- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
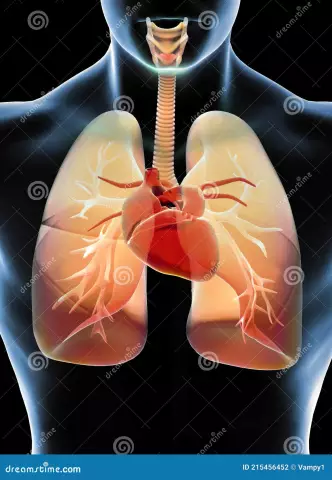
Modern medicine pays a lot of attention to the issue of heart pathologies, and among others, the study of acute and chronic heart failure is traditionally considered especially important. The stages of the disease, its signs, features of diagnosis and treatment options - all this is considered by the brightest minds of our world in order to find effective methods of preventing and timely detection, treatment of a disease associated with an increased risk to the patient's life.
General information
Before understanding what the progressive and initial stages of heart failure are, it is worth paying attention to the general terminology, to consider the condition described by this term. HF is a pathology in which the contractile capacity of the heart diverges from the needs of the body, which leads tometabolic failure. The disease is widespread. The disease is especially common in the elderly. People of all genders are susceptible to HF in various forms.
Causes and consequences
Perhaps, a person will have to figure out from his own experience what are the stages of heart failure according to Strazhesko, which means a diagnosis made by a doctor if he had a heart or vascular disease - such pathologies often entail HF as a complication. Particular risks are associated with a heart attack, atherosclerosis, localized in the vascular system that feeds the heart directly. The likelihood of developing HF is high if a person suffers from heart defects - inherited from birth or acquired over time. Risks associated with high blood pressure, cardiac tamponade, cardiac myopathy, arrhythmia.
If the doctor has established any stage of heart failure (2b, 2a, first or third) in relation to the ventricle on the left, this may be caused by a disease of the respiratory system - COPD, hypertension, other lesions.
Risks and dangers
It is noted that it is especially important to know how to detect heart failure at an early stage for people with chronic high arterial pressure, since this condition carries significant risks of heart failure. More often, a compensated form of the pathological condition develops. Similar consequences can lead to insufficient functioning of the kidneys, brady-, tachycardia. A compensated variant of the pathology is often formed against the background of a coronary syndrome that occursacute, with pulmonary embolism.
Certain risks of developing heart failure are associated with a medication course if the patient is taking drugs that adversely affect the heart. Another source of the problem is also possible: if the doctor has prescribed drugs for heart failure, but the patient violates the given regimen, the symptoms of the condition may be disturbing.
Manifestations indicating HF often accompany fever, fever, anemia. Severe infection, hyperthyroidism can lead to similar consequences. Risks are associated with abundant consumption of water, s alt, alcohol. More often, symptoms of heart failure are observed in smokers, pregnant women. It is possible to identify stage 1 heart failure (and other levels of development) against the background of a violation of the ability of the heart muscle to contract.
How to notice?
It is possible to assume any stage of chronic heart failure or acute if orthopnea appears, in which a person takes a stable unnatural posture, due to the preservation of which it becomes somewhat easier for him physically. Loads provoke shortness of breath, for some, breathing problems accompany being at rest. Suffocation comes in attacks, coughing bothers at night.
You can notice CH by a weak state and confused consciousness, a tendency to get tired at the slightest load. In the daytime, diuresis is reduced, dizziness is often felt, a feeling of discomfort is born under the ribs on the right, especially strong if there is an insufficiency of the right ventricle. In addition, there is swelling, especially pronounced in the evenings. Some in various stages of heart failure(2, 1, 3) ascites appears, that is, a condition in which the peritoneum becomes an area of localization of the accumulation of liquid secretions. HF can trigger acrocyanosis.
Clarification of the diagnosis
To say at what stage heart failure (3, 2, 1) is observed, only a qualified doctor can. Before making a diagnosis, the doctor will conduct a series of examinations and tests to determine exactly what had to be de alt with. Blood tests are considered basic - general and biochemistry. The patient is referred for an x-ray of the sternum. As a rule, ECG, ECHOCG are shown. A patient suspected of having HF is recommended to undergo ventriculography, coronary angiography.

