- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
In the human body, the tricuspid valve is needed as a fuse to prevent back flow of blood. Placed on the line of separation of the right atrium and the corresponding ventricle. The structure of the valve consists of connecting plates. Violation of his work is dangerous to human life.
Building
The tricuspid valve, according to the scientific literature, is also called tricuspid. When the heart moves, all processes occur synchronously. If a blockage occurs in one of the departments, an insignificant temporary one, the body immediately feels that the state changes significantly. The state of he alth immediately worsens, it becomes difficult to breathe and it is impossible to move.
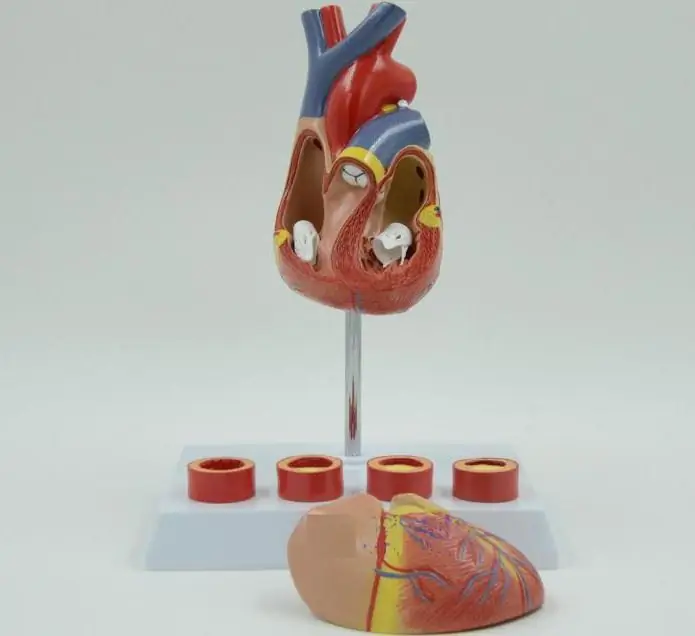
The tricuspid valve is located on the left side of the sternum. It is part of a pumping system for pumping blood. It is a kind of cap that opens under the pressure of the ejected blood. Closing occurs due to the reverse forces of the liquid automatically due to pressure on the surface of the valves.
Incomplete closure of the tricuspid valve occurs due to the relaxation of the heart muscle, when it is no longer able tofunction normally. Due to a violation of the redistribution of internal pressures, tissues begin to collapse, which, as a result, threatens the formation of heart disease. Some diseases become provocateurs of such pathology.
Organ work
The tricuspid valve is part of the human circulatory system. A huge amount of blood goes from the conclusions of the heart to the aorta, passing through all the arteries and capillaries, it exchanges oxygen with the cells, and receives carbon dioxide. Along with this, saturation with decay products from processed useful trace elements occurs and it becomes dark in color. This blood is called venous.
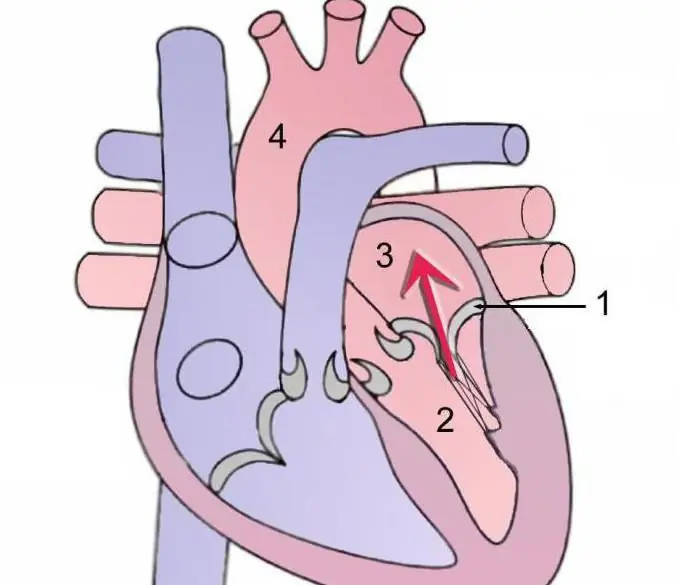
Further there is a redistribution to the right area of the heart, further movement occurs through all the arteries of the lung, for oxygen enrichment. The tricuspid valve is not the only one that has the ability to block the reverse flow. This is necessary to separate the jointly working: left, right ventricles and atria.
