- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Rupture of the biceps (biceps tendon of the shoulder) is considered to be a complete or partial separation from the place of its attachment to the bone. Typically, such an injury is diagnosed in males who play sports or are associated with power loads. This pathology is quite common today. For its therapy, surgery is most often used.
Characteristics and description of the problem
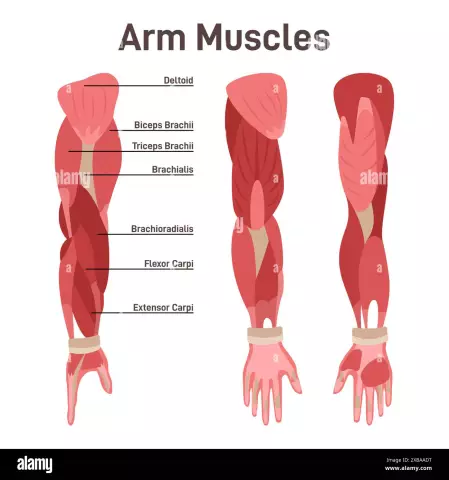
Biceps tear is a common injury that occurs in 90% of cases in its proximal section. The biceps muscle is involved in the process of arm activity, it flexes it at the elbow joint. It has two tendons that are attached to the shoulder blade. When detached from the place of attachment of the biceps, the entire upper limb suffers, as the strength of flexion in the elbow joint and rotation of the forearm outward decreases. Important vessels and nerves are located in this place, so surgery can in some cases provoke complications.

Biceps tendon tear leads tothat a person is less able to tolerate physical activity. So, there is a limitation of movements, acute pain. Most often, the gap occurs on the dominant hand. In the absence of therapy, a pronounced cosmetic defect will be observed, the functionality of the entire upper limb will be impaired.
Rupture of the tendon can be partial, when the injury does not completely cover it, and complete, which divides the tissue into two parts. Most often, damage begins with small perforation gaps, then, with the progression of the pathological process, the biceps is completely torn. Most often, its long head is damaged.

Why does pathology occur?
The reasons for the detachment of the biceps can be different. Sometimes this happens due to chronic inflammation (most often with rheumatoid arthritis, elbow bursitis) and chronic microtrauma in the subacromial zone. These injuries lead to a decrease in the strength of the tendon, increasing the risk of rupture after a minor injury. Tendon detachment occurs frequently during excessive force exertion in sports. Also, bicep detachment can occur in old age due to damage to the rotator cuff.
Smoking, taking certain medications, steroids is a trigger that often leads to damage.
Biceps tear most often occurs under the influence of these risk factors:
- Old age. In this case, the increased load on the biceps is observed for a longer period of time than at a young age.
- Heavy lifting associated withoccupational activities, causing the tendons to wear out faster.
- Strong stress on the shoulder joint. Most often, biceps tear occurs in athletes involved in swimming or tennis.
- Smoking. It is known that nicotine affects the delivery of nutrients to the tendons - it slows it down.
- Taking corticosteroids.

Symptoms and signs
With a partial rupture of the biceps, there is pain in the cubital fossa, swelling, weakness when bending the arm in the elbow joint, while movements do not suffer. There are also negative changes in the soft tissues in the damaged area, the biceps muscle of the shoulder is deformed as a result of the upward displacement of the biceps. It becomes difficult for a person to turn their hand down or palm up.
Often during a bicep tear, patients hear a characteristic pop or click, a bruise appears that goes from the shoulder down to the elbow. In some cases, the injury is asymptomatic, with only a bulge or induration in the area between the elbow and shoulder.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosing a bicep tear is easy. To make a diagnosis, it is usually sufficient to make a visual examination and study the anamnesis of the pathology. Radiography will not give important information in this case, it is carried out to rule out fractures.
In some cases, the doctor may order an ultrasound or MRI. Usually, instrumental examination methods are used to exclude other pathologies.

Therapy
Treatment can be conservative or surgical.
In the first case, the doctor recommends applying a cold compress for 20 minutes twice a day to reduce swelling. He will also prescribe NSAIDs, such as Ibuprofen or Naproxen, to relieve pain and inflammation. It is necessary to avoid power loads, movements with raised arms. The mobility of the limb will help restore physiotherapy.
Some patients require surgery. The operation is also prescribed for the ineffectiveness of conservative therapy, when negative symptoms persist for a long period of time.
The purpose of the operation is to attach the tendon to the bone. The doctor develops a treatment regimen in each case. The intervention is performed under general anesthesia. Below and above the cubital fossa, the surgeon makes incisions, through which he identifies the torn tendon, stitches it and fixes it to the bone with buttons, anchors or screws. The affected limb is then immobilized with an orthosis for three weeks.
Complications after surgery are extremely rare. They can only occur in the absence of therapy. In this case, the muscle may not heal properly, which will have a negative impact on its functionality. Also, if left untreated, a chronic defect may appear, it will be impossible to eliminate it even with a surgical method.
Today it is advisable to apply an individual therapy strategy, taking into account the characteristics of the body of each person. She assumesfollowing steps:
- Full examination of the patient to determine the pathology of the shoulder and elbow.
- Analysis of the benefits and harms of surgery, taking into account the age, profession of the patient, the presence of pain, etc.
- Carrying out a full rehabilitation for maximum restoration of limb functions.

Rehabilitation period
Sports and heavy lifting should be avoided for six months after surgery. At this time, it is recommended to perform therapeutic stretching exercises to restore the range of motion in the joints. Physiotherapy in this case is an important factor that affects the time to return to daily activities.
In some cases, with successful surgery and physical therapy, there may be a decrease in elbow flexion strength by 30% compared to a he althy limb. But usually it is possible to fully restore the functioning of the muscle.

Prevention
To prevent pathology, it is necessary to warm up the muscles well before training, you can’t overstrain them and subject them to heavy loads, swing your arms over your head, you need to avoid injuries. Doctors recommend leading a he althy lifestyle, adhere to proper nutrition.