- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
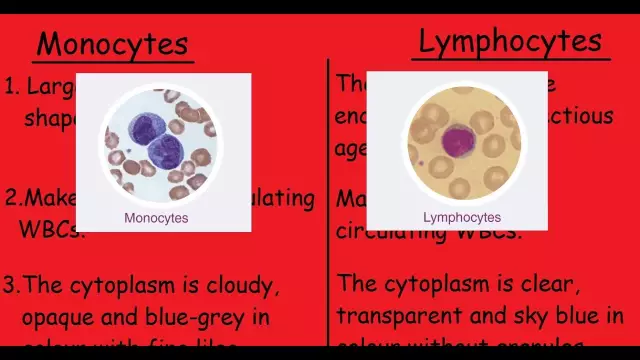
Lymphocytes are blood cells. They are an integral part of the immune system. An increased percentage of lymphocytes in the blood is called lymphocytosis. This pathology is most often a response to external influences.
Why are there elevated lymphocytes in the blood?

Children have physiological lymphocytosis. So, after the birth of a child, the number of lymphocytes increases and until the 4th day of life is equalized with neutrophils (the first leukocytic crossover). At the end of the first year of life, the percentage of lymphocytes is maximum and is 65, and neutrophils - only 25. At the age of four, the number of these cells equalizes again. This is the second leukocyte decussation, after which the number of neutrophils gradually increases, and the number of lymphocytes decreases. By puberty, the indicators of the leukocyte formula reach values that are characteristic of adults.
To find out the number of formed elements, they take a general blood test. Elevated lymphocytes are a reactive response of the body or a sign of severe disorders that require appropriate treatment.

Pathological lymphocytosis
There are a number of diseases that are accompanied by a change in the number of lymphocytes. Among them, the following should be mentioned:
- infectious diseases, especially rubella, as well as chickenpox or measles;
- inflammatory processes with a chronic course;
- detect elevated blood lymphocytes in children with infectious mononucleosis or acute lymphocytosis;
- hyperthyroidism;
- whooping cough.
In addition, there are significantly increased lymphocytes in the blood of children who are diagnosed with a malignant lesion of the bone marrow, and are called "lymphocytic leukemia". This disease occurs with the manifestation of weakness, bleeding of mucous membranes, as well as with an increase in the liver, lymph nodes, spleen, soreness of the bones, hemorrhages.
Pathological lymphocytosis is found in the tuberculous process, infectious-allergic diseases (for example, in bronchial asthma), in the presence of B12-deficiency anemia or Crohn's disease. Elevated lymphocytes in the blood in children occur when they are malnourished and have signs of alimentary dystrophy.

What you need to know?
Based on a simple blood test, it is impossible to distinguish between reactive lymphocytosis and cancerous disorders. If necessary, complex laboratory tests are carried out. They determine subpopulations of lymphocytes, detect abnormalities in lymphocytic nuclei, conduct molecular genetic tests, cytological examination of the bone marrow.
If the level of lymphocytes is high, do not panic, you should consult a qualified hematologist. To obtain additional diagnostic data, you should determine the state of the immune system, undergo an ultrasound scan, and, if necessary, an x-ray examination or computed tomography.
As a rule, lymphocytosis is a consequence of contact with viral or bacterial infections, therefore, after recovery, the leukocyte formula returns to normal without any direct effect on the number of lymphocytes. With the development of tumor diseases, patients should consult an oncologist, since lymphocytosis of this etiology requires correct and long-term therapy.