Blood fills the left side of the heart, then from the atrium it flows into the ventricle. After this, circulation occurs in a large circle of blood circulation. Venous blood returns to the right atrium, then to the right ventricle and enters the pulmonary circulation. After oxygen saturation, the great circle cycle repeats again through the left atrium and ventricle.
Valve functions
Since the left and right parts of the heart work synchronously, it is necessary to block the reverse current between the departments in time. After all, blood circulation occurs cyclically:there is a moment of fluid accumulation in the ventricle, followed by a powerful ejection of blood into the aorta. The valve system is working properly:
- Located in the left region of the heart is referred to as the mitral valve.
- Triskupidalny.
- Valve in the artery of the lungs.
- Aortic, as the fuse of the largest system.
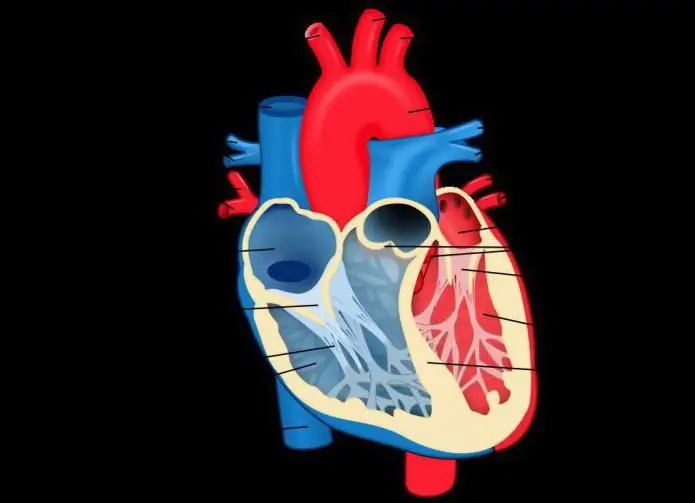
Doctors use the definition of regurgitation, which refers to the phenomenon of blood flowing backwards through the valves. To prevent this from happening, the listed blockers must work out in time according to the following rules:
- The mitral valve is open only at the moment of pumping blood from the left atrium to the corresponding ventricle. It closes when the accumulated fluid is ejected into the aorta. There are two leaflets in the structure of the valve.
- The tricuspid aortic valve closes the passage between the right atrium and the corresponding ventricle. The work is similar to the mitral. The building has three doors.
- Pulmonary refers to the area between the pulmonary trunk and the right ventricle. Serves to block the reverse current at the moment of relaxation of the heart muscle.
- The aortic is located in the left ventricular outlet canal. It blocks the reverse flow of blood from the aorta at the moment of relaxation of the heart muscle. Consists of three semilunar valves.
Development of heart defects
Tricuspid valve insufficiency causes blood regurgitation or backflow from the atrium to the ventricle. This occurs at the time of systoleright ventricle). Relaxed valves sag under blood pressure.
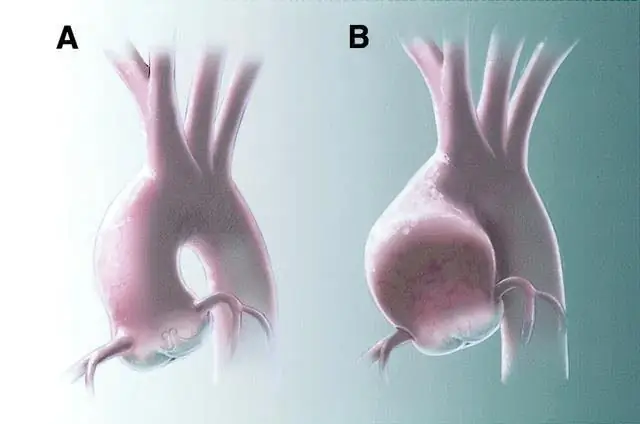
This condition can be formed by mechanical blockage of the aorta. Most patients acquire the disease during their lifetime. But there are examples of congenital heart defects.
Forms of pathologies
Valve malfunction occurs for the following reasons:
- Lack of essential trace elements in the body, which determine the density and elasticity of the tissues that form the valve plates.
- Disruption of the functionality of the tricuspid valve may occur due to a malfunction in the neighboring parts of the heart.
Due to the stagnation of blood in the body, incomplete closure of the tricuspid valve of the heart occurs. May render a person incapacitated. Hypertrophic walls of the atrium are formed due to dilatation (expansion) of the right ventricle. From here, stagnant processes are formed in the arteries and veins.
