- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-06-01 06:18.
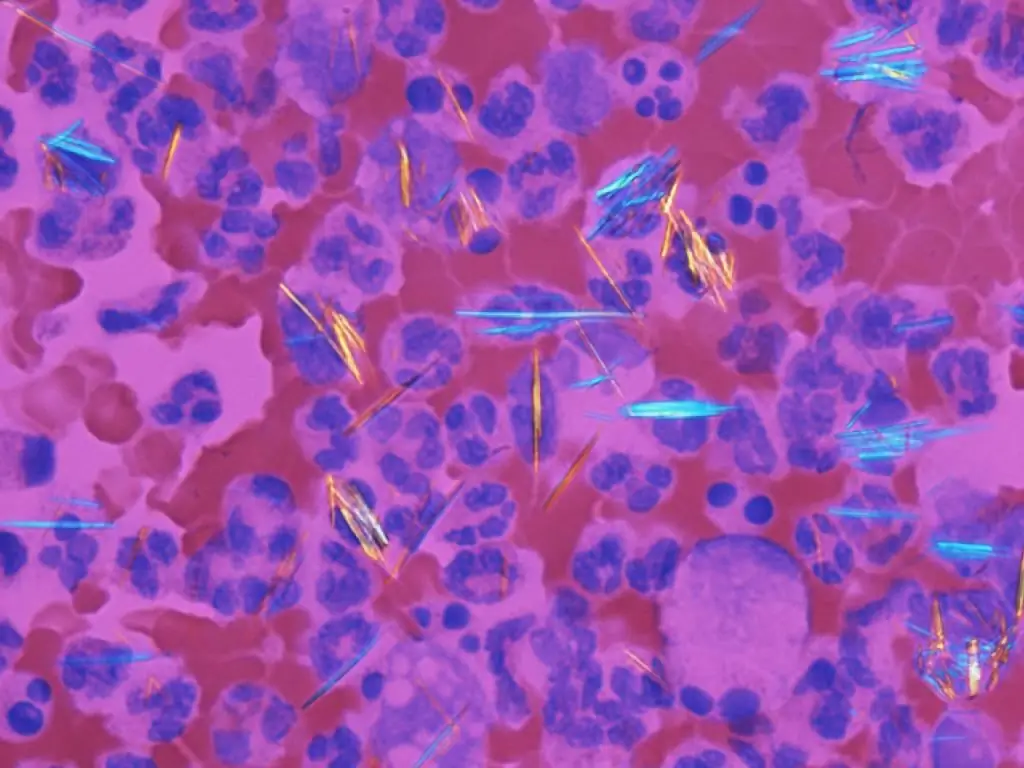
According to the presence of uric acid s alts in urine, the degree and nature of the metabolism of purines, which come with food and from the cells of the individual's body, are assessed. The reason for the formation of s alt crystals in the sediment is considered to be an increased content of uric acid in urine. This condition is typical for serious ailments - urolithiasis, gout and others. In addition, a high concentration of acid changes the internal acidity of the body. Read more about this in the article.
What is uric acid?
Toxic product resulting from the breakdown of proteins and purines, which are part of the structure of most cells, and also enter the body from the outside. For example, with food, it is called uric acid. The intestinal mucosa, as well as the liver, synthesize an enzyme substance that breaks down this compound into uric acid. In a practically he althy individual, it is formed from twelve to thirty grams. This isabsolutely normal process and is due to purine metabolism. Having previously dissolved in the blood, it enters the kidneys, undergoes filtration and leaves the body. With urine, about seventy percent of it is excreted, the remaining thirty percent penetrate the gastrointestinal tract. One part is excreted during the act of defecation, and the other is absorbed by intestinal microorganisms. An increase in the concentration of uric acid adversely affects the state of he alth. In this case, it is excreted by the kidneys in the form of crystals, since it does not dissolve in water.