Types and forms
In medicine, consider the stages, functional classes of heart failure. All cases are divided into acute, chronic. For the second type, it is customary to single out several steps of state progress. The easiest is when an intense load provokes heavier breathing, the heart beats faster than normal, the sensations become strong. If there were no such manifestations earlier under load, but over time they appeared, they speak of the first stage of HF.
When allocating functional classes, stages of heart failure, they speak of a condition where moderate activity already provokes breathing difficulties. At the same time, there is a lack of blood flow, manifested by coughing and heart failure, muffled pulmonary rales and spitting up blood. This condition belongs to stage 2a. Gradually appearmanifestations of insufficiency of blood flow in a large circle. This reveals itself as swelling of the legs, especially strong in the evenings.
Stage 2b indicates hepatic hypertrophy, leg swelling, ascites, and cyanosis. Respiratory disorders are observed even at rest, the heart is disturbed by soreness and instability of functioning. The patient is diagnosed with oliguria, hydrothorax.
Status Progress
The third stage of heart failure manifests itself as blood flow disorders in both circles. Examination of the respiratory system shows pulmonary irreversible changes. There is pneumosclerosis, hepatic cirrhosis. The therapeutic course in most cases shows inefficiency. Based on the areas of lesions, they speak of heart failure in the left ventricle. In the large circle, the amount of moving blood decreases, and congestion appears in the small circle. HF in the right ventricle leads to stagnation in the large circle, while the small one becomes poorer.
Possible third stage heart failure with mixed symptoms. As a rule, congestion is localized in both ventricles.

Group system: American version
A specialized NYHA classification proposed by New York cardiologists has been developed. This division method involves dividing all patients into four large groups. The first class includes persons who, during normal physical activity, characteristic of everyday life, do not have shortness of breath. The second class is such a stage of heart failure,when the patient is faced with minor restrictions, it becomes more difficult to cope with physical exertion. The third group includes people whose activity causes significant problems. The fourth category includes people who have trouble breathing even when completely at rest.
How to fight: general information
If studies have indicated any stage of heart failure (decompensation, compensated), it is necessary to start treating the pathological condition. The choice of therapy remains with the doctor, who is able to assess the nuances of the case and take into account the characteristics of the patient's body, its characteristic allergic reactions. First of all, they identify what provoked the failure of the organ, and form a program to eliminate the root cause.
The patient is shown to take funds that effectively fight congestion in the circulatory system. To do this, at different stages of heart failure, you will have to drink diuretics, Asparkam, Veroshpiron. The drug "Panangin" has proven itself well. The patient will benefit from means that optimize cardiac output, normalize the functioning of the circulatory system, supply oxygen and nutrients to the tissues. If the therapeutic course does not give the desired result, the patient may be referred for surgery.

Consequences
If the end stage of heart failure is detected, the patient neglects the advice of the doctor and does not treat the treatment in detail, there is a high probability of a variety ofcomplications. In particular, sudden death of the heart threatens. High probability of thromboembolism, thrombosis. A person faces an increased risk of liver failure, conduction failures, rhythmic contraction of the heart muscle.
Can I warn you?
In order not to learn from experience what end-stage heart failure is, it is wise to lead a he althy lifestyle. Primary disease prevention includes early detection of any diseases that affect the heart and responsible treatment of these pathologies. If a person is affected by factors that are more likely to cause HF, they should be eliminated or changed whenever possible.
Secondary prevention involves eliminating manifestations of organ failure and preventing deterioration.

Compensated and non-compensated insufficiency of blood flow
NK - circulatory failure - a pathological condition in which organs, tissues do not receive the necessary nutrition through the circulatory system. This affects the ability of cells to work, affects the course of plastic processes. It is customary to talk about compensated and uncompensated forms. In the first case, the symptoms are detected after exercise, the second option is the presence of signs in a resting, relaxed person.
Since there are acute and chronic forms of HF, therefore, we can talk about a combination of signs when determining featurescase. For example, a doctor can identify a patient with chronic heart failure in the stage of decompensation. This will be called a condition in which symptoms appear only after certain loads, while the case develops slowly, and the probability of death at the time of the attack is small.
Terminology and features
CH is commonly referred to as the state in which circulatory hypoxia is formed. The quality of the blood flow is disturbed, which leads to a lack of oxygen. Sometimes the condition is observed with an increase in pressure on the heart muscle due to the release of exudate, in some cases, HF can be provoked by electrical damage, bruising, injury. HF is possible with prolonged ischemia, an acute form of such a disease.
Chronic heart failure in the stage of decompensation can develop if the heart is faced with too high loads. It is customary to divide all the causes leading to HF into two classes: initiating pre-, afterload in excess of the norm. Preload refers to blood flowing towards the heart. It fills the ventricles, and inflow in excess of standard volumes can provoke insufficiency in the functioning of the valvular system, hypervolemia, hemoconcentration, polycythemia.
Afterload is the resistance of an organ to the movement of blood from its cavities into the blood vessels. The increase in OPSS leads to an increase in afterload. Often the condition is observed with increased pressure, valvular stenosis, hydropericardium. The reason may be a decrease in vascular aortic, arterial lumens.

