- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Rotavirus infection, when it enters the human body, provokes an infectious process characterized by a short incubation period and an acute course. This disease mainly develops in children. This is due to a weakened immune system.
In adults, this infection is much less common and proceeds quite easily. Rotavirus manifests itself in the form of intoxication, respiratory and dyspeptic disorders. The main clinical manifestations continue for a week, after which recovery occurs. In especially severe cases, dehydration is observed.
Features of the disease
There are several types of rotaviruses that are similar in structure. That is why they are combined into one common group. Such microorganisms provoke the development of acute intestinal infections. All of these viruses are the main cause of gastroenteritis. The susceptibility of children under 5 years of age to rotaviruses is due to low stomach acidity and insufficient maturity of the immune system.

Worth itIt should be noted that a child at this age often repeatedly suffers from this infection. Moreover, the risk of getting sick increases significantly if he attends a kindergarten. Since there is always contact with a large number of children, among whom there may be a sick child.
Older children get sick much less often, as a mature immune system can fully fight infections. In addition, previously ill babies are already immune to certain types of rotavirus, which helps prevent infection.
Rotavirus infection in children under one year old is quite rare, especially if they are breastfed, since all the required antibodies are obtained from breast milk.
Causes of occurrence
To be able to correctly diagnose and choose the treatment of rotavirus infection in children, you must know what exactly provokes the onset of the disease. According to experts, infection occurs when the causative agent of rotavirus enters the body, which is transmitted by airborne droplets or the fecal-oral route. The main causes of infection are neglect of hygiene rules or the consumption of unwashed products.
It should be borne in mind that poultry or fish, as well as fermented milk products, can become a source of infection. In addition, dirty toys that children put in their mouths all the time can provoke infection into the body.
In case of re-infection in a child, the signs are less pronounced, since the body is already producingantibodies. Rotavirus refers to epidemic diseases, as there is a high risk of infecting others. The child becomes contagious when the first signs appear within 1 week.
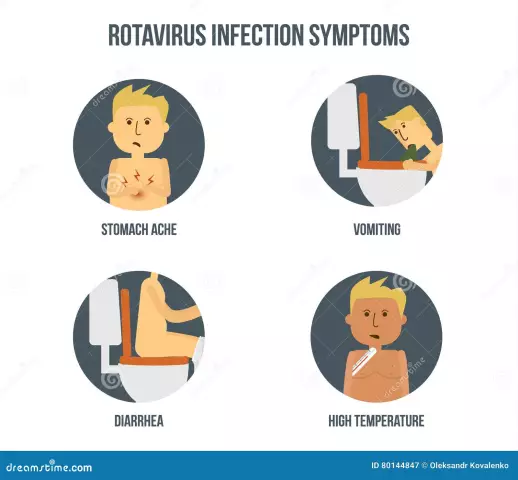
Main symptoms
The incubation period for rotavirus lasts for 1-2 days. The acute stage lasts about 4 days, and then gradually the signs of infection begin to decrease. Parents definitely need to know exactly how rotavirus infection manifests itself in children so that the presence of violations can be recognized in a timely manner. Among the main signs, one can distinguish such as:
- prolonged vomiting;
- fever;
- watery stool;
- pain and cramps in the abdomen;
- pallor and dry skin;
- plaque on the tongue;
- inflammation of the tonsils and sore throat;
- runny nose;
- dry cough;
- red eyes;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the tonsils, pharynx and nose is observed in almost every case of infection. With a severe course of rotavirus infection in children, vomiting is repeated and very plentiful. As a result, signs of intoxication of the body begin to appear, which is quite dangerous for the life of the patient. Features of the course of intestinal flu in children are expressed in:
- severe intoxication;
- prolonged vomiting;
- signs of respiratory disease;
- pronounced bowel disorders;
- dehydration.
The disease is quite acute. Sharpthe temperature rises, there is a decline in strength and appetite disappears. Initially, signs of a cold begin to appear, and then symptoms of gastroenteritis begin to appear.

