- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
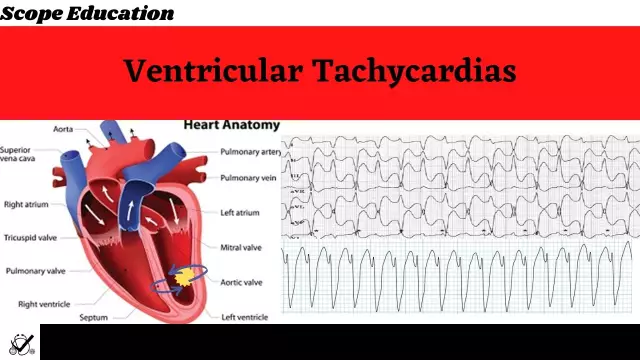
Ventricular tachycardia is characterized by an acceleration of the heart rate over 100 bpm. with origin in the stomach. In 90% of cases, it occurs in people who have organic lesions of the heart rhythm. Most often, rhythm disturbance is associated with ischemic disease. Myocardial infarction, congenital and rheumatic heart defects, or various complications after therapy with psychotropic drugs or some anesthetics can also lead to tachycardia.

Symptoms
The likelihood of this disease increases with age. Men are more susceptible to it than women. In people younger than 35 years of age, against the background of myocarditis, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, ventricular tachycardia may also develop. The symptoms here are:
- feeling of a strong heartbeat, dizziness,anxiety;
- shortness of breath, chest pain;
- a feeling of pulsation in the neck;
- In some cases, attacks of weakness and fainting are possible.

Pathophysiology
Ventricular tachycardia occurs in two manifestations: monomorphic and polymorphic tachycardia. The monomorphic variety is characterized by the fact that the sequence of impulse excitations is kept constant. It happens that the manifestation of this type of tachycardia occurs in people with a structurally he althy heart. In these cases, the clinical prognosis is usually favorable. Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia is distinguished by variability in the sequence of ventricular activation. The cause of the disease can be myocarditis, ischemia, or genetic abnormalities in the structure of ion channels.
Treatment of tachycardia
Ventricular tachycardia is treated by exposure to antiarrhythmic drugs, which takes place against the background of measures to eliminate the underlying disease. Lidocaine is commonly used as an antiarrhythmic agent. It is administered intravenously at the rate of 1 mg per kilogram of the patient's weight. As a rule, this dose reaches 100 mg and is administered in a few minutes. If there is no effect within 15 minutes, the drug is used again in the same

dosage. If ventricular tachycardia is accompanied by a drop in pressure, it is increased using pressor amines. This will restore sinus rhythm. Atintoxication with cardiac glycosides, ventricular tachycardia is treated with potassium chloride and lidocaine, or the drug "Obzidan" is used.
Continuation of treatment after recovery of heart rhythm
When the rhythm is restored, the prognosis is assessed and a management plan is drawn up. He is prescribed drug therapy or the installation of a cardioverter-defibrillator, or catheter ablation. There are also combined treatment options. They are usually applied if there is a serious structural pathology of the heart. Catheter ablation, for example, could increase the effectiveness of antiarrhythmic therapy or reduce the rate of shocks from an implanted cardioverter-defibrillator.