- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
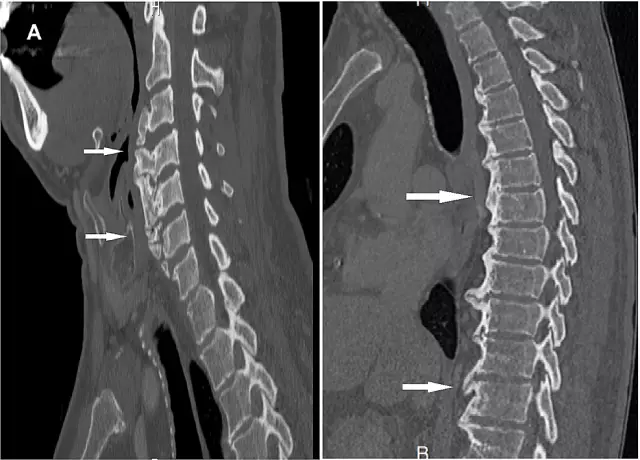
Osteophytes of the spine are pathological bone growths. They look like sharp spikes or small elevations. Most often, these growths are formed in the cervical, less often in the thoracic and lumbar spine. Sometimes osteophytes provoke the fusion of bone tissue. A large number of such growths causes a serious disease - spondylosis.
Causes of osteophytes

Unfortunately, osteophytes of the spine are not such a rare occurrence. Basically, spondylosis is detected in people over 45 years of age. The reason for its development, as a rule, lies in metabolic disorders. As a result, the body accumulates a mass of excess lime s alts, which are deposited on the vertebrae.
Also, the cause of the development of osteophytes can be long-term hard physical labor. According to statistics, men suffer from spondylosis almost twice as often as women. In young people, the appearance of growths may be associated with a curvature of the spine. There may be other reasons for the development of thispathology. So, most often lead to the appearance of osteophytes:
- spinal injuries of varying severity;
- regular spinal overload;
- serious violations of metabolic processes in the body;
- old age.
Most often, spondylosis affects only one specific area of the spine: cervical, thoracic or lumbar.
Symptoms of development of osteophytes on the vertebrae

It is natural that such a pathology as spinal osteophytes cannot go unnoticed by a person. She will certainly let you know. The very first symptom of spondylosis can be considered the appearance of moderate, and then severe pain in the affected area. In this case, a partial restriction of mobility will occur, which will interfere, for example, during the rotation of the neck or lower back.
But these are only visible symptoms. In fact, osteophytes cause much more complex disorders in the body. They can provoke:
- decreased sensitivity of nerve endings;
- circulatory disorders;
- frequent dizziness;
- partial numbness of the limbs.
Diagnosis of spondylosis

Diagnosing such a serious disease as spondylosis should only be done by specialists. If in the initial stages it is quite difficult to detect developing growths, then an already progressive pathology is easy to notice on an x-ray. On theit determines the presence and configuration of the lumens of the intervertebral spaces and, of course, the presence or absence of the osteophytes themselves.
The most commonly diagnosed cervical spondylosis. Other forms are less common. As a rule, osteophytes of the cervical spine in humans cause headaches and dizziness, which is associated with pinched spinal nerves.
Spondylosis, localized in the lumbosacral region, is much easier to detect. Its symptoms are stiffness of movements and severe pain, especially during turns and tilts of the torso. These unpleasant sensations occur in the lower back, since in this area of \u200b\u200bthe spine there are joints of moving and fixed parts. Fusion in these places of bone tissue and causes stiffness.
Osteophytes of the thoracic spine are diagnosed even less frequently. Their symptoms are less pronounced. This is usually pain in the upper part of the spinal column.
Traditional treatment of spondylosis

Spondylosis is a very dangerous disease, as it gives frequent complications and can progress rapidly. In addition, it is quite difficult to diagnose it in the early stages. Spinal osteophytes are treated by wearing an orthopedic corset (or collar). But the late stages of this disease are practically not amenable to conservative treatment. In such cases, surgical intervention is necessary. Problems with overgrown osteophytes can be solved in the following ways:
1. Facectomy -complete removal of the facet joint, on which the growth is localized.
2. Foraminotomy - a small increase in the space between two vertebrae to reduce pressure on the nerves.
3. Laminectomy - partial, less often complete removal of the plate.
4. Laminotomy is a small opening in the bone plate that protects the spinal canal.
Possible complications of surgery
Of course, any surgery associated with the spine is always associated with the risks of developing the following complications:
- infection;
- damage to the integrity of the spinal cord;
- further spinal instability;
- difficult urination;
- the appearance of pain in the legs and spinal column.
In addition, the operation cannot guarantee a further full recovery. Spondylosis often relapses, so the chances of getting rid of osteophytes forever are small.
Osteophytes of the spine - treatment with folk remedies

In combination with traditional treatment, it is very useful to use time-tested folk remedies. These are infusions and decoctions of various herbs. There are many such recipes, they can help reduce pain.
The most popular are decoction of hawthorn flowers and elderberry tincture. These traditional medicines were used by our grandmothers for the treatment of back diseases. A decoction of hawthorn flowers is prepared in the following way. For 500 ml of hot water is taken3 tablespoons of dried flowers of the plant. Everything is thoroughly mixed and infused for at least 1 hour. You need to drink half an hour before meals, 50 ml. Elderberry tincture is prepared a little differently. A tablespoon of grass is taken and 250 ml of boiling water is poured. Then the infusion is simmered for another 10 minutes in a water bath. Take 100 ml four times a day.
Osteophytes of the cervical spine: treatment

The most frequently diagnosed form of the disease is cervical spondylosis. With this pathology, complex treatment is recommended. It includes regular intake of medications, as well as certain procedures. Traditional treatment consists of the use of anti-inflammatory and painkillers. They help relieve pain and spasms. The intake of B vitamins is also recommended. To stimulate the production of cartilage tissue in the body, nicotinic acid is needed.
Don't forget about minerals. To reduce muscle tension, you need magnesium, calcium and phosphorus. Osteophytes of the cervical spine can disrupt blood circulation. Warming ointments are used to avoid this problem.
Prevention of spondylosis
To prevent the development of spondylosis, it is necessary, first of all, to maintain an active lifestyle. It will also be useful to follow a number of rules. Firstly, if your work activity involves many hours of sitting in an office chair, then you need to develop the habit of doing a little exercise at least once every two hours. Stretch your neck, chest and lower back muscles. It will take no more than 5-10 minutes. Second, watch your posture. Thirdly, normalize your diet. The menu should certainly include dishes rich in vitamins and minerals. Osteophytes of the lumbar spine are often found in overweight people. So try to avoid overeating. And the last thing: once every three months, take a massage course - this is perhaps the most powerful preventive measure.