- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Medics believe that the most common disease in children on Earth is rotavirus infection. According to WHO, 125 million babies are infected with rotavirus every day on the planet! How many adults does this microbe infect? There is no such data. However, regarding children, the statistics are sad. The same WHO reports that every year 500,000 children under the age of 5 die from complications caused by rotavirus. The microbe is especially dangerous for babies.
Rotavirus does not cause much harm to adults, because their body is stronger and able to resist the pathogenic activity of the microorganism. In the case of a stool disorder, many adults tend to consider this a consequence of poor-quality food, they do not associate such a symptom with an infection, do not treat it, continue to go about their daily activities, go to work, go among people, not suspecting that they are the source of a dangerous disease.
In children, rotavirus infection is much more pronounced, and the symptoms are more severe, since the child's body is not yet ready to cope with toxic substances,that microbes secrete as a result of their vital activity. Therefore, this disease is often called childhood. There are rules on what to do when infected with rotavirus, what medicines to give the child, what complications can be with this disease. Information about this is presented in our article.
We will also consider what should be the diet for rotavirus infection in children, what can and cannot be done to a sick child, how to prevent the disease.
Microorganism in brief
For a Russian person, the word "rotavirus" is automatically associated with the mouth. But "company" does not mean part of the face, but "wheel" in Latin. The microbe was so named because it has a round shape, outwardly resembling a wheel with a clear rim and short spokes. It does not exceed 75 nm in diameter. Rotavirus is surrounded by three layers of proteins (capsid), so it cannot be harmed by gastric juice, intestinal enzymes and many antiviral drugs.

After entering the intestine, the microbe invades the limbic enterocytes located on the cilia of the intestine. These structures perform very important functions - the digestion of food, the absorption of nutrients, the release of enzymes necessary for the breakdown of food fragments. Having penetrated into the enterocyte, the microbe destroys it. Therefore, rotavirus infection in children is accompanied by a sharp violation of the digestive activity.
Microbes multiply at a fantastic rate. At the same time, they release toxins and some substances that cause symptoms similar to colds.diseases. For this, rotavirus is often mistakenly called the intestinal flu. However, he has little to do with a cold.
Routes of infection
In the vast majority of cases, rotavirus is introduced into the human body like any other intestinal infection, that is, by the fecal-oral route. Rotavirus infection in children is called the disease of dirty hands. Very often, mass infection occurs in kindergartens and other institutions where there is a large concentration of kids. Rotavirus can get into the mouth of a child, and from there penetrate into the intestines when using toys contaminated with microbes, when using household items, when hygiene is not observed, and also when in close contact with a sick person.

Komarovsky, a well-known doctor, says about rotavirus infection in children that it doesn't really matter how often and thoroughly the mother makes the child wash their hands. This cannot with a 100% guarantee protect against infection. Only vaccination helps. It must be done if you plan to go to the sea with your child.
It should be said that rotaviruses are very tenacious. They withstand very high and low temperatures, can exist in the external environment for a long time. Outbreaks of infection often occur in the cold season, which some experts attribute to the weakening of the body's defenses.
Symptoms
The incubation period of rotavirus infection in children can last only one day from the moment of infection. This applies to weakened babies and infants. Whymicrobes do not immediately manifest their introduction into the intestines? Because they need to breed there first. While few enterocytes are destroyed, the child's digestion is carried out close to normal, and a small number of microbes release not so many toxins that they can have a strong impact on the functioning of body systems. The stronger the baby and the older he is, the longer the incubation period of rotavirus infection in children. For many of them, it lasts up to five days, and in some cases it can stretch for a week.
In infants under 6 months of age, rotavirus infection does not occur, as they are protected by the mother's immunity. After six months, it stops working. Such children are the most vulnerable to rotavirus, as their digestive system is just beginning to function smoothly, and the body is still very weak.
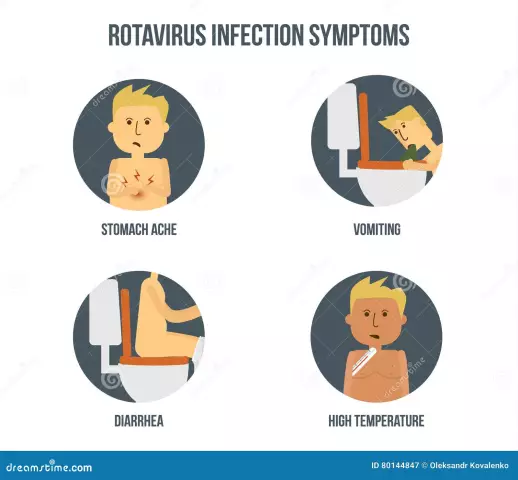
The disease develops abruptly:
- Baby has diarrhea. Potty trips can be more than 15 times a day.
- Vomiting at the same time.
- Severe abdominal pains appear.
- The temperature is rising.
- There is increased flatulence.
- Child becomes lethargic, refuses food.
Simultaneously with the "intestinal" signs of rotavirus infection, children also have "cold" symptoms, which often confuses parents.
This is:
- Treatment in the throat, its redness.
- Cough.
- Rhinitis.
- Pain when swallowing.
- Conjunctivitis.
- Plaque on the tongue.
- Inflammation of the lymph nodes.
Talking about the signs of rotavirusinfection in children, renowned pediatrician Komarovsky explains how to distinguish it from other intestinal disorders.

