- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2024-01-17 01:02.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
The nervous system is the most important of all systems in the body, because it is involved in coordinating the activities of all organs, shaping a person's mood, and regulating his well-being. Without the nervous system, neither emotional, nor mental, nor physical activity is possible.
Scheme of the nervous system
Given the global role of the nervous system in the body, it is important to understand that it can be classified according to its structure and activity. For general development and a better understanding of the work of your body, it is important to know which departments of the system exist and what functions they perform.
In order to have a general idea of what the scheme of the nervous system looks like, it is necessary to study the picture. After that, you can begin to consider each item of the classification in more detail.
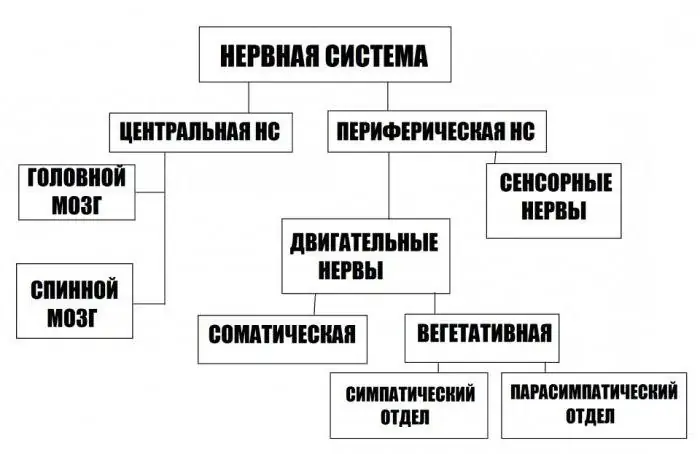
Organs of the nervous system
Classification of the nervous system is, first of all, its physical structure. It consists of:
- brain;
- spinal cord;
- nerves;
- ganglia and nerve endings.
The brain is the most important organ thatdeals with the regulation of the activity of all organs, and in which stimuli (commands) are formed that are sent to the cells of internal organs and muscles.
The brain consists of several sections, each of which is "responsible" for certain functions.
| Part of the brain | Main Functions |
| Medulla oblongata and pons | Deciding to launch reactions that regulate the most important life functions: breathing, the work of the heart and blood vessels, the process of digestion and wakefulness. |
| Cerebellum | Automation of movements: maintaining balance, movement in space, arbitrary movements (for example, writing). |
| Midbrain | Reaction to stimuli, attention to what is happening. |
| Diencephalon | Regulation of the endocrine system, "filtering" signals to the brain. |
| Cerebral cortex | Smell, short-term memory, speech, thought process, will and initiative. |
The brain actively exchanges signals with the spinal cord, which is located along the entire length of the spine, consisting of 31 fragments - vertebrae. The spine consists of four sections, each of which controls a certain "floor" of the body:
- cervical: neck, arms and diaphragm;
- chest: organsperitoneum and chest;
- lumbar: legs;
- sacracoccygeal: pelvis.
Thus, the signal of the nervous system from the brain enters the corresponding section of the spinal cord, and from there - to the necessary organs, cells, tissues. And the path from the spinal cord to specific nerve endings lies along the nerves, or, to be more precise, along the axons of neurons in the form of short electrical impulses.
CNS and PNS
Knowing what organs the scheme of the nervous system consists of, it is possible to consider its primary division: into central and peripheral. The first organs are the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system includes motor and sensory nerves.
The activities of both systems are closely interconnected, they cannot exist independently. However, they have a number of distinct differences.
Central nervous system
The CNS is considered the main part of the human nervous system. It is responsible for the formation and implementation of reflexes, both simple and complex. The ability to these processes allows you to save energy inside the body. This made a significant contribution to the development of the nervous system. From an evolutionary human point of view, it adapts to external factors, making life processes easier and faster.
The structure of the central nervous system is the brain and spinal cord. Both organs of this system are reliably protected from damage: the brain is located inside the skull, the spinal- inside the spine. The brain is also protected by the blood-brain barrier, which protects the organ from exposure to chemicals. In the event that any of the organs of the central nervous system is damaged, the quality of life of a person and his he alth will at least deteriorate, and in some cases death is possible.
Peripheral nervous system
In order to ensure the relationship between the central nervous system and organs, there is a peripheral part of the nervous system.
The peripheral nervous system includes nerve endings, neurons, and nerves. The main function of the PNS is the management and control of the muscles of the skeleton, the regulation of the work of all organs, as well as the maintenance of homeostasis. That is, after the brain sends a signal to the spinal cord, its corresponding section sends a synaptic signal through the axons of nerve cells to the desired organ. It can be both an exciting signal (for example, muscle contraction) or a relaxing one.
PNS provides two-way communication between a person and his environment: he can not only perceive signals, but also respond to them with the help of movements, facial expressions.
Somatic nervous system
The somatic department of the nervous system is engaged in the conscious control of the body, in contrast to the vegetative system, which a person is not able to control directly. The somatic department is sometimes called the animal, because the activity of this system in animals and humans differs slightly.
The somatic division of the nervous system consists of the following organs:
- muscles;
- leather;
- throat;
- larynx;
- language.
With the help of these tissues and organs, a person has the ability to control his body and feel tactile touches. The possibility of conscious control lies in the fact that a person can independently decide whether to go, squat or not move, but a person cannot decide what pulse or blood pressure he should have at the moment. Since these tasks are within the competence of the vegetative system.
Vegetarian
Classification of the nervous systems of people according to their structure is not the only way to separate its departments. Of great importance is the autonomic nervous system, which directly controls the organs of all systems. A person cannot consciously control the activity of vegetative medicine, but information about how it works sometimes helps to correct the state of he alth in case of vegetative disorders, for example, with a common disease - VVD (vegetovascular dystonia).
The activity of the autonomic nervous system is carried out by two departments-antagonists: sympathetic and parasympathetic. That is, when the sympathetic department is activated, the activity of the parasympathetic automatically stops.
Sympathetic department
The sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system is responsible for its activity. It triggers bodily reactions, which are conventionally called "fight or flight." That is, sympathy is triggered in response to a situation requiringactivity.
Physically it manifests as follows:
- increased muscle tone;
- increase heart rate;
- pupil dilation;
- increase in blood pressure.
During the work of the sympathetic department of vegetatives, the energy accumulated by the body is actively consumed. In order to restore energy reserves, it is important that the activity of the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions alternate.
Parasympathetic division
Opposite to the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system is the parasympathetic division. It is believed that it is responsible for relaxing the body, since when it is activated, the heartbeat slows down, the pupils dilate, breathing becomes deeper and more measured.
But, in fact, one system begins to work only after the parasympathetic is activated. And that system is the digestive tract.
In addition, such a classification of nervous systems by vegetative divisions suggests that the parasympathetic is responsible for storing energy.
It is important to understand that the division of the nervous system into functions and departments is conditional, since the activity of this most important system for a person is carried out in a complex manner, and all the categories described are closely interconnected. For example, it is known that the mental state has a direct impact on the physiological state. There are diseases called psychosomatic, which occur exclusively under the influence of psychogenic factors.(stress, anxiety, phobias). Also, many dangerous somatic diseases, such as heart attack, stroke, and, according to some reports, oncology, can occur under the influence of emotional stress.
Therefore, understanding what classifications of nervous systems exist, how they differ, and how they are interconnected, allows not only to positively influence one's own erudition, but also to prevent the development of neurological diseases, to help eliminate psychogenic disorders.