S alts of uric acid, which should not be contained in urine during the normal functioning of all organs and systems of the body. Nevertheless, their single detection is not considered a deviation and is quite acceptable. Contribute to an excess of s alts and acids such factors as:
- failure of water-s alt balance;
- changes in blood properties;
- acidic urine;
- infectious processes in the urinary tract;
- diabetes mellitus;
- excess intake of foods high in purines and alcohol;
- AIDS;
- cancer;
- drug use;
- Regular use of diuretics.
As a result of an excess of uric acid accumulates in organs and systems in the form of sediment. In the urinary system, stones are formed that provoke severe pain, and its deposition in the joints leads to the development of gout and arthritis. In addition, it is the cause of such pathologicalconditions like arthrosis, rheumatism, osteochondrosis.
Urine study
Uric acid in the urine indicates a failure of purine metabolism, while it becomes a brick color. Biomaterial for analysis is collected in a dry and clean container, during the day. After completion of the collection on the bottle indicate its volume. Further, it is mixed and poured about fifty milliliters. They must be delivered to the institution's laboratory for research.
The content of uric acid is affected not only by the diet, but also by the work of the kidneys, medication, nucleotide exchange and more. In he althy individuals, its concentration increases if the foods consumed have a high content of purines and, conversely, decreases with a low purine diet. Uric acid analysis is recommended for:
- lead poisoning;
- blood diseases;
- suspected dietary deficiency of folic acid;
- diagnosing endocrine ailments and failures of purine metabolism.
An overestimated level of this indicator is observed in such pathological conditions as viral hepatitis, epilepsy, gout, leukemia, croupous pneumonia and some other ailments. Concentration below the permissible values is recorded with muscle atrophy, lead poisoning, lack of folic acid, taking quinine, potassium iodide and atropine.
Causes of uraturia
S alts of uric acid in the urine appear as a result of various physiological disorders and malnutrition. In the first case, provocative factors are:
- Diseases -some types of leukemia, gout, inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system. In these cases, uraturia is a side effect.
- Failure of the kidneys - their omission, circulatory disorders in the renal arteries, blood clots, atherosclerosis. Existing for a long time at high temperatures.
- Violation of water-s alt metabolism - excessive exercise, vomiting, diarrhea, inability to quickly replenish the body with fluid.
- Medication - anesthetics, antibiotics, analgesics, NSAIDs.
The following are foods whose excess intake contributes to the failure of metabolic processes, the result of which is the precipitation of uric acid s alts in the urine in the form of sediment:
- alcoholic beverages;
- legumes;
- tomatoes;
- smoked mushrooms;
- canned food;
- spinach;
- fatty protein foods, predominantly of animal origin;
- as well as very spicy dishes and strong tea.
Urates
These are sodium and potassium s alts. Their excess leads to the appearance of crystals that appear in the urine in the form of a precipitate. A large amount of urate in the urine leads to the formation of stones in the bladder, kidneys, and urinary tract. This situation arises with prolonged fasting, diabetes, excessive consumption of protein foods, excessive physical exertion, and fever. The main reason for their appearance is an imbalance in the body, which occurred for the following reasons:
- hereditary predisposition;
- monotonous food;
- protracted stress;
- a history of urinary tract infections;
- uncontrolled intake of certain groups of medications;
- leukemia;
- thrombosis;
- pancreatitis;
- hepatitis;
- pyelonephritis;
- prolapsed kidney;
- gout.

Urate in the urine in large quantities contributes to the crystallization of stones, which negatively affects the functioning of the body, as it loses water. Poisoning and intoxication provoke diarrhea and vomiting. Heavy physical work, prolonged exposure to damp and cold rooms, as well as exposure to the scorching sun accelerates the formation of urates. Some products also contribute to their increase:
- drinks containing raspberry, viburnum and linden;
- canned food;
- meat and fish broths;
- pork;
- veal;
- offal;
- spices;
- smoked meats;
- spices;
- virtually all legumes;
- spinach;
- cabbage;
- sorrel;
- bow.
Over time, the size of the stones only increases, and their movement from the kidneys to the bladder causes an inflammatory process.
Urate in pregnant women. Reasons
When carrying a baby, changes occur in the female body. Therefore, the formation of uric acid s alts is possible, which are detected in the analysis of urine. In the early stages, the cause of this phenomenon is vomiting and slight dehydration, which is typical for toxicosis. If the levelurates slightly exceeds the permissible limit, then there is no cause for concern. With a significant increase, the doctor may suspect:
- Violation of a balanced diet by the expectant mother.
- Low fluid intake resulting in dehydration.
- Violation of urine flow, leading to inflammation in the urinary organs.

Prolonged and severe toxicosis, in which urates are constantly present in the urine, requires observation and treatment of a woman in a hospital
Uraty in a child. Reasons
The appearance of uric acid s alts in children's urine does not mean a he alth problem. Often they are formed due to an incompletely formed urinary system. The consumption of a large amount of fish and meat products also acts as a provocative factor. Incorrect preparation for it also affects the results of the analysis. For example, urine collection is carried out against the background of taking antibacterial or antipyretic drugs, vomiting or diarrhea, and high fever. In addition, refusal to eat, prolonged exposure to the sun, excessive consumption of tomatoes, sweets, cheese and some other products affect the result. If the doctor reveals that any of the above factors has taken place, then he will recommend adjusting the diet. In the absence of effect, instrumental and other types of examinations are indicated. The content of a large number of urates indicates kidney stones, an imbalance of microflora, the presence of parasites in the intestines, etc. If the child's parents are diagnosed with gout, diabetes mellitus, obesity, diseases associated with the spine, then he must be under constant dispensary observation at a he althcare facility at the place of residence, as he belongs to the risk group.
Symptomatics
It is quite difficult to diagnose uraturia in the early stages, that is, a condition in which there is a large amount of uric acid s alts in urine, without laboratory tests, since it does not manifest itself outwardly. Symptoms appear when stones have formed in the kidneys, or an infectious inflammatory process has occurred. The occurrence of such states is preceded by:
- lack of B vitamins;
- long-term use of anesthetics;
- unbalanced diet;
- increased synthesis of uric acid;
- low rate of urine formation;
- sedentary lifestyle.

