- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
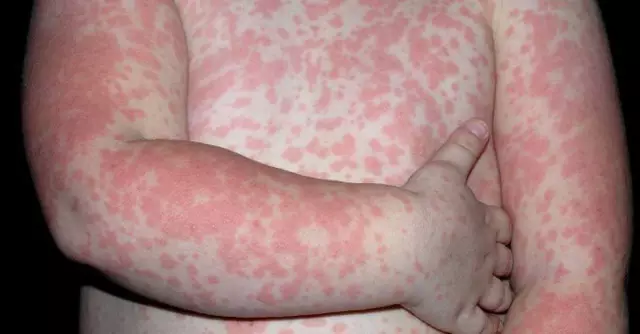
Runny nose, wheezing, tearing, itching, difficulty in breathing are the most common symptoms of an allergy to poplar fluff. Such hypersensitivity, which is a consequence of the struggle of antigens with antibodies, affects about 15% of the world's population every spring. Poplar fluff allergy symptoms occur when the body overreacts to invading foreign particles such as pollen and fine dust.

Poplar fluff itself is extremely rarely a pathogenic factor in various allergic reactions, since it consists of fairly large particles. In the vast majority of cases, the pollen and spores of various plants carried by them play a pathogenic role. When such small elements are inhaled into the body, they immediately attach to certain cells, thereby triggering the release of antibodies, including histamine. This is what causes allergy symptoms.poplar fluff, as irritation of the mucous membrane, shortness of breath, signs of conjunctivitis, headache, urticaria, general malaise and many others.
The most common type of allergic reaction in this case is one that triggers the production of specific antibodies (lgE). Once formed in the body, these antibodies continue to circulate in the blood until they join special membrane proteins of mast cells of the skin, eyes, nasal apparatus and lungs. Such cells are covered with granules containing potent biologically active compounds. The next time foreign particles enter the body again, they cause a degranulation reaction, which means the release of the substances contained there. That is why down allergy is periodic, cyclical.

In addition, some substances, such as histamine, released by cells in response to exposure to foreign agents, cause many more severe effects. The accumulation of fluid in the tissues, smooth muscle spasms, cardiac arrhythmia are also symptoms of an allergy to poplar fluff. But such hypersensitivity is not a frequent phenomenon, and it depends primarily on the individual physiological characteristics of the organism and the person's genetic predisposition.
Inhalation allergy, the prevention of which is the most important and most effective method of dealing with it, is the most common among all types of such reactions. It is impossible to get rid of it completely. Allergyon fine particles of poplar fluff can persist throughout life, and its symptoms become more pronounced and acute. The only encouraging thing is that in quite rare cases, the immune system becomes less sensitive to the effects of foreign agents over time.
Thus, although there are many methods of therapy and a lot of drugs for the treatment of allergic manifestations, they cannot give a stable, reliable and long-term clinical effect. Therefore, the most realistic way to deal with such an ailment is its prevention. The most effective method in this case is avoiding direct contact with the allergen. However, this type of inhalation allergy is not always successful.

But certain measures still need to be taken. First, you should do wet cleaning at home as often as possible. Secondly, it is desirable to open windows less often in the room where you are. You can also hang gauze moistened with water or a fine-mesh mosquito net on the windows. And most importantly, carry a low-dose corticosteroid nasal spray with you at all times.
As for the therapeutic methods themselves, they are usually aimed at alleviating various symptoms and preventing possible further reactions. Today, there is an extremely wide range of antihistamines that block the production of this substance. Steroid drugs inhibit the development of immune reactions, which makes them irreplaceable in the prevention and reduction of the severity of manifestations.allergic asthma. In addition, corticosteroid transdermal ointments are very effective for treating skin reactions.
At the first symptoms of anaphylactic shock, the patient should be injected with adrenaline. In addition, in the process of desensitizing therapy, the patient is given an allergen in small doses for a certain period of time. Although at present such a clinical method is rarely used and only in exceptional cases due to the long duration of the process and the likely severe complications, which include anaphylaxis, which carries an immediate threat to life. In any case, self-medication should not be done. Only a qualified allergist can prescribe the correct and effective course of treatment.