- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Convergence of the eyes is the convergence of the visual axes when fixing on a closely located object. During this, the pupil constricts. Eye convergence occurs reflexively in binocular vision. Its deficiency provokes the development of divergent strabismus.
The role of eye convergence
Eye convergence plays an important role in binocular vision during the alignment of monocular visual images, creating the necessary conditions for their fusion. It is often disturbed in children.

Disorders of convergence often lead to the appearance and intensification of myopia, the development of axial myopia. The phenomenon is serious and undesirable, especially for children and their parents. To do this, the convergence of the eyes must be diagnosed. How to check?
- An adult needs to put the child facing him, close one eye.
- Approximately in the middle of the distance, put the pencil vertically so that an adult with an open eye sees it superimposed on half of the child's face, and the upper end is at the level of his eyes.
- Invite the child to look into the open eye of an adult and find out how many pencils he sees.
- If the child sees"one" pencil, this completes the process. He has impaired binocular vision.
- If there are "two" pencils, it is necessary that he looks only at the top of the object, which should be slowly brought closer to the child's face.
- If there is no convergence, as the pencil approaches the child's face, one eye tends more towards the nose, the other towards the temple.
- In the presence of convergence, the child's eyes turn symmetrically towards the nose until the distance decreases to 5 cm.
- Then ask the child to look at the pencil for 1-1.5 minutes. If the convergence of the eyes is stable, they should be equally turned towards the nose.
- Invite the child without a pencil to focus both eyes to the nose. If this works, then he has "volitional convergence".

Treatment of convergence disorders
If there is no eye convergence, a healing exercise should be done daily:
- Set a pencil at a distance of 30 cm and look past it. At the same time, two images of the object should be seen.
- First you need to look at the image of the "right" pencil so that the "left" one is also visible, then look at the "left" without losing sight of the other one.
- Continue to do this fixation further, first at a slow, then at an accelerating pace.

To strengthen convergence, exercises are used that are done daily. They may alternate throughout the day.
Exercise 1. Set the pencil vertically 20 cm from the eyes, look far away for 20 seconds, fixing attention on the double images of the object, then look at the pencil and look at it for 5 seconds, then look into the distance again and repeat the actions.
Exercise 2. Set the pencil vertically at arm's length, slowly bring it closer to the eyes until it doubles, then slowly move it away from you.
Exercise 3 to apply with volitional convergence. Stand facing the window so that the horizon is visible. By an effort of will, bring your eyes to the bridge of your nose, holding in this position for 7 seconds, then look into the distance and again reduce your eyes.
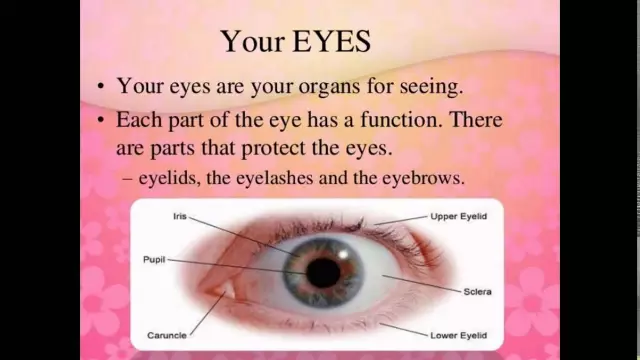
The structure of the human eye
More than 80% of information people get from what and how we see. The structure of the visual organ is very complex. It depends on the function of the eyes.

The human eyeball is an irregularly shaped sphere. It is located inside the orbits of the skull. Eye sockets double in size from birth to death.
The optic nerve occupies an important place. It transmits information to the occipital cortex, then analyzed.
The lacrimal gland keeps the surface of the eye moist. Tears lubricate the conjunctiva well.
In the structure of the human eye, the muscles of the eyeball act in concert with each other. Eyelids cover the eye, protecting from negative factors. Eyelashes perform a similar function.
The relationship between the structure and function of the eyes
To understand the structure of the visual organ, one shouldcompare it to a camera. It creates an image by focusing on the subject and allowing a certain amount of light to pass through the aperture.
When the beam enters the eye, it passes through the cornea where 75% of the light is focused. Then it enters the pupil, where its amount is regulated.
The lens is the second lens of the eye. Its shape is changed by tension or relaxation of the muscles. Focused light reaches the retina, where it is transformed into a nerve impulse. When the image reaches the brain centers, it becomes possible to enjoy the world, look at colors and objects. In other words, everything is as we see it in real life.

The structure proves how complex the eyes are. Specialists still cannot find a way to transplant the muscles of the eyeball, because the optic nerve is very sensitive.
Central vision
It got its name because it is provided by the central part of the retina and the fovea. Such vision allows a person to distinguish shapes and small details of objects.
If it decreases even slightly, it will immediately become noticeable to a person.
The main characteristic of central vision is sharpness. Her study is important in assessing the human visual apparatus as a whole, to track various pathological processes.
Visual acuity is the ability of the eye to see two points that are close to each other, at a certain distance. Also there the concept of the angle of view, which is the angle,which is formed between the extreme points of the observed object and the nodal point of the visual organ.
Peripheral vision
Thanks to him, a person can navigate in space and see in the semi-darkness.
You should turn your head to the right and catch some object with your eyes, let it be a picture on the wall, and fix your eyes on its separate element. If it can be seen well, it indicates central vision. However, in addition to this object, other large things come into view. For example, a door to a room, a closet, a dog sitting next to it on the floor. These objects are not clearly visible, but are in the field of view, and it is possible to detect movement. This is peripheral vision.
People's eyes, without moving, can cover 180 degrees of the horizon and a little less (about 130o) along the vertical meridian. Central visual acuity more than peripheral. This is due to the fact that the number of cones from the center to the peripheral part of the retina is much reduced.
What vision is considered normal
Normal vision in a person is associated with the refraction of the light beam in the eye, not deviated from the norm. This means that the lenses, the cornea, and the lens transmit the image of the image to the retina, to the macula.

Each person has his own norm of vision. It is determined by what line the patient sees on the Golovin-Sivtsev table. A known unit means that it reads line 10. This is normal vision.
Refraction disorder
Refraction is calledrefraction of light in the eye.
If the beam is refracted correctly, the image is focused exactly on the retina. The opposite situation (violation of refraction) provokes the development and appearance of farsightedness and myopia. If they are present, the image is seen blurry, doubling. For correction, medical glasses and lenses are used, forcing the light beam to focus on the retina.