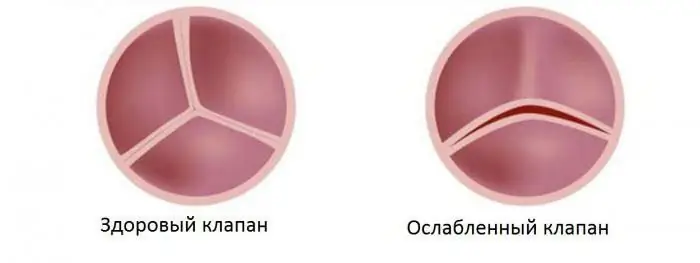
Pathology can be detected by internal sensations and by the swelling of a vein in the neck at the time of expulsion of blood from the heart. Venous pressure usually rises. The liver is greatly enlarged.
Causes and symptoms
Among the established causes of a weakened tricuspid valve are the following:
- Carcinoid syndrome.
- Consequences of developed rheumatism.
- With endocarditis of infectious origin.
- Mechanical damage to papillarymuscles or rupture of chords.
- A consequence of myocarditis.
- After cardiomyopathy.
- Consequence of severe conditions of thyrotoxicosis.
Congenital pathologies often occur in conjunction with other abnormalities in the structure of the heart. Stenosis of the tricuspid valve can lead to retraction of the chest, which the doctor detects by palpation. Also, while listening to heartbeats, significant noises appear during systole (ejection of blood from the ventricle).
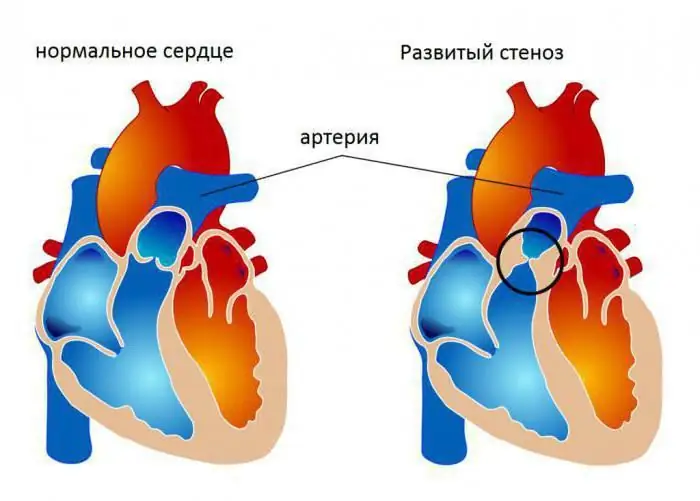
However, murmurs can only be detected in severe deficiency. Less severe symptoms are often ignored. An instrumental examination on the devices is required for an accurate diagnosis.
Diagnostic Methods
When diagnosing, systolic murmur during inspiration is important. This indicates insufficiency of the tricuspid valve. However, it should be remembered that this phenomenon is not permanent and may disappear completely for some time. To confirm the preliminary diagnosis, an electrocardiogram is taken.
On the resulting graph, pathology is observed:
- electric axis deviation to the right;
- increase in the size of the P wave (in the area of the second and third chest leads).
X-ray may also be used. The picture shows dilatation of the ventricle or atrium. Deviations are also noticeable on echocardiography images, where abnormal movements of the cardiac septa are established. When analyzing the statepatient take into account the following points:
- Type of noise and area of its manifestation.
- The size of the heart, it is often enlarged.
- The presence of congestion in the circulation.
- Venous pressure value.
- Liver size.
- Chest condition.
- Right atrial pressure.
Physical pathologies
Narrowing of the valve opening is called stenosis. This phenomenon occurs under the influence of rheumatism, congenital malformations, as well as prolonged mechanical stress. As a result of the disease, there is an increase in pressure on the walls of the heart. The atrium is enlarged. Stagnation in the circulatory system begins.
For the treatment of mild cases of pathology, preventive actions are carried out. Starting with the second degree of severity, surgical intervention is already recommended. The valve is processed with a scalpel, as a result, it is often necessary to sew the plates together or leave only two instead of three. According to statistics, about 14% of patients do not survive after surgery.
But even after successful treatment, the patient is already becoming disabled. It is required to avoid physical exertion and undergo periodic examinations to exclude further progression of the pathology.






