- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
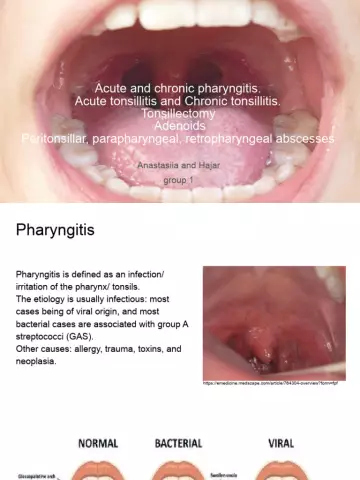
Chronic pharyngitis can develop as an independent disease, but most often it is the development of an untreated acute form of the disease. In the general case, this pathology is understood as an inflammatory process that affects the lymph nodes of the pharynx and its mucous membranes. It belongs to one of the most common ENT diseases. The most frequent occurrence is observed in children.
Classification of pharyngitis
There are two types of this disease:
- spicy;
- chronic pharyngitis.
The first type can develop as a result of exposure to irritating substances, dust entering the respiratory tract, overheating or, conversely, hypothermia, microbes or fungi. It is divided into several varieties:
- traumatic;
- allergic;
- fungal;
- bacterial;
- viral;
- caused by the influence of various factors: irradiation, hot steam, chemicals, boiling water.
In the chronic form, the following varieties are distinguished:
- hypertrophic;
- atrophic;
- catarrhal (simple).
During the course of the disease, various forms can be combined, in this case they speak of mixed pharyngitis.
Reasons
Chronic pharyngitis in adults and children is mainly due to frequent and (or) undertreated acute forms of the disease.

The main reasons for this process are as follows:
- work in positions associated with high voice loads (teachers, announcers, singers);
- employment in hazardous industries;
- reception of very hot or cold, as well as spicy food, inhalation of superheated or supercooled air, dust;
- long-term medication with certain drugs, inhalation of chemical fumes, gastroesophageal reflux;
- stressful situations over a long period of time, beriberi;
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract: gastroesophageal disease, cholecystitis, atrophic gastritis, pancreatitis;
- endocrine diseases and hormonal disorders;
- cardiac, pulmonary, renal failure, diabetes mellitus;
- smoking, including its active and passive forms;
- colds that periodically occur in the body, leading to a drop in immunity.
Chronic pharyngitis in ICD
In our country, the ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases of the Tenth Revision) was introduced in 1999 as a regulatory document for accounting for morbidity, reasons for citizens to apply tomedical facilities and causes of death. It contains all possible pathologies of various organs. Chronic pharyngitis was no exception. In ICD-10, it belongs to the X class "Diseases of the respiratory system", section "Other diseases of the upper respiratory tract", it is assigned the code J31.2.
Symptoms of the disease
Often they are similar in different forms. The main symptoms of chronic pharyngitis in adults are:
- slight increase in temperature may or may not be observed;
- fatigue;
- dry and obsessive cough;
- slightly enlarged lymph nodes in front, pain on palpation;
- discomfort may radiate to the ear;
- feels lumpy and itchy when swallowing;
- dry throat.
The third and last two signs are almost always present in chronic pharyngitis.

When it occurs against the background of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, heartburn and abdominal pain can be felt. Thus, the symptoms of chronic pharyngitis and treatment in adults should be linked depending on the associated pathologies. This disease has similar symptoms to some other colds. So, chronic tonsillitis and pharyngitis differ from each other in that during the first ailment, there is a dynamics in the paired tonsils of the palate, and it can be the cause of infection for the development of the last disease.
The concept of the granulosa variety of the disease
With the development of this disease on the back of the throatgranules are formed, which include particles of lymphoid tissue and dead bacteria resembling nodules. It is characterized by constant tickling or burning, and pressure pain is felt when swallowing.
Chronic granulosa pharyngitis can occur in those citizens whose relatives have been exposed to adverse factors. In addition to the causes listed above, characteristic of all forms of this disease, this form may occur due to carious formations, abnormal structure of the nasal cavity, curvature of the nasal septum.
In this disease, pus flows down the throat wall. If the patient develops a cough, then attacks of nausea and vomiting may follow. The mucous secretions dry out, crusts form in the throat. There is a feeling of a foreign object in the throat.
Atrophic and subatrophic varieties of the disease
In the first form, bloody crusts gradually appear on the nasopharyngeal mucosa. They turn pale, thin, become dry. The surface of the throat may become covered with dried mucus.
In the hypertrophic form, swelling of the mucous membranes is observed, foci of hyperplastic lymphoid tissue are formed on the back of the pharynx, hyperemia is noted.
With subatrophic pharyngitis, tickling and a feeling of a lump in the throat, dryness are noted. Coughing does not occur, sputum does not stand out, there is a dry cough. The wall of the pharynx accumulates mucus, crusts appear, and an unpleasant odor comes from the oral cavity. The cough is irritating and causes insomnia.
Diagnosis