He says to pay attention to the consistency of the baby's feces. With rotavirus infection, the stool is always watery, grayish in color and smells very unpleasant, and with other problems with the stool - mushy.
The second sign is that the vomit may smell like acetone.
As the disease progresses (about day 3), the feces become clay-like, grey-yellow in color, and the urine takes on a darker tint (as in hepatitis).
In general, the disease proceeds with signs of gastroenteritis and enteritis.
Classification
It is often asked how long a rotavirus infection lasts in children. The answer directly depends on the form in which the disease proceeds:
- Easy. In a baby, the stool becomes more frequent slightly (up to 3-5 times a day), vomiting occurs once, the temperature rises no higher than 37.5 degrees. The general condition remains satisfactory, although there is a decrease in appetite and the child refuses to play actively. In this form, the disease can last 2-3 days.
- Average. Diarrhea in a child is observed of moderate intensity (up to 10 times a day). Other signs of the disease: rumbling in the abdomen, flatulence, temperature of 38 degrees, there are symptoms of a cold. With an average form, the disease can last up to a week.
- Heavy. It is not often seen. In this case, the symptoms are as follows: temperature 39-40 degrees,incessant vomiting, diarrhea 13-15 times a day, watery stools, abdominal cramps, signs of flu (cough, runny nose, hyperemic throat, conjunctivitis), lethargy, dry mucous membranes, rare urination. This form of the disease lasts 10 days or more.
When answering the question of how long rotavirus infection lasts in children, we must not forget about the recovery period. Its duration is from 3 to 7 days.

Dehydration
Doctors explain that rotavirus infection is not as dangerous as its consequences. They are the ones that lead to death. Dehydration is the most dangerous consequence of rotavirus infection in a child 3 years of age and younger. At an older age, fluid loss is also a very serious indicator of a child’s condition, but babies, especially infants, have more “chances” to die from this. That is why in infants the treatment of rotavirus infection at home is not carried out, it is necessary to put the patient in a hospital. Signs of dehydration:
- Weakness.
- Dry mucous membranes.
- Cry without tears.
- Reduce the number of urination.
- Reducing the amount of urine. In infants, this can be determined by the fullness of diapers.
- Sunken eyes.
- Pointed nose.
- Loose skin.
- Tachycardia.
- Thirst.
- Low blood pressure.
- Thick blood (sign for doctors).
Such complications are observed not only in infants, but also in weak, very thinchildren, especially those with a history of pathologies of the kidneys, heart and intestines.
Other complications
Rotavirus infection in a child 2 years of age and younger (who is very difficult to get to drink plenty of fluids) without urgent action can lead to the following complications:
- Pneumonia.
- Disorders of the nervous system.
- Bacterial intestinal infections.
- Convulsions.
In the hospital, children are immediately put on drips to replenish their water-s alt balance.
Pneumonia is a bacterial disease. It joins the rotavirus infection due to the weakening of the protective function of the lungs due to the loss of electrolytes, as well as with thickening of the blood. The main external sign of this complication is a very high temperature. In the future, the diagnosis is confirmed by laboratory tests (blood test) and x-ray results. With signs of pneumonia, the child needs to be urgently hospitalized.
Cramps are also a consequence of dehydration. Most often they occur at high temperatures. If the child is not given professional help, he may die due to spasms of the respiratory system.

