- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Fibromyalgia is a pathology that manifests itself as chronic pain in the muscles and joints. This disease is also called fibrositis. It is characterized by anxiety and depression, poor sleep, a feeling of constant fatigue and disruption of the intestines.
Etiology
Fibromyalgia syndrome is recorded most often among women aged 40-55. In men, this pathology is diagnosed much less frequently - only in 16% of cases. Pain in fibromyalgia has the ability to disappear and reappear, migrating throughout the body, so diagnosis is difficult. At the same time, fibromyalgia in adults is a common occurrence, since adolescents and children suffer from this disease very rarely, although they may experience periodic pain in the muscles or joints.

The causes of this disease are unknown. Often it develops in patients with concomitant rheumatoid arthritis. Provoking factors are constant stressful situations, overwork and depressive states. In some cases, there is a genetic predisposition to fibromyalgia.
Features of fibrositis
Previously thoughtthat fibromyalgia is a pathological condition of inflammatory etiology, but today these assumptions have been refuted, since neither signs of inflammation nor manifestations of arthritis are observed. A feature of this disease is that patients register a low level of somatotropic hormone. This can be attributed to the fact that with fibromyalgia, the deep sleep phase is disturbed, namely, during this period, the pituitary gland is able to synthesize this hormonal compound.
It is also worth noting that patients with fibromyalgia experience pain even on the action of stimuli that usually cannot be perceived as pain. In addition, patients have high levels of neurotransmitters (the so-called substance P), as well as growth factors in the CSF (cerebrospinal fluid). If we examine the nature of the pain, we can assume the presence of CNS hypersensitivity, as well as pathological perception of pain stimuli.
Also, patients who are diagnosed with fibromyalgia, the causes of which are unknown, have a history of severe physical or psychological trauma or a complex infectious disease. They also have a small amount of slow eyeball movement during sleep, resulting in a feeling of fatigue or frequent nocturnal awakenings.
Clinic
When fibromyalgia develops, symptoms include the following:

• rapid muscle fatigue;
• "goose bumps";
•sleep disturbance;
• general fatigue;
• frequent headaches;
• temporomandibular disorders in the form of pain in the face and jaw area, as well as resonance in the ears.
Patients also have an imbalance in the mental sphere. Thus, when fibromyalgia is present, the symptoms of this pathology can include poor memory, attention disturbances and emotional disturbances, which are often referred to as depression.
Patients also complain of dizziness, pain in the abdomen, especially during palpation. Sometimes prolonged hyperthermia can be observed for no apparent reason. In addition, patients with fibromyalgia are prone to colds and notice joint stiffness in the morning (after waking up).
It should be noted that the course of the disease is stationary. Manifestations of fibromyalgia can be observed for many years, changing slightly under the influence of certain external factors. Pain sensations, as a rule, are permanent, asymmetric or generalized. If the pain reaches a critical level, then they speak of a “fibrositis storm.”
Feature of pain syndrome in fibromyalgia
When fibromyalgia is diagnosed, 100% of the symptoms of the disease include pain. It has certain features:

• pain in the musculoskeletal system is common and can last more than six months;
• Quite often, chronic pain syndrome in fibromyalgia is combined withsymptoms of other diseases;
• pain is accompanied by autonomic disorders and changes in the psychological sphere.
When fibromyalgia develops, symptoms can also include fluid retention, intestinal irritation, vestibular disorders, osteoporosis, and other disorders. Clinical manifestations in each case are individual and require careful diagnosis.
It should be noted that the pain occurs in different parts of the body and can be concentrated on both sides. Most often, pain is localized in the neck, shoulders and chest, that is, in the upper body. Zones that have increased sensitivity are characterized by a clear location. Thus, when fibromyalgia occurs, tender points can serve as a definite diagnostic criterion.
Tender Points (TP) - tender points for fibromyalgia
TR are important modern criteria in the detection of fibromyalgia, although patients are not even aware of their existence. These points are characterized by the following properties:
• slight pressure is needed to cause pain;
• Pain is observed on palpation, which occurs spontaneously in the patient;
• TRs are placed in strictly defined locations, so there are specific maps for these areas.

It should be noted that the exact amount of FR is unknown, although it correlates with the intensity of clinical manifestations. The most common localization of pain points is the neck, neck,the area of the trapezius muscle, the place of attachment of the second rib to the sternum, the lateral part of the shoulder, the buttocks, as well as the medial fat pad in the area of the knee joint.
Despite the presence of TR, patients with fibromyalgia develop various algic syndromes with different localization. So, pain can be observed not only in the muscles, but also in the abdominal cavity or heart, which makes diagnosis difficult. In addition, panic attacks, hyperventilation syndrome, loss of consciousness, tunnel neuropathies are characteristic.
Features of the diagnosis of fibromyalgia
To date, there are no specific tests or examinations that would help identify this disease. They are prescribed only to exclude other pathologies. Diagnosis is based on history and physical examination. It is when specific pain points are identified and in the absence of other diseases that fibromyalgia can be detected.
It is worth remembering that many pathologies have a clinical course reminiscent of fibromyalgia syndrome:
• hypothyroidism;
• vitamin D deficiency;
• hyperfunction of the parathyroid glands, which is accompanied by an increase in calcium levels;
• polymyositis or other muscle fiber disorders;
• bone diseases;
• oncopathology;
• infectious diseases.
As a rule, the level of thyroid hormones, alkaline phosphatase, creatine phosphokinase, as well as ESR, C-reactive protein, antinuclear factor and sialic acid are determined to rule out other lesions. Atfibromyalgia these indicators are within the normal range.
What are the criteria for a correct diagnosis?