When the disease is severe, many are interested in how long the temperature lasts with rotavirus infection in children. The fever may last for several days. A distinctive feature of rotavirus is the violation of the stool, and the color of diarrhea changes from the moment the infection enters the intestines.
Only complex treatment will help get rid of the existing problem and normalize the child's well-being.
How to distinguish rotavirus from other diseases
To distinguish the disease from other intestinal manifestations, it is imperative to know how rotavirus infection occurs in children, since it can often be confused with dysentery or salmonellosis. Dysentery proceeds quite sharply with an increase in temperature. After that, loose stools appear, the frequency of which is about 10 times a day, but it can be more often. During defecation, there are strong, pulling pains, which are often quite pronounced.
When salmonellosis occurs, the stomach and small intestine are affected. The disease begins quite acutely with an increase in temperature. After this, vomiting appears, as well as foamy stools. Among the main differences, one can single out the absence of signs from the respiratory organs.
Rotavirus infection can occur in children without fever, and that is why it can be confused with poisoning. That is why in the early daysimpossible to make an accurate diagnosis. If after 2-3 days the child does not feel better, then most likely he has food poisoning.
Features of leakage in infants
Newborns are mainly infected from the mother or medical personnel. Often, infection occurs with seasonal outbreaks. The disease in newborns and infants mainly affects the digestive organs, and inflammation of the mucous membranes is practically not expressed.
The main signs of a rotavirus infection include drowsiness, weakness, sunken eyes, deepening of the fontanel. Restless behavior of the baby and rumbling in the stomach indicate the presence of painful sensations. The child often vomits, which can be repeated, but often the next day it disappears. Among the main signs, diarrhea can be distinguished, while the stool is yellowish-white in color, sometimes it is frothy. As a result of this, dehydration of the body is observed, and the baby begins to lose weight dramatically.
If you find signs of dehydration, you should immediately consult a doctor, as urgent hospitalization is often required. This will avoid serious complications. In infants with severe diarrhea in the first few days, intoxication of the body develops. Its main signs are high fever, apathy, convulsions, chills. The child refuses to eat.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of rotavirus infection is based on the complaints of the patients themselves, as well as the existing symptoms. In addition, it is necessary to carry outstudies like:
- coprogram;
- enzymatic immunoassay;
- electron microscopy;
- PCR.
When an acute form occurs in the blood, a patient has leukocytosis and an increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Leukocyturia, proteinuria, casts are noted in the urine. Feces in a child are quite plentiful, frothy, and also with pieces of undigested food. Signs of an inflammatory process in the feces may be completely absent.
After a comprehensive study, the doctor prescribes treatment for rotavirus infection in children, which will eliminate bacteria and improve the baby's well-being.
Features of treatment
Treatment of rotavirus infection in children must be directed to:
- normalization of water balance;
- detoxification;
- eliminate signs of disease;
- prevention of secondary infection;
- restoring the functioning of the cardiovascular system and kidneys.
Hospitalization is required only if there are severe signs of dehydration, as well as in severe forms of the disease.
Drug therapy
Treatment of rotavirus infection in children is selected by a qualified pediatrician, which is why you should immediately consult a doctor when the first signs of the disease occur. There are no special drugs for the treatment of this disease, and the entire therapeutic course is aimed at eliminating the accompanying symptoms, as well as normalizing the functioning of the digestive organs.

During a severe degree of rotavirus, doctors recommend the use of droppers, especially with severe dehydration. In some cases, the child may have a rash all over their body. If this happens, then the use of antiallergic drugs is indicated. In some cases, an antiviral for children with rotavirus infection may be required, this helps to eliminate pathogens much faster.
To stop the gag reflex, the child can be given Motilium or Cerucal. Against accumulated toxic substances, you need to take Enterosgel or activated charcoal. In addition, such drugs are prescribed for rotavirus infection, such as Laktovit or Linex. They help provide reliable protection for the intestinal mucosa. Enterofuril will help prevent the growth of bacteria. If there is a fever, doctors recommend taking antipyretic drugs.
Folk techniques
You can use folk methods to relieve symptoms of rotavirus. A saline solution has a very good result, which helps prevent severe dehydration. To prepare it, you need to dilute 1 tsp. s alt and 5 tsp. sugar in 1 liter of water and take small sips throughout the day.