Diagnosis
As noted above, with rotavirus infection in children, the incubation period lasts from 1 to 7 days. At this time, as a rule, no signs of the disease are observed.
Suddenly appearing vomiting and diarrhea can lead parents to think that the child has been poisoned by some food, and "cold" symptoms - to the fact that he hasflu or SARS.
To make an accurate diagnosis, tests are required:
- Blood common. It is ineffective for confirming rotavirus infection. However, it helps to identify the possibility of complications and decide how to treat rotavirus infection in children. In this analysis, the presence of a child is determined: leukocytosis (increased leukocytes), leukopenia (decreased leukocytes), lymphocytosis (increased lymphocytes), hematocrit. The latter is an indicator that determines the ratio of blood cells to its liquid part; in children older than 1 month, it should be 45%. Gradually decreasing, it reaches 37% by the age of 5, and then increases again. Deviations can be harbingers of problems with the heart, brain, kidneys. Pay attention to ESR.
- Urine common. It is also not informative, accurately indicating the presence of rotavirus in the body, but allows you to identify disorders in the genitourinary system.
- Coprogram. Allows you to determine how disrupted the process of absorption of nutrients in the intestines and the level of damage.
- PRC. With the help of this analysis, the presence of the virus in the feces is determined.
- Saliva, vomit, other biomaterial.
- Express test. It can be carried out at home. This test is sold in every pharmacy. It comes with detailed instructions, a cone with a solution and an indicator panel with two windows. The sample is placed in one, the result is shown in the other. Near this window there are two letters "T" and "C". If a red stripe appears against the first one, and a green stripe against the second one, the resultpositive. If nothing appears against the letter "T", the test is negative. If there are other options, the test is corrupted and should be repeated.
How to distinguish rotavirus infection from other diseases
Determining how to treat rotavirus infection in children, you must first differentiate it from other problems that occur in babies in the intestines:
- Enteritis and gastroenteritis. These conditions may also present with fever, diarrhea, dehydration, and seizures, but no signs of a cold.
- Flu. Common symptoms are fever, cough, runny nose, lethargy, loss of strength, sore throat, swollen lymph nodes, headache. However, vomiting is extremely rare (as an individual reaction of the child to the virus), and diarrhea is not typical at all.
- Dysentery. The incubation period of the disease (as with rotavirus) is 2-3 days. The manifestation is abrupt. Symptoms: frequent diarrhea, vomiting, high fever, weakness, rumbling in the abdomen, abdominal pain. Distinguishing features: in the feces with dysentery, one can observe characteristic greenish mucus, sometimes with blood streaks, vomiting occurs 1-2 times, no more, and there are no symptoms of a cold.
- Food poisoning. This pathology makes itself felt already in the first hours after ingestion of poor-quality food, that is, an incubation period of several days, as a rule, is not observed. Symptoms: vomiting, diarrhea, high fever, dark urine, weakness, pallor of the skin, rapid breathing, low blood pressure, but nocough, runny nose, sore throat.
To make sure you have/absence of rotavirus at home, you need to do a rapid test.