Fibromyalgia can be suspected in the following cases:
1. The patient has diffuse and symmetrical pain that occurs spontaneously and is chronic (lasting 6 months or longer).
2. The examination reveals 11 pain points out of 18 generally accepted, which are characteristic of fibromyalgia.
3. No symptoms of any primary pathology.
It should be noted that in clinical practice it is not always possible to detect these criteria, but it is they that guide specialists in making a diagnosis. The combination of depressive disorders and chronic muscle pain is also taken into account. Often, psychological disorders are considered as a consequence of a constant pain syndrome.
When making a diagnosis of fibromyalgia, many other pathological conditions are identified. As a rule, depression, bulimia nervosa and sleep disorders, chronic illogical syndrome are observed simultaneously. They also pay attention to the level of serotonin, which decreases with this disease.
Fibromyalgia and menopause
After the age of 45, involutional changes begin in the female body, which consist in a decrease in the level of sex hormones, as well as in the suspension of the ovaries. During this period, the functioning of organs and systems changes functionally, and the relationship between the hypothalamus, pituitary gland and ovaries is disrupted.

As a rule, the manifestations of menopause are typical, although they may have individual characteristics, since each body reacts to hormonal failure in its own way. The most common symptom of menopause is hot flashes. They are a sudden sensation of heat in the face, neck and chest, accompanied by palpitations, excessive sweating and redness of the skin.
It should be noted that there are no clear diagnostic methods by which one could detect the end of the reproductive period. Fibromyalgia with menopause is a fairly common occurrence, as women suffer from insomnia and pain throughout the body. In addition, they are emotionally unbalanced, so the symptoms of this disease during this period are more pronounced.
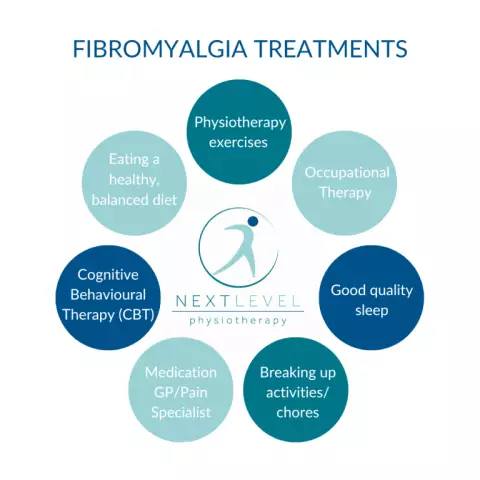
Fibromyalgia Therapy
When fibromyalgia develops, symptoms and treatment depend on the nature of the course of this pathology, but the most effective therapy is a combination of pharmacological and non-pharmacological methods.
As a rule, patients are prescribed tricyclic antidepressants, which improve sleep, relieve muscle pain and eliminate fatigue. Most often, Amitriptyline and Doxepin, as well as Lyrica or Neurontin, are used for therapeutic purposes. In addition, drugs that increase the concentration of serotonin and norepinephrine (Cymb alta, Savello), non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics can be used.
Among non-drug methods of treatment, massage, acupuncture and exercise therapy are used. It is useful for patients to swim (hydrotherapy), walk, ridecycling, aerobics. Focus on improving sleep. Patients should also avoid stressful situations that can provoke an aggravation of the clinic.

When fibromyalgia is diagnosed, treatment with folk remedies also gives good results. As a rule, natural adaptogens are used that activate the immune system and the work of muscle tissue (infusion of Chinese magnolia vine, ginseng, St. John's wort).
Phytotherapy helps to neutralize intoxication, has antibacterial and antiviral effects, and also causes a calming effect. Herbs commonly used in the treatment of fibromyalgia oxidize pyruvic and lactic acid, the main fatigue toxins.
It is worth noting that herbal remedies should be taken under the strict supervision of a physician. Only the right dosage can improve appetite, calm and mobilize the functional activity of the body.
Fibromyalgia Diet
Today, there are no clearly established principles of dietary nutrition for this disease, however, there are a number of substances that are recommended to be limited in the diet of patients:
• Aspartame, often found in sweeteners. This compound has been shown to exacerbate the clinical manifestations of fibromyalgia by stimulating pain receptor responses.

• Dietary supplements containing monosodium glutamine and nitrates as theypredetermine the intensification of the pain syndrome.
• Simple carbohydrates - patients are advised to limit their intake of sugar and bread.
• Caffeine. With fibromyalgia, you should not drink coffee, tea, a lot of chocolate. With their restriction, the condition of patients improves in just a week.
• Various baked goods that contain yeast and gluten.
• Scientists believe that dairy products of any fat content can negatively affect the dynamics of fibromyalgia.
• Nightshade - peppers, potatoes, tomatoes and eggplant. These foods can exacerbate both arthritis and fibrositis.
If fibromyalgia develops, the symptoms and treatment of this pathology depend on the duration of the pathological process and the presence of other concomitant diseases. With timely diagnosis and therapy, the prognosis is favorable.