- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Everyone knows that babies need milk. It delivers to the child's body everything necessary for normal growth and development. But in some cases, the baby cannot drink milk or eat products containing it. For 10% of babies, this he althy drink becomes poison, causing a severe allergic reaction. Most often, this is intolerance to milk proteins, one of which is beta-lactoglobulin.
Milk protein allergy
Intolerance to various foods is becoming more common in children now. The body reacts especially strongly to foreign proteins, such as milk proteins. Allergy to milk affects one fifth of all babies under one year old. Moreover, the negative reaction extends to cow, sheep and even goat milk, as well as products based on them.
This is due to the peculiarities of the digestive system of babies. The microflora of the digestive tract has not yet formed, so the walls of the stomach are permeable to allergens, which can cause a strong negative reaction. In addition, babies do not yet have enzymes to break down suchcomplex proteins into simple amino acids. These enzymes appear in a child after a year, so only 2% of adults suffer from milk allergy, mostly people with pathologies of the immune system.
Milk has a complex structure. In addition to useful trace elements and vitamins, it contains a large number of antigen proteins that can cause an allergic reaction in the body. But out of almost three dozen proteins, only four most often cause allergies. This is casein, which contains 80% in milk, serum albumin, alpha-lactoglobulin and beta-lactoglobulin. Allergy to the latter manifests itself most often, but this pathology does not proceed as seriously as others. Moreover, in most cases, intolerance to this protein disappears on its own after a year.

What is beta-lactoglobulin
This is one of the milk proteins. It contains about 10% in milk, in this respect it ranks second after casein. Beta-lactoglobulin is found in all milk except breast milk. It is found in almost all dairy products, even baby food. A feature of this protein is that it is destroyed during prolonged heating and lactic fermentation. Therefore, people with sensitivity to it can safely consume hard cheese.
Allergy Causes
The main reason for intolerance to this milk protein is the immaturity of the child's digestive system. After the birth of the baby, she is adapted only to the digestion of breast milk. And the rest of the food is perceived by the body as foreign, thereforean immune response occurs. Usually, by the age of 2, when the microflora is formed and the body has enzymes for digesting proteins, the allergy disappears. But still, about 2% of adults suffer from a lifelong milk intolerance.
The risk of developing allergic reactions increases if the mother's pregnancy proceeded with pathologies, severe toxicosis, if the mother did not eat properly while carrying the child, and also if the family lives in an ecologically unfavorable area or close relatives also suffer from allergies. In addition, such a pathology is often found in babies who were weaned early, fed poor-quality mixtures, or began to introduce complementary foods very early.
In children after a year and adults, an allergy to beta-lactoglobulin can develop for the following reasons:
- hereditary predisposition;
- being allergic to other substances;
- enzyme deficiency;
- inflammatory bowel disease;
- excess specific immunoglobulin in the blood.

How allergies manifest
Milk proteins are absorbed by the body only after splitting them into simpler chains of amino acids. If this does not happen, and complex protein molecules enter the bloodstream, the body's immune response occurs. Most often, a child's allergy to beta-lactoglobulin is manifested by gastrointestinal disorders:
- in infants it is frequent spitting up, in older children it is vomiting;
- baby chair becomesliquid with undigested pieces of food or curdled milk;
- there is pain in the abdomen, so the baby is constantly crying;
- due to a violation of the microflora, intestinal infections often develop.
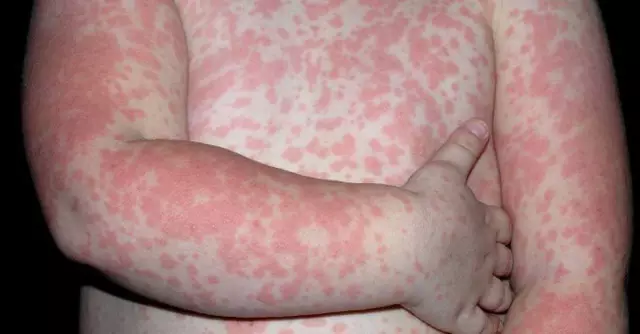
Characteristic signs of allergy to milk protein are skin pathologies. It can be atopic dermatitis, eczema, crusts on the head, urticaria. In the most severe cases, Quincke's edema develops. The respiratory system is also often affected in children. The child sneezes, he has a runny nose, shortness of breath. It is dangerous if laryngospasm develops. In addition, an allergy to milk protein can be a trigger for the development of bronchial asthma in a baby.

Diagnosis
To understand that a child is allergic to beta-lactoglobulin, and not, for example, lactose intolerance, you need to see a doctor. An experienced specialist, after talking with parents and analyzing the symptoms, can immediately make a diagnosis. But usually additional examination methods are also prescribed:
- coprogram;
- fecal analysis for dysbacteriosis;
- blood test for immunoglobulins;
- skin prick test.

Beta-lactoglobulin: what foods contain
A child with intolerance to this type of protein should be removed from the diet of all products containing milk or even traces of it. Only hard cheeses are considered harmless, sometimes cottage cheese or kefir is allowedown cooking. A mother who is breastfeeding a child should also refuse these products. Formula-fed babies should be switched to hydrolysate formulas. In addition, you need to know where else beta-lactoglobulin can be found. What products contain this protein, mothers do not always imagine, although now manufacturers must indicate such information on the packaging. What kind of food can be dangerous for a person with an allergy to beta-lactoglobulin? List includes:
- cookies, cakes, bread, pastries;
- butter;
- marshmallows, ice cream, chocolate and some other sweets;
- any dairy desserts;
- milk powder and baby milk porridge.

What to do if your child is allergic to milk protein
When beta-lactoglobulin intolerance appears, the first thing to do is to change the diet, removing all dairy products from it. If the child is breastfed, this should be done by the mother, but breast milk should not be refused. In severe cases, when swelling develops, severe itching or respiratory failure appears, you should consult a doctor. After all, only with the help of special drugs can you get rid of such symptoms.