- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
In the article we will consider acute and chronic sinusitis.
This is an inflammatory or allergic disease of the paranasal sinuses.
According to the ICD-10 system, acute sinusitis has code J01, chronic - J32.
Most often, such inflammation appears in the maxillary sinuses (then they talk about sinusitis), there is also a pathological process of cells of the ethmoid labyrinths (with ethmoiditis), the frontal and sphenoid lobes may suffer with sphenoiditis and frontal sinusitis. However, more often the disease spreads to several sinuses at once, and then a person develops polysinusitis. When all paranasal areas are involved, then pansinuitis develops. Let's talk further about acute and chronic sinusitis and compare these diseases.

Acute form: causes
So, let's take a closer look at what sinusitis is. Symptoms and treatment will be described below.
Causes of acute formoften there are acute respiratory illnesses along with viral infections (eg influenza), hypothermia, colds, common bacterial infections and injuries. The course of the disease can be aggravated by a deviated septum in combination with hypertrophy of the lower or middle shells, impaired immunity, an allergic process, an increase in the nasopharyngeal tonsils (adenoid vegetation in children).
Not everyone knows what kind of disease - sinusitis.
Acute symptoms
Equivalent to this:
- Having a runny nose for more than seven to ten days without showing signs of improvement.
- Presence of nasal congestion, purulent or mucous discharge.
- Drainage of pathogenic mucus down the back of the pharynx along with abundant purulent sputum mainly in the morning.
- The occurrence of headache, heaviness and discomfort in the area of inflamed sinuses. Sometimes discomfort goes to the area of teeth, eyes, cheekbones, cheeks.
- Presence of increased sensitivity of the facial skin in the projection of the affected sinuses.
- Increase in temperature to thirty-eight degrees and above. As a rule, such a symptom is observed in an acute case. In chronic processes, the temperature rises very rarely or can stay at a low-grade mark, that is, at thirty-seven degrees.
- Appearance of weakness, fatigue, irritability. The occurrence of photophobia, tearing, loss of appetite, sleep disturbances.
- Weakening of the sense of smell or its complete absence.
- Appearancepuffiness of the cheeks and eyelids.
To compare acute and chronic sinusitis, you need to understand the causes of these pathologies.
Causes of the chronic form of the disease
The main factors in the development of this form of pathology, in contrast to the acute type, include:
- Presence of deviated septum.
- Development of chronic rhinitis.
- The appearance of anomalies of the anastomosis between the nasal cavity and the sinus.
- The occurrence of allergic reactions.
- Decrease in human immunity.
- Presence of a focus of chronic infection (presence of chronic tonsillitis, dental pathology).
- Effect on the body of a polluted environment.
- Presence of fungal infections.

A factor that provokes an exacerbation of sinusitis can be a viral infection along with hypothermia. In odontogenic processes, dental manipulations can be the starting lever. With rhinogenic deviations, swelling of the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity and sinuses occurs along with a violation of natural cleansing and stagnation of pathogenic secretions (that is, mucus). Such stagnation, combined with impaired ventilation, is a trigger for the activation of inflammatory processes.
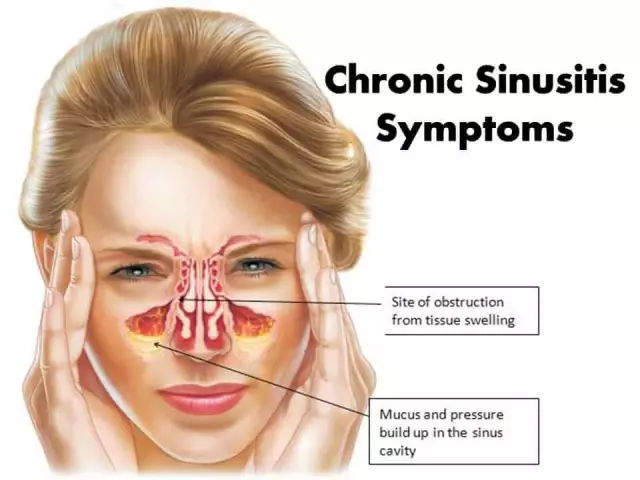
Symptoms of chronic sinusitis
The manifestation of chronic sinusitis depends on the form of the disease. Outside of an exacerbation, symptoms can be very scarce or absent altogether. Actually, this is the main difference between this type of sinusitis and its acute form. Most often a personworries:
- Presence of nasal congestion along with difficulty in nasal breathing.
- Appearance of scanty mucous or purulent discharge from the nose. This can occur in the form of drying crusts, while constant leakage from the nose is observed, which provokes cracks and abrasions of this organ.
- Occurrence of mucus runoff and along the back of the throat.
- Presence of dryness in the throat.
- The appearance of a headache.
- Presence of bad breath.
When the disease worsens, symptoms that are characteristic of an acute form of sinusitis may appear.
Diagnosis
As part of the diagnosis, the following examinations of patients are carried out:
- Performing an otorhinolaryngological examination.
- X-ray (or computed tomography) of the paranasal sinuses.
- Sinus ultrasound. It is worth noting that this technique is safe, has no contraindications, is used to diagnose sinusitis and as part of the control over the therapy process.
- Laboratory diagnostics (we are talking about a general blood test, sowing discharge from the sinuses or flushing on the flora, and so on).
- Performing an endoscopic examination of the nasal cavity and nasopharynx to establish the features of the anatomical structure.
Continuing to find out what sinusitis is. Its symptoms and treatment are interrelated.
Therapy
It is worth emphasizing that in the acute form of sinusitis, therapy is carried out in several directions. BeforeIn total, it is necessary to remove pus from the sinuses. In the vast majority of situations, conservative therapy for acute sinusitis is performed without puncture.

