- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Where is it in the body
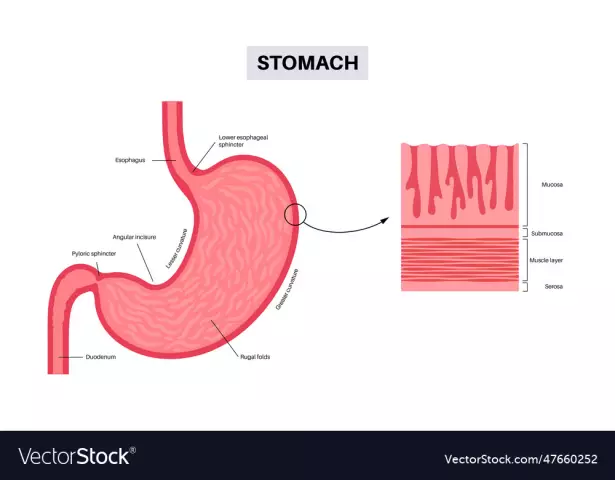
The mucous membrane is a structure that lines the outside of any organ that has a cavity. There are a lot of those in our body, this is the entire gastrointestinal tract, the gallbladder with its ducts, the respiratory system, including the nasal cavity, vagina and uterus, urinary tract and bladder. Everywhere, the shell consists of connective tissue, is arranged in the same way and is represented by the following layers: the outer one is the mucous membrane itself, and the submucosal base, which lies from the inside. The top layer in different organs can have different structures, such as folds, papillae, villi.

Their presence determines the functions performed by the body. Also in the thickness of the mucous membranes there are a lot of different glands. These are both simple, secreting mucus, and complex structure, secreting digestive juices. The mucous membrane of any organ is very rich in nerve endings and blood vessels. Since it is a kind of barrier between the internal environment of the body andthe outside world, it contains a large number of lymph nodes. The latter consist of accumulations of immune blood cells - leukocytes and lymphocytes - and perform a protective function. Very many diseases of organs are associated precisely with the defeat of their mucous membranes, both an inflammatory process and those of a different nature.
What is stomatitis and what are its signs

For example, inflammation of the oral mucosa is called "stomatitis". The oral cavity has complex conditions that can adversely affect her he alth. The constant presence of food residues, traumatization of the mucous membrane and a huge number of microorganisms are a trigger for the development of inflammatory diseases.
The presence of the following diseases and conditions can cause the oral mucosa to become inflamed: a drop in immunity due to any cause, allergies, problems with the digestive tract, autoimmune and rheumatic diseases, caries, viral, fungal and bacterial infections. Also, poor quality dentures and lack of oral hygiene can cause an inflammatory disease of the oral mucosa. Other damage to the mucosa as a result of other mechanical, thermal, chemical and radiation effects often cause stomatitis.

It is manifested by such signs as redness, swelling of the mucous membrane, white or yellow plaque, soreness,possibly increased salivation, bad breath. Quite often, regardless of the cause, ulcerative defects occur. The patient may experience deterioration in general condition, rise in body temperature, weakness, depression.
How is it treated
This pathology is treated by dentists, sometimes consultations of other specialists are needed. Local (local) therapy is needed, which affects the process on the mucosa, antiseptics and antimicrobials are used, including rinsing with infusions of medicinal herbs. Also, the general disorders in the body that caused the cause should not be overlooked, they should also be diagnosed and treated.