- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
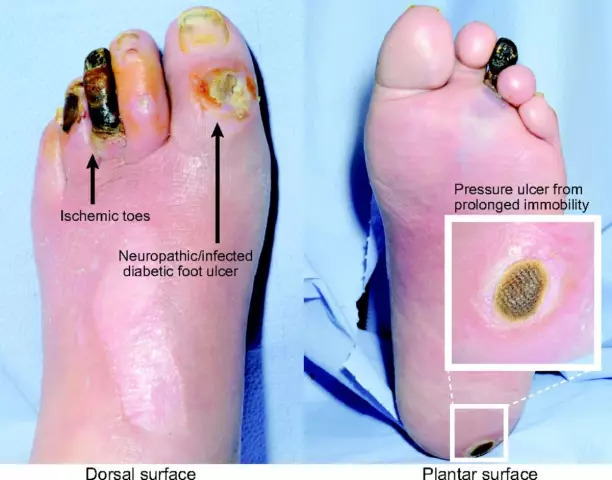
The diabetic foot is a complex of anatomical and functional changes that can occur in diabetic patients. In general, pathology is a serious lesion of the skin, arteries and capillaries, bone, muscle tissue and nerve cells. While there are many factors that cause diabetic foot development (the photo will only give a partial idea of this problem), its main cause is the toxic effect of blood sugar.
High concentration of glucose leads to impaired innervation and blood supply to the lower extremities. Against the background of diabetes mellitus and natural loads on the foot, soft tissues are damaged and their subsequent destruction. The rate of progression of the disease is largely determined by the duration of the course of the underlying disease and the quality of its treatment. Diabetic foot, in simple terms,is one of the most dangerous complications of diabetes.
Why the soft tissues on the legs are affected
Because this syndrome occurs late in the development of diabetes, its causes are directly related to the prolonged exposure of small and large vessels to sugar, present in destructive concentrations. In diabetics, all internal organs, muscles, bones, cartilage suffer, but given that the lower limbs (especially the feet and ankles) are located far from the heart, their blood supply worsens due to the disease. In addition, it is known that poorly controlled diabetes mellitus can provoke the development of atherosclerosis and other vascular diseases that interfere with normal blood circulation.

A diabetic patient eventually develops peripheral neuropathy, in which he practically ceases to feel damage to the foot, and since the maximum weight pressure when walking falls on the lower limbs, the wounds heal for a long time. Damaged nerves do not allow the patient to fully feel their legs. In the initial stages of a diabetic foot (it is difficult to see any shocking changes from the photo), patients are not always able to determine the position of the legs and fingers when walking and balancing. A he althy person with normal innervation feels that his shoes are rubbing his skin or a stone has got into his shoe and prevents him from walking further. A patient with diabetes, on the other hand, may not perceive a stone, scratch, or callus.
A fungal infection carries a similar dangerepidermis or nails, therefore, at the first symptoms of damage or bacterial damage to the skin, it is urgent to be examined. A person suffering from diabetes for more than a year cannot ignore even such a “trifle” as an ingrown toenail.
Who is at risk
The chance of developing diabetic leg ulcers increases several times if the patient:
- Often feels numbness, tingling or burning sensation in the lower extremities.
- Has a history of pathology of peripheral vessels that prevent proper blood circulation.
- Wears poor-quality, ill-fitting shoes. Incorrectly chosen shoes are uncomfortable, and if a he althy person feels this, then a patient with diabetes may not notice red spots and calluses for a long time.
- Suffers from foot abnormalities (e.g. flat feet or hallux valgus).
- He has had diabetes for over 10 years.
- Smokes and abuses alcohol.
If a person falls into a risk group, then in order to prevent the development of a diabetic foot, he must definitely inform his doctor about potentially dangerous factors.