Removal can be done using the YAMIK technique. This procedure is performed using a device called the YAMIK catheter. The bottom line is that through a catheter in the nasal cavity, controlled pressure is created and pus is pumped out through a natural fistula (hole), and then a medicinal substance is injected (it can be antibiotics or mucolytics).
Sinusitis tablets will be discussed later.
In addition, the organ and paranasal sinuses are washed using the displacement technique. It is carried out with the help of a special suction, namely through an aspirator, during the procedure, the pathological contents are removed and drugs are injected into the sinuses.
But despite the existence of effective methods of non-puncture therapy of sinusitis, in some cases, punctures of the maxillary sinuses are still required. This procedure is carried out strictly according to indications and with mandatory anesthesia. After anesthesia, a low-traumatic needle is inserted through the nose into the sinus. All purulent contents are removed through the needle and the drug is injected. As a rule, the puncture is carried out completely painlessly, but at the same time it is safe. In the future, punctures with sinusitis do not affect the condition of the nose and its sinuses, and the small hole left by the needle heals without a trace.
Additional treatmentacute and chronic sinusitis, swelling in the nasal cavity can be eliminated, ensuring a normal outflow of contents from the sinuses. In an acute course, vasoconstrictor drugs intended for independent use are necessarily prescribed, and anemization of the nasal middle course is also carried out in the conditions of an otolaryngological office. Mucolytic agents (which thin the mucus) are given along with antiseptic and antibacterial drugs in the form of sprays and nasal drops. Very good effects are achieved when using a saline solution for washing the nasal cavity. Homeopathic medicines are also widely used.
No less important is the appointment of antibiotic treatment. Antibacterial general therapy for sinusitis is often prescribed for purulent inflammation against the background of fever and intoxication. It is very important to make the right choice of antibiotics, observing the dosage and duration of the drug. In any case, antibiotic therapy should be prescribed only by a specialist. With the use of combined treatment, absolute recovery in case of acute sinusitis is achieved within seven to ten days.
Complications
In the absence of adequate treatment, a person may develop the following general and local threatening complications:
- The appearance of an abscess or phlegmon of the orbit.
- Development of an intracranial abscess.
- Appearance of meningitis.
- The onset of sepsis.
If such complications develop, urgent surgical intervention is necessary.
Comparisonacute and chronic sinusitis we had. Now consider the general recommendations.