What to give a child with rotavirus infection
When initial symptoms occur, not all parents rush to call an ambulance, trying to cope with diarrhea and fever on their own first. Talking about the treatment of rotavirus infection in children, Komarovsky explains in detail what not to do:
- Give your child medication for "diarrhea". The fact is that viruses are removed from the intestines with feces. You can count them in the trillions. If diarrhea is abruptly stopped, all of them will remain in the intestines, which will significantly aggravate the course of the disease. In addition, the stagnation of feces promotes the absorption of toxins into the bloodstream.
- Give your child antibiotics. In this case, they only bring harm, since they do not act on viruses, but weaken the immune system even more. These drugs are needed only if pneumonia or bacterial infections of the digestive tract have joined the rotavirus.
- Buy homeopathic medicines ("Anaferon" and analogues). Komarovsky believes that they are of no use, but they significantly reduce the family's budget.
- Force feed the baby. Only if he insistently asks for food should he be offered a light porridge.
Let's consider what to give a child with a rotavirus infection:
- Plentiful drink. If the child refuses to drink water, tea, compote, then he must be forced to drink, pouring liquidlittle by little.
- Rehydrants. Humana Electrolyte, Regidron. If they are not at home and in the nearest pharmacies, you should make the following solution: dissolve sugar (2 tablespoons) in a liter of water, a spoonful of s alt with baking soda. These drugs should be given by force if the baby refuses to drink them voluntarily. You can use a spoon or a syringe without a needle for this purpose.
- Sorbents. Suitable "Smekta", "Enterosgel".
- Antipyretic at high (more than 38 degrees) temperature.
The need for treatment with antiviral drugs, many doctors, including Komarovsky, consider it not entirely justified, since there are no drugs yet that have been proven effective against rotavirus.
But many pediatricians prescribe Arbidol, Cycloferon, Viferon, Kipferon suppositories for children with this disease.
What to feed a child with rotavirus infection
Above, we noted that you should not forcefully give food to a child. Lack of appetite is a protective reaction of the body, because all digestion processes are disturbed in the patient's intestines.
Babies should continue to give their mother's milk. It will help fight infection, although in the acute period it can cause increased diarrhea. If babies are bottle-fed, they should be switched to lactose-free formulas, as rotavirus often causes lactase deficiency, which means intolerance to this enzyme.
For children of other age categories, there are rules for feeding when infected with rotaviruses:
- Giving foodvery small portions.
- Take small breaks between feedings.
- Steam everything.
In the first day or two, doctors advise offering the baby to eat an apple (baked), banana, croutons and boiled rice.

Diet for rotavirus infection in children is that you can leave on the menu:
- Porridges on water without oil and sweeteners (semolina, oatmeal, buckwheat, rice).
- Vegetable broth on water with rice.
- Steamed omelet, meatballs, lean fish, chicken.
- Crackers.
- Baked apples.
- Boiled vegetables (zucchini, carrots, some potatoes).
- Homemade fruit marmalade.
- Dairy products (low-fat cottage cheese, kefir, yogurt) can be offered to a child if his body tolerates lactose well.
What to feed a child with rotavirus infection? We have de alt with this. Now let's see what he should not be given:
- Fatty first courses, broths.
- Sausages, sausages.
- Pasta.
- Sweets.
- Porridge (barley, wheat, millet).
- Raw fruits (except banana).
- Raw vegetables (cucumber, tomato, onion).
- Nuts.
- Chocolate.
- Any pickles and marinades.
During the recovery period, you should also follow a diet. Not recommended for children:
- Whole milk.
- Ice cream.
- Beans.
- Fatty dishes (meat, fish).
- Rye bread.
- Milletporridge.
In closing
About rotavirus infection in children, Komarovsky says that up to 5 years, as a rule, 98% of children get sick with it, and the rest will be infected with this virus later. That is, knowledge about its symptoms and treatment is relevant for each of us. There are no effective preventive measures that protect against rotavirus. The only thing that can help is vaccination. In those who have been ill, immunity is observed only in the first months, that is, you can catch this infection several times.
The main thing that parents should do when characteristic symptoms occur is to call an ambulance, and also start giving the child plenty of fluids at room temperature. If the doctor suggests hospitalization, you cannot refuse it. If the form of the course of the disease is not severe, you can walk with the child in the fresh air, but at the same time he should not be allowed to communicate with other children. The baby remains contagious until fully recovered, even if he no longer has dangerous symptoms (vomiting and diarrhea).
In order to prevent rotavirus infection for other children, the parents of a sick child should not send him to child care until the tests confirm that the disease is completely cured.