Syndrome classification
Based on the reasons that cause the development of a diabetic foot, doctors distinguish several main forms of the syndrome:
- neuropathic;
- ischemic;
- combined.
In the first case, damage to nerve cells predominates, with an ischemic diabetic foot (they are not shown in the photohave fundamental differences) there is a violation of blood flow. The combined form of the disease is characterized by manifestations of neuropathic and ischemic varieties.
Signs of illness
At the first symptoms of a diabetic foot, treatment (a photo of the appearance of the foot is placed in the review) should be started immediately. Suspecting an ailment, it is urgent to visit a specialist who will draw up further therapy tactics. Signs of diabetic foot include:
- Wounds, erosions, ulcerations, blisters. Even minimal damage to the epidermis is dangerous. Harmless at first glance, corns and corns can become a favorable condition for the penetration of a bacterial or fungal pathogen, which will complicate the already difficult course of the disease. The main sign of infection is the flow of pus from the wound.
- Nail damage. Fungus and ingrown toenails can also cause severe inflammation on the skin of the foot and affect deeper tissues.
- Hyperemia. Redness of the epidermis may indicate an infection, especially if there is an open wound surface nearby, abrasions, calluses on the foot.
- Itching. If the skin is constantly itchy, this symptom is often regarded as a harbinger of a diabetic foot. The initial stage of this disease in most patients begins with redness, burning and severe itching.

Persistent pain. This symptom may indicate damage to the ligamentous apparatus, bruising, bruising, excessive load on the legs,tight shoes or infection
Patients with diabetes experience severe walking difficulties. By the way, lameness sometimes indicates the development of Charcot osteoarthropathy. This pathology is rare, but with inadequate treatment, it almost inevitably leads to disability. The cause of this complication is considered to be peripheral neuropathy, frequent mechanical injuries, osteoporosis.
At the initial stage of the diabetic foot, there is a change in its color. Starting from the ankle to the tips of the toes, the foot can take on a different shade: from red to bluish-green or even black. Along with a change in the color of the skin, swelling may appear, which is a sign of poor venous circulation.
In later stages of diabetic foot, patients also report other symptoms:
- pain in lower limbs radiating to thighs and buttocks;
- limping that increases with fatigue;
- numbness and occasional tingling in the legs;
- lack of hair on shins;
- high body temperature;
- epidermis shines, looks too tight, tight.
Main stages of the disease
Depending on the complexity of the lesion of the vascular bed and nerve endings in the lower extremities, a clear staging is attributed to the pathological process. The gradual course of the disease was first described in 1997. In accordance with it, the following stages of diabetic foot are distinguished:
- Initial. In the photo, lesions of the zero stage are practically not noticeable, but ifexamine the patient closely, you can find the first signs of deforming osteoarthritis, thinning of the epidermis, grayish-cyanotic or reddish tint of tissues, slight swelling.
- First. At this stage, a shallow superficial erosion appears, which exposes the subcutaneous fat. Muscles and tissues lying deeper until they are involved in the necrotic process.
- Second. Muscle tissue, tendons, bones and joints are affected. If the patient seeks help from specialists at this stage, the diabetic foot can be cured without surgery.
- Third. For this stage of the disease, purulent fusion of bone matter is characteristic. Abscesses appear in deep tissues - limited areas of the purulent process, most often caused by anaerobic bacteria. Leg ulcers emit a fetid odor.
- Fourth. At this stage, gangrene and tarsus develop. Due to necrotic changes, the tissues of the fingers turn black, while there are no clear boundaries of the affected areas. The patient completely lacks sensitivity in any part of the foot. At this stage, the treatment consists, as a rule, in the amputation of the fingers and dead parts of the limb. In some cases, operations are also performed to restore the blood supply to the foot.
- Fifth. It is difficult to imagine what a diabetic foot looks like at this stage. Without proper treatment, gangrene spreads higher and higher, destroying not only the foot, but also the tissues of the lower leg, affecting the thigh. To save the patient's life, the only possible treatment option is highlimb amputation.
Diagnostic tests
To accurately determine the disease, examination alone and the patient's complaints are not enough. Medical diagnostic evaluation also includes laboratory tests, instrumental screenings and consultations with highly specialized specialists. For example, qualified assistance from an angiosurgeon and an orthopedic surgeon may be needed. Doctors of these speci alties are directly involved in the treatment of diabetes mellitus and infections associated with circulatory disorders in the lower extremities.
Clinical tests that are prescribed for patients with diabetic foot represent a whole range of studies. These include:
- Detailed blood test. The study will help to find out the presence of infection, its severity. The indicators of lymphocytes and leukocytes will help the specialist in this - their increased content indicates that the patient's body is fighting an infectious disease.
- Blood test for sugar level. For patients with diabetes and diabetic foot, this is a must.
- Renal function tests, liver enzymes and other screenings are ordered by the doctor if appropriate, which he determines on a case-by-case basis.
In addition to laboratory diagnostic procedures, a patient with a diabetic foot will definitely be sent for x-rays. The study will determine the degree of damage to bone tissue, assess the damage to he alth from infection, detect foreign bodies in soft tissues, and evenearly development of gangrene, which will be evidenced by porous muscles and gaps in the picture.