It is carried out when the patient consults a doctor. In the presence of a pathogen, the latter is detected from a smear submitted for bacterial culture. A complete blood count is also performed to detect bacterial culture. In case of complications after chronic granulosa pharyngitis, laryngoscopy is additionally prescribed.
Examination of the throat by an otolaryngologist is carried out using a pharyngoscope with optimal lighting.
If necessary, endoscopic examination of the larynx and pharynx, tomography of these organs can be performed.
Treatments
In order to understand how to treat chronic pharyngitis, you need to establish the causes that caused the appearance of this disease. If the pathology proceeds in uncomplicated forms, then antibiotic therapy is not resorted to.
In this case, they resort to symptomatic treatment, which includes steam inhalations, diet, hot drinks, warming the throat, rinsing. The latter can be performed with antiseptic solutions. At the time of treatment, you must completely stop smoking.
Thus, the symptoms and treatment of chronic pharyngitis in adults are interrelated.
Taking antibiotics
If a pathogenic microflora is identified as the cause, the doctor prescribes these drugs.
In addition to the main active substance that is part of the drug, the antibiotic includes essential oils and anesthetics to eliminate pain.
For pharyngitis, the following are prescribedmedicines of this series:

"Octenisept". With its help, they fight not only bacteria, but also herpes viruses, fungi and chlamydia. The release form is an aerosol, the action occurs 1 minute after application and lasts for one hour. The drug is safe, does not have a toxic effect on the body.
"Bioparox" is a brand name of the medicinal substance fusafungin. It has anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial activity. It is mainly used for acute pharyngitis in the form of an aerosol.
"Geksoral". Released in the form of a solution or spray. Has broad antimicrobial and antifungal activity. Also provides deodorization, anesthesia, enveloping. Has an antiseptic effect.
Other drugs for drug therapy
When figuring out how to cure chronic pharyngitis, antibiotics alone may not be enough.

In this case, the following means are used:
- "Strepsils".
- "Septolete".
- "Pharingosept". These three items refer to lozenges and lozenges for sucking - they are mainly prescribed for mild forms of the disease.
- "Iodinol".
- "Imudon".
- "Ambassador".
- "Hexaspray".
- "Ingalipt"
- "Kameton".
Some of these drugs can cause allergies, sotheir use is limited.
Some drugs like Sebidine, Drill find narrow use because they contain chlorhexidine which is toxic.
In addition, the throat can be gargled using furacilin or a weak solution of potassium permanganate.
Using traditional medicine
When determining how to treat chronic pharyngitis, you can use not only traditional medicine medications. Not bad can help in combination with the latter and decoctions of medicinal herbs with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effects, warming the throat, thermal inhalations, large volumes of warm liquid taken.
You can also do herbal baths in which essential oils are added. To alleviate the condition, every 3 hours you can chew a clove (2 buds each) or gargle with a s alty warm solution, 1 tsp. s alt in 500 ml of water.
Infusions for inhalation are prepared from the following plants:
- sage;
- plantain;
- chamomile;
- calendula;
- lavender;
- lime blossom;
- peppermint;
- yarrow.

To prepare an infusion, 10 g of dry herb is poured into 200 ml of boiling water, after which it is infused for 1 hour, filtered, 30 ml of water is added for inhalation.
The back wall of the throat in chronic pharyngitis can be treated with a composition on a daily basis, having the following components: 1 part of 10% alcohol infusion of propolis and 2 partsglycerin and peach oil.
To relieve the symptoms of inflammation, take 10 g of Chinese magnolia vine, 5 g of mint and string, pour 200 ml of water and boil for 3 minutes on low heat. This composition is infused for an hour, after which it is filtered and taken 50 ml in a warm form. Honey can be added to improve taste.
Camomile tea also has an anti-inflammatory effect. In addition, it helps soften fabrics. It is prepared as follows: for 1 tsp. crushed leaves of the plant take 200 ml of boiling water, pour the phytomass, infuse, filter and either drink it warm or use it as a rinse.
An infusion prepared from equal parts of sage leaves, currants and chamomile inflorescences has a similar effect. 10 g of this mixture is poured with one glass of water, boiled for 5 minutes and infused for one hour. It is consumed warm at night, adding 3 drops of fir oil.
To mitigate irritation and eliminate coughing attacks, prepare a decoction of hop cones, lemon balm leaves, sage, oregano, St. John's wort, which are taken in equal proportions. At night, 2 tbsp fall asleep in a thermos. of this collection, pour 500 ml of boiling water, cover with a lid and leave to infuse throughout the night. In the morning, filter and drink a third of a glass several times a day or gargle with this infusion.
Prevention

You need to give up such a bad habit as smoking. If possible, avoid the influence of irritating and harmful factors on the body,stick to a proper diet, strengthen immunity.
It is necessary to correct dental problems in time.
Excessive dryness in the room during the heating season should be eliminated with humidifiers.
In the presence of such a disease as gastroesophageal reflux, it is necessary to raise the head of the bed during sleep, which will prevent the acidic contents of the stomach from entering the esophagus and eliminate irritation of the pharyngeal mucosa.
In closing
Chronic pharyngitis can occur as an independent disease with frequently occurring acute forms or be a continuation of an untreated disease. Unlike the latter, fever is rarely observed with the pathology under consideration. A form such as chronic granulosa pharyngitis can be inherited, as well as in the presence of dental problems. Antibiotics, antiseptics, lozenges and lozenges for resorption in mild forms, as well as herbal remedies can be used as treatment.