Mechanisms of pathology
It is customary to evaluate the primary mechanism for the formation of a pathological condition. They analyze the work of the veins through which blood moves to the heart, and the contractility of the muscle structures of the organ. The primary cardiogenic form is diagnosed when the ability of tissues to contract decreases, while the volumes of blood coming from the veins are close to standard. This form of pathology can be provoked by damage to the myocardium of a diverse nature. Sometimes the cause is a focus of inflammation, in other cases, ischemia, poisoning.
The secondary form is observed when the volume of blood flowing through the veins to the heart is reduced while maintaining the contractility of the organ. This condition is possible if there is a significant loss of blood or fluid secretions accumulate in the pericardial area. Muscles cannot relax at the moment of diastole, as a result, full filling of the ventricles is impossible. Paroxysmal tachycardia can provoke a pathological condition.
Metabolism and overload as sources of CH
Metabolic HF is diagnosed when coronary blood flow is impaired. The same is possible when a focus of inflammation appears in the heart, a metabolic failure, and a disruption in the functioning of the endocrine system. Arrhythmia can provoke metabolic HF. The basis of such a pathology is metabolic failures that normally occur in the heart muscle, due to a lack of oxygen and energy reserves. Enzyme structures are disturbed, the balance of electrolytes is disturbed, the regulation of the body's work throughimpulses of the nervous system.
Overload HF is observed in vascular, cardiac defects, high blood pressure, an increase in the volume of fluid in the circulatory system. The pathological condition is explained by a prolonged increased load on the myocardium associated with an excess of inflowing blood or a weakening of the outflow. First, the condition develops into compensatory hyperfunction, then organ hypertrophy is observed. The third stage is cardiac decompensation, that is, the failure of the organ to function. A progressive lack of oxygen in the myocytes of the heart leads to dystrophy affecting protein and lipid structures. Myofibrils die, lack of energy increases, muscle tone of the heart decreases.

Drug therapy: features of drugs
For heart failure, ACE inhibitors are often used. Studies were organized in our country that showed the reliability and safety of the use (in accordance with the instructions) of the drugs Fosinopril, Trandolapril, Captopril. The medicines "Ramipril" and "Enalapril" have a good reputation. Medications of the ACE inhibitor group are recommended to be taken in CHF at any stage of pathology development. The etiology of the disease, the features of its development and the functional class of the case do not play a role. The absence of this group of drugs in the therapeutic program is associated with an increased risk of death. The earlier the patient started taking an ACE inhibitor, the slower the progression of the chronic disease. It is recommended to use medicinesthis group with blood pressure of 85 units or more. With reduced rates, the effectiveness of the funds is preserved, which means that the drug course should still include ACE inhibitors, however, in reduced concentrations. On average, half the standard doses are prescribed.
Hypotension has been noted to occur shortly after initiation of ACE inhibitors. This is due to the effect of the active compound on neurohormones in the circulatory system. The use of a titrating dosage allows you to avoid this effect or reduce it to a minimum by the 14th day of using the drugs. A long course of ACE inhibitors is effective due to the blockade of neurohormones. In order for the treatment to be as effective as possible, it is necessary to use ACE inhibitors without combining drugs with beta-blockers, nitrates or CCBs. When hypotension is eliminated, a combined drug course is started.
Aldosterone antagonists in HF
Spironolactone medications are often prescribed for HF. This substance is widely used in medicine and has been used as an element of complex treatment since the middle of the last century. It belongs to the class of potassium-retaining diuretics. The main indication for the use of the composition is CHF in decompensated form. The drug is prescribed for excessive accumulation of fluid in the body. Spironolactone is usually combined with loop, thiazide diuretics.
If it is necessary to achieve a compensated state, spironolactone is considered a classic and indispensable element of the therapeutic course. Almost always, this remedy is prescribed for CHF of the third orfourth type. It is necessary to combine the composition and ACE inhibitors in an increased dosage. The program is prescribed for a long course. The task of medications is to ensure stable positive diuresis. As the compensated state is reached, instead of the abundant use of spironalactone, neurohormonal formulations in small volumes are shown.

Diuretics
Diuretics should be used for symptoms that indicate the accumulation of excess fluids in the body. When choosing drugs and the nuances of taking them, the negative effect of the drugs on the patient's body, in particular, on the system of renin, angiotensin, and aldosterone, is taken into account. Drugs can cause electrolyte imbalance.
Diuretics are always prescribed in combination with an ACE inhibitor, thereby reducing the effective dosage. The weakest effective drug should be used. Shown to be mandatory to have a backup type, dose used in case of decompensated condition.