A subtype of X-ray examination is angiography - a method for diagnosing blood vessels, which involves the use of a contrast agent (most often gadolinium). According to the angiographic image, it is possible to adequately assess the functionality of the vessels, determine the degree of elasticity and thickness of their walls, and the extent of the pathological process. Surgery to restore blood circulation must be preceded by angiography, which is performed under local anesthesia.
Is it possible to cure the foot with pills
In the treatment of diabetic foot (photos once again confirm that diabetes mellitus is a dangerous, life-threatening disease), the use of medications allows you to partially neutralize the high level of glucose in the blood and start the process of regeneration of the affected tissues. As basic means, drugs of the following pharmacological groups are used:
- insulin replacement;
- antibacterial;
- antifungal;
- anti-inflammatory;
- painkillers;
- local antiseptics.
Systemic drugs and antibiotics
For the effective treatment of diabetic foot, strengthening the immune system with the help of immunomodulators is of great importance. They also prescribe neurotropic drugs (for example, Milgamma, Compligam), which contain B vitamins, support the work of the heart, kidneys,prevent thrombosis. To improve the general well-being of the patient, therapy is carried out with anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs, tricyclic antidepressants to reduce pain.

Antibacterial agents are prescribed without fail with the progression of the necrotic process and the deepening of ulcers. Usually, doctors, without waiting for the results of bacteriological culture, which is carried out to determine the sensitivity of pathogenic microflora, prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotics from the group of cephalosporins and fluoroquinolones:
- Zefter.
- Cifran ST.
- Avelox.
- "Tsiprolet A".
- Hinemox.
- Invanz.
Depending on the severity of diabetic foot symptoms, combinations of antibiotics may be used. For example, a pair of "Clindamycin" - "Ciprofloxacin" demonstrates good efficiency even with ischemic ulcers at an advanced stage.
In addition to antibiotics, patients are prescribed drugs of complex action. These include the class of heparinoids, which have a powerful antithrombotic effect. Most of these drugs are available in capsules (Sulodexide, Lomoporan), but in some cases solutions for parenteral infusion are also used. For complex ischemic ulcers caused by the destruction of blood vessels, Prostavazin, Alprostadil are prescribed. These drugs dilate blood vessels, minimize blood viscosity, and prevent platelets from sticking together. Shows excellent results"Trental 400" - this medicine is most often used to treat diabetic foot, as it quickly improves microcirculation in the affected tissues. Its analogues have the same properties:
- "Vulostimulin".
- Delaskin.
- Fuzicutan.
To restore sensitivity to the foot, the loss of which occurred due to damage to nerve fibers, use preparations with thioctic acid in the composition. These include "Thioleptu", "Thioctacid", "Berlition".

How to flush ulcers
An undoubted reason for going to the doctor is the absence of pain in diabetic foot syndrome. Conservative therapy for terrifying leg ulcers requires thorough care for them and the competent use of local medicines.
The success of treatment largely depends on how responsibly the patient approaches the implementation of medical prescriptions. Extremely important:
- keep the wound clean at all times;
- don't let it get wet;
- change dressings regularly with recommended medications;
- at home wear socks, slippers;
- minimize physical activity and walking.
Special attention should be paid to high-quality cleaning and washing of the wound with antiseptic solutions, followed by the application of sterile dressings. Doctors believe that the best way to clean the wound is the surgical method. With the help of a scalpel, dead tissue particles, purulent masses can be removed from a deep ulcer. Mechanical cleaning methodallows only he althy tissue to remain in the wound.
Rinse the ulcer at home, the patient will be able to independently. Compared to surgical cleaning, this method is safer. To wash the wound using saline. Sodium chloride has no toxic side effects. In the absence of this remedy at home, you can prepare a solution of 0.9% concentration of sodium chloride. It is also recommended to clean the ulcer with a “standard” 3% hydrogen peroxide solution - this disinfectant removes pus and destroys anaerobic bacteria. If it is necessary to frequently wash the wound, the peroxide solution is diluted with saline. Both components are taken in equal proportions.
It is convenient to use Miramistin antiseptic for wound irrigation. By the way, this tool has a number of advantages in comparison with solutions of manganese, iodine, brilliant green - Miramistin does not slow down the healing process and stops tissue death. At the same time, its analogue "Chlohexidine" is used mainly in the first stages of a diabetic foot. The thing is that this remedy loses its disinfectant properties in a purulent environment.

All of the above wound cleansing products are recommended to be diluted if used too often, alternate with each other, do not use the same preparation all the time.
Topical treatments
In itself, the treatment of diabetic foot with external medicines will not give any result. To stop the destructive pathological process, it is necessaryuse antiseptics in combination with the method of surgical cleaning of the wound. Before applying a bandage with medicine, Iruxol and Dioxicain-P ointment is put into the wound - these agents contain the enzymes collagenase and protease. It is necessary to use these drugs with extreme caution in case of bacterial damage to the wound, as they can have a toxic effect not only on pathogenic microbiota, but also on he althy tissues.
Ulcers on the extremities, accompanied by purulent discharge and swelling, are treated with creams and ointments, which include iodine and polyethylene oxide. These include:
- "Yodopyron".
- Brownall.
- "Lavacept".
- Dioxidine.
The use of local medicines implies regular inspection of the wound due to the risk of overdrying of its surface during the regeneration process. For the treatment of deep erosions with a significant amount of necrotic tissue, Purilon gel is used - a drug that stimulates regeneration processes and natural cleansing of a wound filled with purulent masses.
Surgery
The radical method of treating diabetic foot of the ischemic type is used more often than conservative therapy. This form of pathology is difficult to respond to other treatment methods. The dynamics of ulcer healing improves dramatically after surgical reconstruction of the arteries by bypass or endovascular intervention. Such operations are aimed at restoring blood flow in the arteries of the lower leg and popliteal blood vessels. Manipulation is carried out under local anesthesia. Duringoperations through an external incision, a catheter is inserted into the femoral artery, through which tiny balloons are placed - they expand the lumen of the vessels and improve blood flow.
In case of severe infection and treatment failure, a decision is made to amputate the limb. Only removal of the affected body part will help stop the spread of infection and save a person's life.

Prevention and advice
Success in the treatment of pathology depends largely on compliance with a sparing regimen, minimizing physical stress on the foot. The best unloading for the lower extremities is bed rest. If it is impossible to comply with it for any reason, the patient should wear only orthopedic shoes with special custom-made insoles. Crutches can also be used to reduce the load on the leg while walking.
If a person with diabetes is at risk of developing foot ulcers, he should take care of himself and purchase a fixing bandage made of polymeric materials. It does not interfere with moderate physical activity and does not irritate the wound surface.
Another measure to prevent diabetic foot is the correct choice and application of wound dressing. The chronic course of the pathology makes it necessary to cover the ulcer, but at the same time provide a sufficient level of permeability for gas exchange. For this purpose, the most commonly usedhydrogel and collagen dressings.
Disease prognosis
Out of ten patients with diabetic foot, seven are diagnosed with a neuropathic form associated with nerve damage. A positive result of conservative treatment is achieved in almost 90% of cases. Less optimistic is the prognosis of ischemic and combined forms of the disease. With damage to the blood vessels, conservative therapy helps to prevent amputation in only a third of cases of ulcerative lesions. In addition, the treatment of diabetic foot syndrome is often complicated by the risk of secondary infection of an open wound, mechanical damage that can enhance necrotic processes, lead to tissue breakdown and gangrene, in which it will be impossible to avoid removal of the limb.

At the first symptoms, treatment should be started immediately. Do not risk your own he alth and life by choosing at random pharmaceutical preparations and folk remedies. An incorrect approach to treatment increases the risk of developing gangrene, which means that the likelihood of remaining disabled for the rest of your days automatically increases.