General recommendations for sinusitis
Sinusitis is an extremely common disease, and this disease can be cured. Therapy is possible on an outpatient basis, as well as at home, subject to the strict implementation of all doctor's prescriptions. Treatment with folk methods can only be used for general strengthening purposes. Traditional medicine will never replace the main therapeutic complex.
Any warming procedure for sinusitis is contraindicated, as it can lead to a worsening of the condition, and at the same time to the spread of inflammation with the subsequent development of complications.
Do not be afraid of an otorhinolaryngologist who will immediately perform a puncture. It is necessary to know that punctures of the maxillary sinuses are always carried out strictly according to the indications, only after an additional examination has been performed, and only when it is absolutely impossible to do without it. And in other cases, they use alternative, not terrible methods.
Sinusitis pills
In the presence of a moderate course of the disease, the drugs of choice are Amoxicillin and Ampicillin. The last remedy is prescribed, as a rule, if for some reason the first is not suitable. Alternative drugs are cephalosporins in the form of "Cefuroxime axetil" and "Cefaclor". Also, a patient with sinusitis can be prescribed macrolides in the form of "Azithromycin", "Clarithromycin" or tetracyclines (for example, "Doxycycline"), fluoroquinolones in the form of "Grepafloxacin" and sonext.
It is important to find out in advance which antibiotics to take for sinusitis.
In severe cases, the following medications are appropriate:
- The use of an inhibitor of protected penicillins in the form of "Amoxicillin", "Ampicillin" parenterally.
- Second and third generation cephalosporins such as Cefuroxime along with Ceftriaxone, Cefotaxime or Cefoperazone parenterally.
- In case of allergy to lactams, doctors prescribe "Ciprofloxacin" or "Chloramphenicol" parenterally.

Amoxicillin
Consider the instructions for use for the Amoxicillin suspension.
This is a child form of the drug. It can be prepared by diluting the granular drug with water. This dosage form of "Amoxicillin" for sinusitis has many advantages in comparison with the tablet:
- The drug in the form of a suspension is intended for the treatment of young children. Therefore, it has a pleasant sweet taste and raspberry smell.
- The spoon contains 250 milligrams of the drug, which makes it possible to determine the exact dosage of the drug, while focusing on the weight of the baby (and not just on his age).
- The composition of the suspension includes simethicone, which prevents the development of colic and bloating in very young children.
As the instructions for use for the Amoxicillin suspension indicate, in order to prepare this medicine, you need to add boiled water to the required mark. Next, the agent is well shaken until a homogeneous mass is obtained. After that, the suspension is ready for use. "Amoxicillin" for children in the form of a ready-made suspension can be stored for no more than two weeks, after which this medicine becomes more unsuitable for consumption. Shake well before each use. Next, we will find out how this disease manifests itself in children.
Symptoms of acute sinusitis in children
The clinical picture of a pathology such as sinusitis differs little from the symptoms of an acute respiratory infection. In children, a decrease in appetite and activity is observed along with an increase in temperature. But other signs are also developing:
- The appearance of bilateral or unilateral nasal congestion along with a change in the timbre of the voice due to this factor.
- Presence of mucous or purulent discharge from the nose, which may show traces of blood.
- Having a dry cough with no relief (common in children at night).
- The appearance of a child's complaints of a headache (its position directly depends on which sinus is inflamed).
- Pain in the head may be aggravated by bending forward and downward (for example, when tying shoelaces).
- The skin of the face over the inflamed sinus may become reddened.
- Smell acuity in babies is greatly reduced, or sensitivity to various odors disappears altogether.
- Dryness of the nasopharyngeal mucosa appears.
- The temperature rises above thirty-eight degrees.
- Facethe baby may look noticeably swollen.
- The onset of irritability along with frequent awakenings during sleep and increased sensitivity to light.
Learn how to cure chronic sinusitis for good.

How to cure sinusitis permanently?
Both forms of this disease are treatable, but for this a person will have to make a lot of efforts, strictly following all the recommendations of specialists. The basic rule is: therapy should be started immediately after receiving the diagnosis. There is no time to waste, because the inflammatory processes will continue until they are stopped, and this can only be done with the help of special medicines.
An excellent effect on sinusitis is provided by antibacterial medicines, such as Azithromycin and cephalosporins, which allow you to get rid of the main causes of the disease, that is, bacteria and viruses. In some situations, local antibiotics are prescribed in the form of "Bioparox" or "Isofra", their main task is to eliminate the infection, and at the same time to stop the inflammatory processes.

For the purpose of mucus outflow, nasal drops with sprays are used, for example, "Otlin" along with "Naphthyzinum", "Naftozolin", "Pinosol" and others. Mucolytic agents are used to remove mucous secretions from the sinus cavity, such as Guaifenesin. Homeopathic medicines are also prescribed for sinusitis, they are based on components of natural origin, whichreduces the risk of adverse reactions. However, drug treatment is not enough for the reasons that it suppresses the development of dangerous microbes, but does not completely remove pus from the sinuses. Along with such therapy for acute and chronic sinusitis, it is important to use alternative methods prescribed by the doctor.