The following are signs that indicate that an individual has serious problems with the urinary system:
- temperature increase;
- increased pressure for no reason;
- appearance of blood in urine;
- severe pain in the abdomen and lumbar region, with pain felt in the lower limb and groin;
- weakness;
- nausea and vomiting;
- apathy.
Kids have a slightly different clinic: high activity, sleep disturbance, tearfulness. They require constant attention and affection. At the same time, the child is ahead of his peers in terms of development. In this case, an untimely appeal to the doctor is fraught with serious consequences:
- The appearance of constipation.
- Vomiting in the morning with normal intracranial pressure.
- Deposition of uric acid crystals under the dermis, as well as in the bags of the joints.
- Asthmatic attacks of unknown etiology.
- Itchy eczema with no causal relationship.
Diagnostic Methods
Diagnostic measures begin with the collection of an anamnesis and examination of the individual. Next, assigned:
- Clinical urinalysis is the simplest and most reliable method for detecting uric acid in urine. A precipitate of bright yellow or reddish-brown color indicates the presence of crystals of potassium and sodium s alts. Thanks to such a study, a malfunction in the work of the kidneys, anemia is detected.
- Ultrasound and X-ray - they are used to detect stones and sand.
- Urography - shows the changes that have occurred with the kidneys.
- CT - Gives a complete picture of available stones, including their shape and size.
Removal of uric acid s alts
For this, it is very important to adjust the diet. Be sure to avoid foods that are high in purines. Include in your diet:
- vegetables such as potatoes;
- cereals;
- fruits - apricots, plums, apples, pears.
Drink mineral alkaline water daily.
There are alternative methods that lead to a decrease in urates. Among them are infusions from medicinal plant materials. For theirpreparations take twenty grams of grass and pour two hundred milliliters of hot water, insist for half an hour.

Nettle, lingonberry, birch are widely used. The course and dose are prescribed by the doctor.
Drug therapy is connected with a natural excess of uric acid levels, and its insufficient excretion when using the above methods. If gout or stone formation is suspected, complex therapy is selected to reduce the concentration of urates.
Medicated treatment
What dissolves uric acid s alts? Another important question. The pharmaceutical industry has a wide range of drugs that help dissolve stones and remove acid.
Pharmacotherapy and a properly selected diet will help to cope with urates, most often used:
- "Potassium magnesium aspartate" - actively removes oxalates and urates. It is forbidden to take in the presence of phosphate s alts.
- "Allopurinol" - inhibits the formation of uric acid. As a result, the amount of urates decreases.
- "Dezurik" - inhibits the absorption of uric acid and increases its excretion by the kidneys.
- "Blemaren" - are effervescent tablets in which the active ingredients are sodium bicarbonate and citric acid. They create an alkaline environment, which facilitates the dissolution of uric acid s alts, and they are easily excreted from the body along with urine.
- "Marelin" - contributesthe passage of stones, is used for urolithiasis.
- "Magurlit" - dissolves and prevents the recurrence of stones. By shifting the acidity of the urine to the alkaline side.
- "Fitolizin", "Urolesan", "Canephron" - do not dissolve s alts. They are used to normalize the outflow of urine.

Joint damage
The reason for the deposition of uric acid s alts in the joints and tissues located near them is considered to be a failure of purine metabolism. Which leads to a disease such as gout. This is due to the inability of the kidneys to remove the required amount of acid from the body of the individual. Urates contribute to the development of the inflammatory process, that is, gouty arthritis. His clinic is characterized by restriction of movement and severe pain syndrome. The most commonly affected joints are the feet and hands. In addition, s alts are deposited in the subcutaneous tissue and soft tissues, which form peculiar nodules, called tophi.

The initial signs of s alt deposition in this pathology are swelling of the joints, redness and pain. At the stage of development of the disease, symptoms appear only after excessive physical exertion, and then at rest. At the first night attack, the pain syndrome affects the metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe.