially fall back. Don't let that scare you, over time you will adapt and work accurately with dumbbells. When performing the exercise, turn your elbows so that they are on both sides of the torso.
The lower part of the pectoral muscles is pumped up during the exercise on the uneven bars. More often collapsible inventory is used. The frequency of classes should be at least 2-3 times a week. You can complicate the exercise by stopping the lower part of the spin for 2-3 seconds. Do 3-4 sets of 15 reps each.
Upper Chest Exercises
Thismost problematic area. To build muscle, you need special equipment; without it, all efforts are in vain. But if you systematically perform one exercise, even if you do not have the opportunity to visit the training room, you can get good results. These are push-ups from the floor when the legs are above the head. The exercise can be successfully performed at home.

Very quickly, the upper part of the pectoral muscles will acquire a relief shape, if you complicate the load, only gradually. This can be done with short pauses at the lowest spin point or with the use of some objects. You can put two stacks of books of the same height on the floor so that the distance between them is wider than your shoulders, and slowly push up. Hands should rest on the piles, and the chest should touch the floor. You need to perform 15-20 push-ups in 3-4 sets.
To pump up the upper part of the pectoral muscles, the so-called explosive push-up helps well, when, while extending the arms, you need to tear them off the floor in order to make a clap.
The most difficult thing is to combine the techniques of the previous exercises. But first you need to master them and learn how to easily perform them.
Barbell muscle training
Exercise on a bench at an incline of no more than 30 degrees using a barbell is considered the most effective if the goal is to work out the muscles of the chest array. You need to lie on a bench and raise your legs, making an emphasis, but so that there is no bridge.
In this position, the back is pressed tightly against the bench. You need to take the bargrip wider than shoulders. In this exercise, it is very important not to touch the chest with the bar at the bottom point, and at the top - do not fully straighten your arms.
Building chest muscle mass

Exercise can be done at home. For this you will need dumbbells. You need to lie on your back on a bench without tilting, raise the dumbbells above you, without bending your arms, palms facing each other. Then lower the dumbbells in different directions. Try to make it as low as possible and you will feel your muscles stretch to the limit.
So that the joints of the elbows do not experience a lot of stress, they can be slightly bent. Then lift the dumbbells up again with the feeling that you want to hug someone tightly. The chest muscles will contract.
Large chest muscles
In the back of the chest, in the lower part, is the latissimus dorsi muscle, which completely covers it. It originates from the six thoracic inferior processes, which are often referred to as the “broad pectoral muscles.”
Part of the muscle fibers originate from the angle of the scapula. In its lower part, they are collected and sent to the axillary fossa, without losing contact with the round muscle. This forms the back wall of the armpit. Then the fibers of the latissimus dorsi, passing a certain path, form tendons.