Well helps to cope with the virus decoction of St. John's wort, which must be taken 3 times a day. It is worth noting that this remedy is only suitable for children over 3 years old, and should be used strictly as prescribed by the doctor.
Rulesfood
To reduce the manifestation of the disease, as well as prevent dehydration, it is important to follow the rules for feeding a child with rotavirus infection. It must be sparing, and a dairy-free diet must be strictly observed. It is worth remembering that fermented milk products are a favorable environment for the reproduction of pathogenic bacteria. The exception is children who are breastfed. From the usual diet of the child must be excluded:
- fresh vegetables and fruits;
- sweets;
- fresh pastries;
- carbonated drinks;
- beans.

If the baby refuses to eat, then do not force feed him. In the nutrition of a child with rotavirus infection, drinking plenty of water should be in the first place. Dishes are best steamed or baked. In the first few days of the course of the disease, you can only consume foods such as:
- chicken broth;
- liquid porridge;
- baked apples;
- lean fish and meat;
- boiled potatoes;
- jelly;
- compote.
After the recovery of the baby for some time, you need to follow a diet for faster recovery and normalization of digestion.
Fight against dehydration
The patient needs to consume as much liquid as possible during the course of the disease. This is necessary to replenish fluid losses along with vomit and loose stools. That is why the child is given water, unsweetened herbal tea, compote.
Bin severe cases, when the baby is not able to drink on his own, the needs of the fluid in the body are replenished with the help of intravenous administration of special solutions. Milk-based drinks and carbonated water should be avoided. Sick children are strictly contraindicated in juices with a high content of fructose, sorbitol or sucrose. It is forbidden to eat foods that lead to fluid retention in the body.
Possible Complications
If the treatment is incorrect and untimely, then quite dangerous complications of rotavirus infection in children can occur, in particular, such as:
- disorders in the circulatory system;
- kidney failure;
- necrotizing enterocolitis;
- gastroenteritis.
In a short period of time, intoxication of the body and its rapid dehydration develops, which can lead to a more severe course of the disease.
Prophylaxis
It is possible to distinguish specific and non-specific prevention of rotavirus infection in children. Among the specific methods is vaccination. It is carried out in accordance with the planned calendar, but only at the request of the parents. Among non-specific measures for the prevention of rotavirus infection in children, there are methods such as:
- observance of norms and rules of hygiene;
- consume only boiled water;
- washing hands with soap;
- sterilization of baby dishes;
- strengthening immunity.

It is worth remembering that the virusIt is highly contagious and also very weakly affected by soaps and disinfectants. Only solutions of iodine, alcohol and chlorine can be effective.
Hygiene rules
During the course of the disease and after a rotavirus infection, be sure to wash your hands regularly, avoid contact with other sick children and adults. It is recommended to use chlorine-containing disinfectants during the acute period of the course of the disease, as well as to thoroughly clean and wash everything that is used to care for a sick child. This rule applies to dishes, doorknobs, toys, toilets.
The hospital also follows hygiene rules and precautions. Disposable gloves are used, and special disinfectants are used. It is worth remembering that the mere observance of sanitary and hygienic rules does not make it possible to fully protect oneself from infection, since the causative agent of the disease is quite stable in the environment.
Vaccination
For the past few years, experts around the world have recommended vaccination as the most effective way to prevent rotavirus. There are currently two types of vaccine available, namely Rotatek and Rotarix. These preparations contain attenuated live, non-pathogenic strains of the infection.

In the first week after vaccination, the child's condition may worsen somewhat. It is recommended to start preventive measures in the first months of a baby's life, when rotavirus is especially difficult.
Rotavirus infection, even if it is mild, can pose a very serious danger, especially for infants, which is why appropriate diagnosis and treatment should be carried out.